World famous for its beautiful harbour setting, Sydney’s Central Business District is undergoing a resurgence. As the hub of Australia’s finance sector, it stumbled during the global crisis. Office vacancies jumped from 5.7 per cent in early 2008 to 8.8 per cent in mid 2009, despite stable supply. Ultimately, though, Sydney was spared the worst, owing to its rise as a staging post for trade and investment in the Asia-Pacific region, which averted the havoc of Europe and North America. Recovery is now underway, if slowly. White-collar employment is picking up and the vacancy rate is down to 7.3 per cent. Landlords are again celebrating the prospect of rising rents.
But there’s a bigger story. This revival is happening amid some notable trends. Post-crisis, the CBD’s functional map is being redrawn by a wave of Asian and other visitors and investors, prominently listed property trusts and pension funds looking for a safe haven, the spatial demands of a transformed white-collar workplace, intensive residential development on the CBD fringe and officials pushing flashy “green” projects. There’s no doubting the importance of these developments, or that they will be hyped by inner-city based media.
In fact, central Sydney has been losing economic clout, in relative terms, to the periphery or suburban hinterland for some time, a polycentric trend observed in other countries. Between the 1981 to 2001 censuses, encompassing the most active period of economic liberalisation in Australia’s history, Sydney’s general population growth was 23 per cent, while outer areas in Greater Western Sydney grew by 38 per cent. The CBD’s share of Sydney’s jobs shrunk from around 30 per cent to 9 per cent during this period. Four of the five strongest growing Local Government Areas (LGAs) in the year to 30 June 2009 were still in the outer west: Blacktown, Parramatta, The Hills Shire and Liverpool.
The latest wave of change will prove significant and long-lasting, but the CBD isn’t destined for a return to metropolitan supremacy.
Sydney CBD
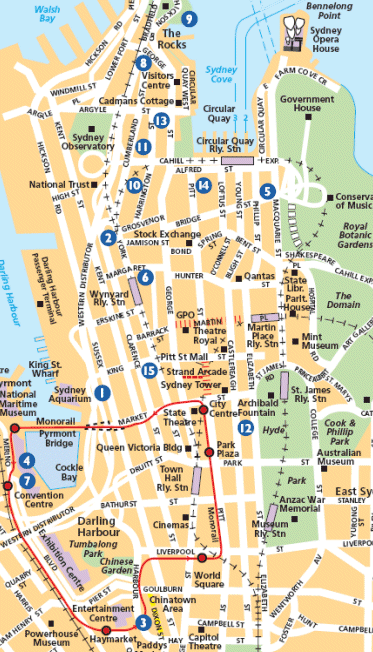
The retail core
For theorists of the CBD, peak land value intersection (PLVI) is a pivotal concept. This is the centrally-located point, usually at the intersection of two thoroughfares, where land values are highest. Without doubt, Sydney’s PLVI is the intersection of George and Market Streets. George Street is the CBD’s spine, traversing a north-south axis from Circular Quay to Central Station. Historically, Market Street was the critical entry route from the west, extending from the defunct Pyrmont Bridge (over Darling Harbour), and now from a branch of the Western Distributor. Blocks surrounding the PLVI are typically occupied by upscale department stores, absorbing peak land prices with high turnover of quality goods on multiple floors. Thus Myer and Gowings stores occupy the north-east and south-east corners respectively, and David Jones a site further east along Market Street (the Gowings site is earmarked for refurbishment as a boutique hotel). The iconic Queen Victoria Building arcade sits on the south-west corner.
According to the “core-frame model”, another tool of CBD theory, activities competing for the highest rents, like upmarket retail and superior grade office towers, concentrate in core blocks, while marginal activities disperse to peripheral blocks. In terms of the theory, the latter are a “zone in transition”, at an intermediate stage between lower grade building stock and future redevelopment. Activities like low-end retail, fast-food, novelty shops, pawnbroking, wholesaling, storage, off-street parking, warehousing and light-manufacturing locate there.
Traditionally, Sydney’s CBD had a retail core around the PLVI bounded by York, Park, Elizabeth and King Streets, south of an office core bounded by King, Clarence and Macquarie Streets and Circular Quay. Judging by the headlines, the retail core is Sydney’s biggest news. Long a feature of suburban life, the CBD is being transformed by the arrival of mall-style shopping, adding to the mix of department stores, arcades and stand-alone shops. In some ways, it’s catching up with the social evolution of shopping as a “complete experience” linked to identity formation.
The catalyst is Westfield’s $1.2 billion development at the corner of Pitt Street Mall and Market Street, just a block east of the PLVI. A pedestrianised section of Pitt Street between King and Market Streets (not a regular mall), Pitt Street Mall is the retail core’s epicentre. Last year, global real estate firm CB Richard Ellis (CBRE) rated it the second most expensive street for retail rents in the world. The first was New York’s Fifth Avenue.
With rents so high, investment dollars are pouring in. Fronting the eastern side of Pitt Street Mall, Westfield’s contemporary glazed-glass structure, box-like at street level but topped by Sydney Tower, converts four properties into 93,000 square metres of retail space, distributed over a six-storey shopping mall. The first stage opened last October. On completion, it will house 330 flagship and specialty fashion outlets, and lifestyle stores, most of them international brands, including Sydney firsts Versace, Gap, Zara and Miu Miu, together with several eateries. Two skybridges link the complex to nearby Myer and David Jones department stores.
