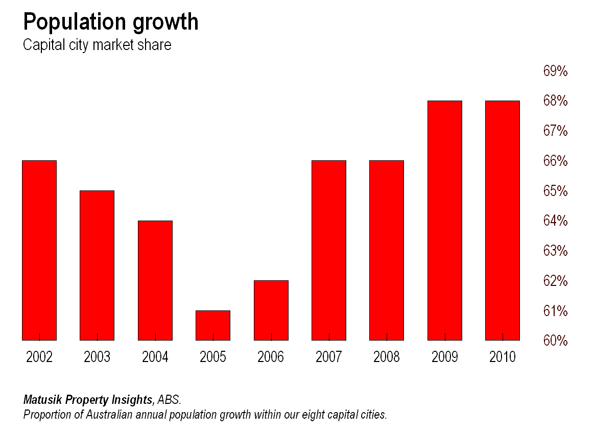
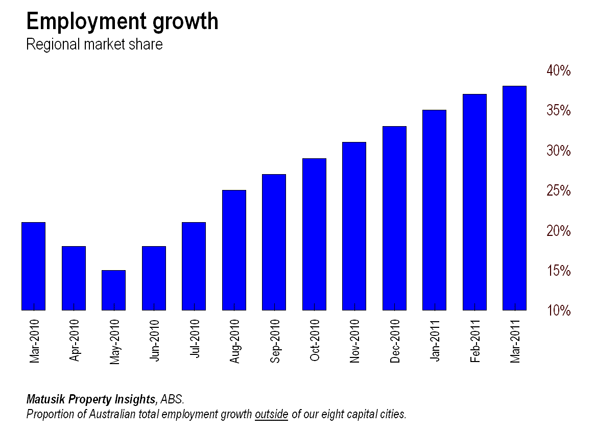
I was recently asked to outline my thoughts on how the Queensland urban landscape might look 40 to 50 years from now. Go on, you can laugh. I did too. It’s hard enough to forecast the next 12 months, let alone two generations away, but I’ve given it a go, of sorts, so here it is:
First though, it might be best to outline my methodology. In short, this forecast will be based on underlying trends, some understanding of human nature, and importantly, the Australian mindset. My outlook is supported by evidence – what people actually do rather than say – and importantly, not by urban myths or fallacies, despite the frequency with which they have been aired of late. Unfortunately, we don’t have the space or the time here to support every claim or go into massive detail; so this discussion is confined to broad shapes – not nitty gritty.
Queensland’s urban future (and that of Australia) can best be summed up in two words – Diverse and Dispersed.
Let’s deal with the second D – dispersion – first. Our regional centres are likely to become a whole lot bigger and at the expense of the already crowded south-east corner of the state. The move away from the world’s bigger cities is already underway, as evidenced in the recent census in the United States, but also throughout much of Europe. Several Asian and Middle-eastern countries are now also following suite As a Mckinsey Institute study recently found, smaller cities, particularly in the developing world, are growing considerably faster than the much discussed megacities.
The annual ABS small-area population data suggests this trend is also very true in Australia and particularly in Queensland, which, over the past decade, been the fastest growing state on the continent, appears to be following the same trend, something likely to be borne out by 2011 Census, due later this year .
Within our capital cities themselves, the much ballyhooed move downtown will slow – again, it already is doing so – as the cost to live within close proximity to the CBD is just too high compared to the real benefits.
The irrational assertions about the trend towards denser living rest on urban myths that promote inner city density over other housing forms. These include the notion that suburban growth worsens carbon emissions and traffic congestion; people are being forced to live far from jobs concentrated in our CBDs and denser development will make it cheaper for them to get to work. These notions are all largely exaggerated or incorrect. More to the point, they stand in opposition to the basic preferences of the market.
Instead of having a single high-density city core, with lower development density radiating outwards, the most likely urban shape in the future will be one of more even distribution of housing density throughout the city; concentrated more, no doubt, around middle-ring transport hubs and new master planned town-centres. Our middle-ring and outer suburbs will have much more compact urban settings but will remain primarily dominated by relatively low density housing.
Diversity relates to the housing stock itself. The current push towards smaller dwellings has little to do with demographics and the market’s wants, but reflects basic reaction to diminished housing affordability. There is a demand for tightly-sized product, but it is nowhere as near as high, nor is the long-term trend towards such as strong, as the urban boosters advocate.
Taking a wider view, Australia (and America too) is still in its frontier or "barbaric" stage of its cultural evolution. We walk with wide gaits, worship most things large from roadside bananas to women’s appendages, and don’t really like crowded spaces or queues Most of us like our space; aren’t really ready to give it up, and are not likely to do so for many decades to come.
Rather than remaining focused on density and concentration, it could well serve the community to focus on what appeals to the vast majority of the population, particularly the middle and working class families. A more practical approach might be to foster the development of smaller, more efficient cities, as well as expansive suburbs and revived small towns rather than engage in a manic drive towards persistent centralization.
Rather a forced density agenda on a largely unwilling population, it makes sense to consider how to make a more dispersed (and diverse) urban future more workable and sustainable. Innovations in work environments, notably increased use of telecommuting and dispersed workplaces, and more fuel efficient cars hold more promise than plans that force Aussies to live a way the vast majority do not prefer.
This article originally appeared in the June/July 2011 edition of the UDIA Queensland’s Urban Developer Magazine.
Michael Matusik is a qualified town planner and director of independent residential development advisory firm, Matusik Property Insights.
Photo by Michael Zimmer.