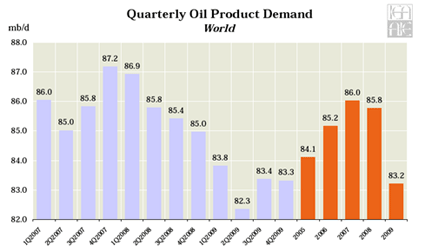
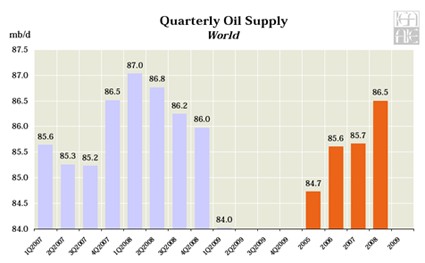
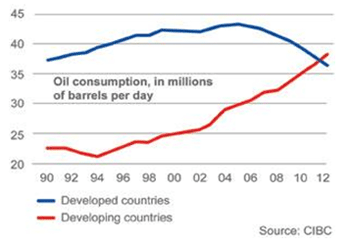
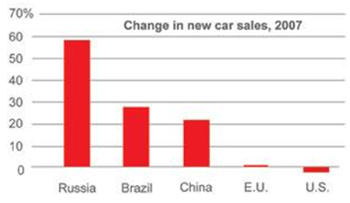
No matter how far the economy falters, there is always a winner. And no city does better when the nation is at the brink of disaster than Washington, DC. Since December 2007, when the current recession formally began, the nation has lost approximately 6 million jobs. Only two states, Alaska and North Dakota, have lost a smaller percentage of jobs than Washington, DC, which has seen a job loss of 0.6%, or 4,400. Simply put, Washington has done better in this recession than 48 of the fifty states when it comes to job performance.
This is not the first time that Washington flourished while the rest of the nation suffered. For the first few, largely prosperous decades of the 19th Century, the district was a backwater, growing more slowly than the national average. It was widely reviled as fetid, swampy place with little in the way of commerce, industry or culture. Even its great buildings were compared to “the ruins of Roman grandeur.”
It was only during arguably our greatest national tragedy – the Civil War – that the District of Columbia grew into an urban center, more than doubling in population from 1860 to 1870. Soldiers from the northern states flocked to the District of Columbia before going to battle, a new military force was established to guard against a Confederate attack, and the management of the war itself became a major federal enterprise. Slavery was abolished in Washington prior to emancipation, and freed slaves added to the District’s growing population.
During the 1930s, FDR created an entirely new set of federal agencies designed to create jobs by financing projects across the country. At the same time, to prevent abuses on Wall Street, Congress created new regulatory agencies, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission, which hired droves of young accountants and lawyers unable to find work in other cities across the country.
The Second World War and the Cold War also played to Washington’s advantage, as a vast military-industrial complex rose to the fore. So it’s not surprising that now, with the nation in the midst of its worst downturn since the Great Depression, that Washington appears about to indulge in yet another orgy of growth.
Washington has always been a one industry town: that’s why it has an intrinsically self-absorbed monotonic culture. Everyone there depends on government for their livelihood. It is fundamentally not a city of competitive industries, but a giant taxpayer-funded office park, surrounded by museums and memorials. The great presidents: Washington, Lincoln, and Jefferson, have their own monuments, while more recent leaders have concert halls and office buildings named after them.
Today Washington, DC appears much as the twenty-first century version of a gold mining town, even if the gold, so to speak, is coming from taxpayers as well as foreign buyers of our increasingly debased US currency. The Bush Administration kicked off this boom when it created the third largest cabinet department, the Department of Homeland Security, (by consolidating unrelated federal agencies into one super-sized department) and made it the employer of airport baggage and security inspectors across the nation. A new federal agency deserves a new headquarters, of course. DHS is now rising on the site of St. Elizabeth’s Hospital in southeast Washington DC, a pre-stimulus stimulus for the District of Columbia.
The passage of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act may be only slowly stimulating the nation’s economy but it is already working wonders in DC. Everyone wants a piece of the action. There is a surge in the lobbying industry, with every school board, regional transit agency and county government hiring a lobbyist to guide them through the new federal grant programs.
Tourism may be temporarily down in DC, but the hotels are filled with local law enforcement officials, university bureaucrats, and housing advocates all trying to create jobs with federal dollars. The National Telecommunications and Information Administration and the US Department of Agriculture have just nineteen months to spend $4.7 billion on broadband communications.
To evaluate the thousands of proposals for federal funding, expert panels will convene in Washington, DC. Where else? Communities across the country may receive grants, but the hotel and restaurant industry in the nation’s capital will also prosper from this new federal program.
The same process will follow other Obama initiatives. Health care and climate change legislation will produce the same rounds of hearings, a growing cadre of regulators and the corps of tassel-shoed lobbyists who will try to influence them.
The heightened emphasis on transparency in government has compelled every federal department to build sophisticated websites to engage the public, to distribute information, and to conduct the entire process of awarding grants and contracts. The demand for website designers and managers has grown so quickly that a Los Angeles-based interactive advertising agency, “Sensis,” a minority owned and operated corporation, recently opened an office in the District of Columbia just to “capitalize on the federal government’s new interest in digital communications.”
There is one unambiguous measure that signals the growth of business activity within a city. Until recently, taxi fares in the nation’s capital were based on zones. These made it very inexpensive for members of Congress to go to and from the Capital. Today, every DC taxi has a meter and the old-fashioned zone-based system has been abolished. Both the municipal government and taxi drivers understand that there are more dollars to be made from those seeking to influence government than those who actually make the laws.
Ben Smith of Politico.com has recently pointed out that five new Washington-based reality television shows are in the planning stages, with Bravo ready to launch “The Real Housewives of Washington, DC.” It is no accident that the entertainment industry has discovered the District of Columbia. A city that thrives in a recession may become the Fantasyland of our generation.
Mitchell L. Moss is Henry Hart Rice Professor of Urban Policy and Planning at NYU Wagner School of Public Service.