Westfield’s opening coincided with a general revamp of Pitt Street Mall, featuring landscaping, paving and tree-planting by Sydney City Council, and reconstruction of the mall-like Mid-City Centre, 52 shops on four-levels fronting the Mall’s western side, almost opposite Westfield, penetrating west to 420 George Street. One Mid-City store, jewellery retailer Diva, is reputedly paying the highest rent in the CBD, $13,500 per square metre a year.
Pitt Street Mall’s face-lift set off a reshuffle of fashion and luxury goods retailers around the retail core, with knock-on effects all the way up George Street. Burberry is moving to refurbished premises at 343 George Street, Louis Vuitton to a new flagship store on the corner of King and George Streets, Dior to Castlereagh Street, and Zegna and Prada to Westfield, from Martin Place. This follows the 2008 opening of the world’s largest Apple store, at glass-clad 367 George Street (roughly opposite Mid-City at 420).

Pitt Street Mall
A sign that the retail core may be busting out of its old confines, and creeping north of King Street, major retail developments are planned in the vicinity of Wynyard railway station, at 301, 333 and 383 George Street. Some of these anticipate the most striking proposal yet: a futuristic commercial and residential precinct on the foreshore of East Darling Harbour, or Barangaroo, seeing the retail core spill into the CBD’s rising “western corridor”, which was a "zone in transition" in the days when Darling Harbour and Walsh Bay were working ports. This $6 billion plan includes 30,000 square metres of retail space and a pedestrian walkway to nearby Wynyard, the CBD’s busiest underground station.
It’s easy to explain such hyperactivity. Sydney is one of a handful of global cities in a developed country which wasn’t flattened by the financial crisis. There’s a clear international dimension to the CBD’s resurgence. According to Cushman & Wakefield’s International Investment Atlas 2011, the Asia-Pacific is dominating global property investment. Ranked eleventh, Sydney joins 6 other Asia-Pacific cities in the top 20. In the 18 months to June 2010, reports CBRE, Sydney ranked fourth in the world in terms of cross-border investment. Foreign investors accounted for 42 per cent of Australia’s property asset acquisitions in the third quarter of 2010, way above the typical level of 10 to 15 per cent. In these conditions, Sydney shot up to ninth out of 65 cities in AT Kearney‘s 2010 Global Cities Index. And a 2010 survey by real estate agents Jones Lang La Salle rated Tokyo and Sydney the most popular Asian cities for investment. At a time when many asset classes carry outsized risks, Australian commercial property is a safe option.
Of course, there’s nothing new about Asian investment in the retail core. Three of its most fashionable shopping arcades belong to Ipoh Pty Ltd, which is owned by a Singaporean fund manager: the Queen Victoria Building, The Strand Arcade between Pitt Street Mall and 412-414 George Street, and The Galleries, on the corner of George and Park Streets, the core’s southern edge.
But urban planners would be wrong to overestimate the impact of all this on the wider metropolitan region. Quite clearly, Westfield’s target market embraces a small minority of Sydney’s 4.5 million residents. Commenting on the mall’s opening, the Group’s managing director hoped it would be a “destination for the people of Sydney, and the 26.8 million domestic and international visitors who come to Sydney each year”. The Australian Financial Review, citing Westfield, reported that it will “service not only 240,000 workers in the [CBD], but 1.5 million in the primary trade area across the richest suburbs and the 26 million tourists who visit the city each year”. David Jones’ CEO expressed similar sentiments, saying “my hope is that Sydney’s CBD retail precinct becomes a world-class shopping destination on a par with the world’s best such as Oxford Street, London, and Rodeo Drive in LA”.
Much of the investment surge is predicated on large numbers of visitors, and the growth of inner-suburbs ringing the CBD. If the travelling patterns of China’s newly cashed-up middle class are any guide, for instance, these hopes won’t be disappointed. The number of Chinese visitors to Australia is forecast to grow by 7.9 per cent a year, reaching 783,000 a year by 2019. Meanwhile, Sydney LGA’s population is ballooning (the CBD and environs). Between 2001 and 2009, it grew by 38 per cent, or 49,000 new residents. Eager to meet the former state government’s target of 55,000 new residential units over the next decade, Sydney Council is presiding over a number high-density projects on derelict industrial or recreational sites. Most of the newcomers will belong to the same demographic as current residents, younger, upper-income professionals with a taste for inner-city living. They are no cross-section of Sydney’s population. Below average in age, their median weekly income is $717, compared to $518 for the whole metropolitan region.
To an extent, Sydney CBD is exhibiting features of the global city phenomenon, when highly-developed zones “secede” from their hinterland and develop stronger ties to distinct occupational classes and overseas markets. The revitalised retail core is unlikely to lure the vast majority of shoppers — who live and work far from the CBD — away from suburban megacentres like Chatswood Chase, Miranda Fair, Warringah Mall, Castle Towers, Minto Mall, Top Ryde City, Westfield’s other centres at Bondi Junction, Parramatta, Burwood, Hurstville, Hornsby and Penrith, local retail strips, or the growing number of Australians who shop online. Just as suburban malls attract customers from their surrounding feeder population, the same applies to the retail core, but with a higher proportion of domestic and foreign visitors.
The CBD’s revival shouldn’t be misinterpreted. It doesn’t herald a return to regional primacy. Calls by green-tinged academics and newspaper editors and columnists for billions to be spent on CBD-centric rail networks are wrongheaded. Such plans can only have a distorting and negative effect on economic vitality across the metropolitan region, especially fast growing outer LGAs. Look at the CBD’s story. For all the contemporary rhetoric linking urban success to green amenity, it owes more to plain old capitalism.
John Muscat is a co-editor of The New City, where this piece originally appeared.
Photo by Christopher Schoenbohm.