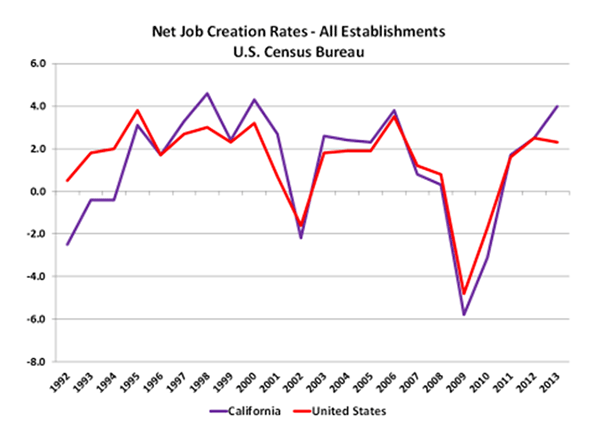
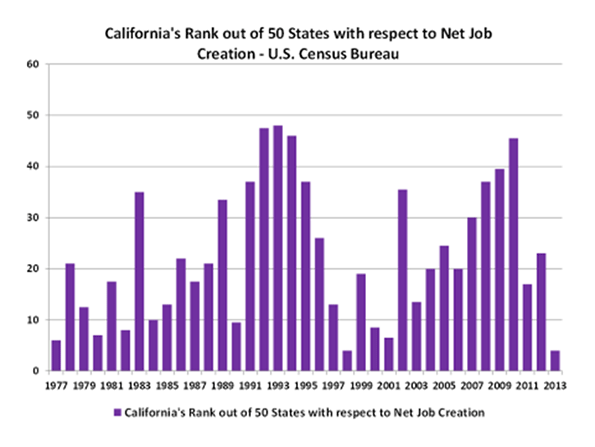
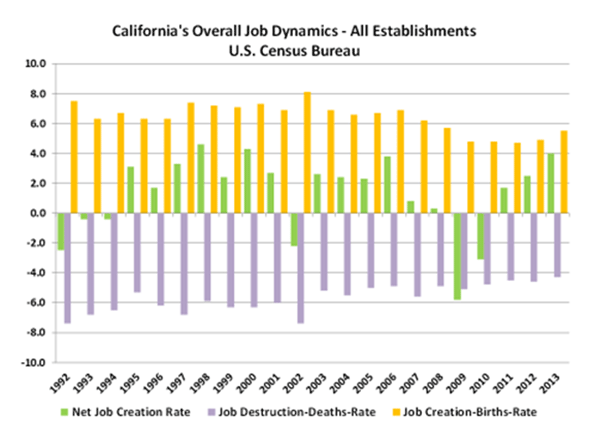
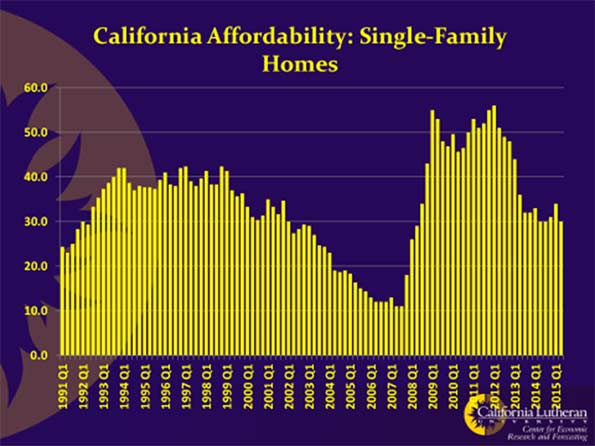
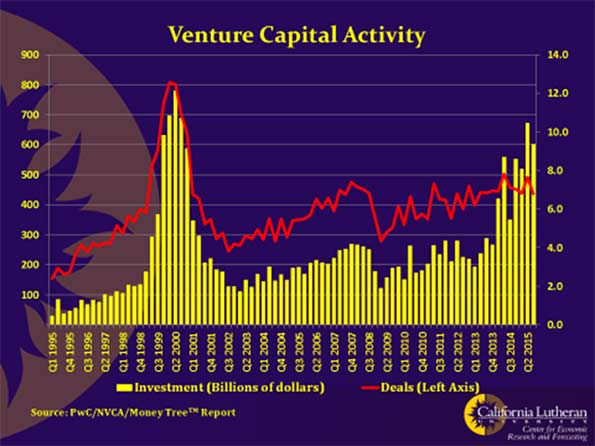
Defenders of California’s status-quo claim to be proud of California’s economic growth and worry about what Trump will do to that growth. If you are so impolite as to mention that this has been California’s slowest recovery in 70 years, as the following chart shows, you will be told that slow growth is good. It avoids the excesses of previous business cycles.

That’s nonsense. Slow growth is anti-poor and anti-minority. Here’s a simple way to analyze economic policy: Ask how the policy changes the probability of a young person finding a job. If the policy increases their chances, it’s good policy. If it decreases the probability, it’s bad policy.
I go farther than that. To me, deliberately enacting a policy that reduces a young person’s prospects is immoral.
California, and the nation, have lots of policies that reduce young people’s job prospects. So, there are lots of opportunities to increase economic growth. Certainly, it’s possible to present a set of policy proposals that would increase California’s economic growth.
Evaluating Trump’s economic plan is difficult, though. So far, it’s a mixed bag. It has policies that would increase economic growth. It also has some that would decrease economic growth. I think the best way to evaluate the impact is to look at his major proposals for their growth impact and probability of becoming law.
Trump has promised to reduce American business’s regulatory burden. That would reduce costs, encourage domestic production and jobs, and provide a strong economic boost. Some of that overhead was created by executive action and can be reversed by executive action. The probability of reversing those regulations is high, as are the economic benefits.
He’s also promised to eliminate or “fix” Dodd-Frank and the Affordable Healthcare Act. Exactly what he intends to do, fix or eliminate, depends on the tweet of the day. It’s also not clear what fix means. Still, any real change will face significant hurdles, even with a Republican controlled Congress. To be conservative, we need to assume that he will be unsuccessful in his attempts to significantly change these laws. If he does, and it’s done in a way that reduces costs, it will be a happy plus.
Then there is his immigration policy, if you can figure out what it is. He’s been all over the map, from shipping out all undocumented residents to only shipping out the criminals. Of course, if he is able, as some fear, to move millions of our workers, the economic impact would be seriously negative.
Realistically, the most he is likely to accomplish is exporting criminals and slowing immigration. The numbers of undocumented criminals is small enough to have no measurable impact on the economy. Decreasing immigration tends to slow economic growth, but it may reduce inequality a bit by reducing competition faced by our low-productivity workers. Overall, Trump’s immigration policies will likely have modest negative economic impacts.
As in all things Trump, his trade proposals are inconsistent and vague. One thing has been consistent. Trump wants to reduce trade. We can only hope that he’s unsuccessful. The economic impacts of reducing trade would be large and negative. Presumably, Congress will effectively resist his most egregious proposals.
Reducing trade would particularly hurt California’s economy, as a large percentage of what the United States exports and imports goes through California’s ports, which are a significant portion of the state’s limited remaining industrial assets.
Taxes are one area of Trump policy clarity. He wants to reduce corporate taxes and reduce the tax impediments to repatriating foreign corporate earnings. By themselves, these would provide an economic stimulus. Repatriating foreign earnings has no obvious downside. By contrast, without some action somewhere else, reducing corporate taxes could increase the severity of our already severe budget challenges. Eliminating deductions, as proposed, would lessen the budget impacts, as would taxing repatriated earnings at the suggested 10 percent rate. These, combined with increased economic activity, potentially brings the long-run budget impact to near zero. Supply-siders would argue that the package would reduce deficits. That’s probably a stretch, although the combination of regulatory reform and tax reform could very well reduce the deficit.
Trump proposes a stimulus package that appears to be another public capital spending spree. This would add to our budget challenge, but it’s far worse than cutting taxes to businesses. Cutting taxes at least has the benefit of generating new economic activity to offset some of the budget impact. Public capital spending at the national level is non-stimulative and inefficient. Given the budget impacts, zero economic impact is the best we can hope for.
Some California leaders worry that Trump will retaliate economically for California giving Hillary Clinton a popular-vote victory. I don’t believe that the presidency has enough power for a vindictive new president to exact revenge by economically punishing states that voted for his opponent. If he does, the presidency is way too powerful.
Overall, it’s likely that Trump’s economic impacts will be a small positive, but with an increase in an already too-large budget deficit. California’s impact could be smaller, or even negative, depending on Trump’s success reducing trade.
Whatever Trump’s impacts on the national economy, they are likely to be far less for California, as his program will be swamped by California’s own unilateral deindustrialization. While the rest of the nation will be enacting a program intended to be pro-business and pro-job, California is firmly embarked on an agenda that promises to be anti-business and anti-job, with increased regulation and costs for businesses and consumers.
Examples of California’s anti-business agenda are easy to come by. Governor Brown has recently asked the Federal Government to ban all offshore oil and gas drilling off of California. In the most recent election, Californians renewed their commitment to environmental purity, embracing carbon emissions targets 40 percent below 1990 levels by 2030. Nothing is beyond the reach of California’s environmentally devout. They’ve already regulated cow flatulence, which could lead to backpacks and plumbing to collect cow gas. More likely, it will lead to fewer cows in California, but more in other places and no change in global bovine emissions.
While it’s entertaining to speculate what California regulates after cow flatulence, there are serious consequences to the state’s regulatory enthusiasm. Unless the rest of the country embraces California’s agenda, very unlikely under a Trump administration, its economy and the nation’s will eventually diverge, even with California’s location, climate, and tech advantages. This will lead to slower economic growth and increased migration out of the Golden State.
Bill Watkins is a professor at California Lutheran University and runs the Center for Economic Research and Forecasting, which can be found at clucerf.org.