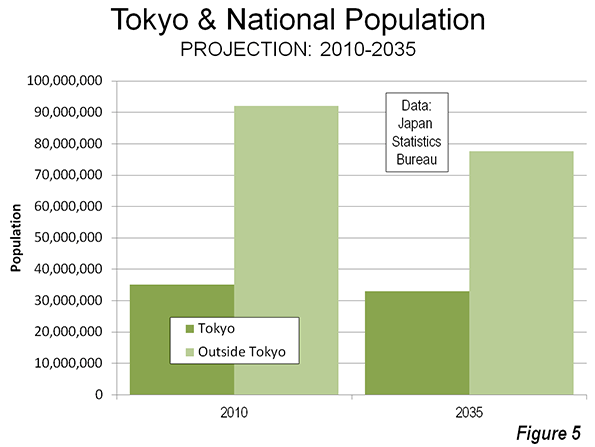
|
Redaction Notice: September 17, 2012 Part of this article from June 28, 2012 has been redacted because of difficulties with the US Census Bureau’s 2011 sub-county population estimates. In fact, these were not genuine population estimates at all, but were largely "fair share" allocations of county population change rates based upon the share of population in each jurisdiction. This issue is further described at was revealed on newgeography.com by Chris Briem and our new URL. However, the fact remains that domestic migration trends continue to be from historical core cities to the suburbs, as the unredacted data below indicates. |
Just released United States Bureau of the Census estimates indicate that the urban cores of major metropolitan areas (over 1,000,000) grew slightly faster than their suburbs between July 2010 and July 2011. Overall, the historical core municipalities grew 1.03 percent, compared to the suburban growth of 0.93 percent. Among the 51 metropolitan areas, 26 urban cores grew at a faster percentage rate than their suburbs (Note 1). However, suburban areas continued to add many more people. Over suburban areas grew 1,150,000, compared to 462,000 for the urban cores, indicating that approximately 75 percent of new residents were in the suburbs. Suburban areas had greater population growth in 43 of the 51 metropolitan areas (Table 1).
| Table 1 | ||||
| DELETED | ||||
As was noted in Still Moving to the Suburbs and Exurbs, the core counties of US metropolitan areas, which contain the greatest portion of the historical core municipalities (Note 2) also grew faster than suburban counties between 2010 and 2011. However, that is not an indication of an exodus from the suburbs to urban cores.
Migration Continues from Cores (County Data)
There was net domestic migration (people moving between counties of the United States) of minus 67,000 in the core counties, while a net 121,000 domestic migrants moved into suburban areas between 2010 and 2011. The stronger core growth was driven by stronger international migration and a larger natural growth rate (births minus deaths).
Limited City Data Confirms the Trend
Migration data is not reported below the county level. As a result, historical core municipality migration data is not available, except where cities and counties are combined. A review of such cases confirms the finding from Still Moving to the Suburbs and Exurbs(Table 2). Among the 12 combined city/counties, there was a net domestic migration loss of 49,000 in the historical core municipalities, while there was a much smaller net domestic migration loss of 1,000 in the corresponding suburban areas.
| Note: Table 2 is retained since the Census Bureau produced genuine population estimates for counties. Table 2 includes only municipalities that are coterminous with counties, and thus were not subject to the "fair share" population growth allocation method inappropriately applied at the sub-county level. |
| Table 2 | ||
| Historical Core Municipality Domestic Migration 2010-2011 | ||
| (Where Cities and Counties are Combined) | ||
| Central City/County | Suburban Counties | |
| PRE-1950 CITY/COUNTIES | (55,441) | (21,306) |
| Baltmore | (3,638) | 2,297 |
| Denver | 8,281 | 11,284 |
| New York | (56,982) | (41,993) |
| Philadelphia | (5,466) | (7,667) |
| San Francisco | 416 | 5,464 |
| St. Louis | (4,959) | (5,301) |
| Washington | 6,907 | 14,610 |
| POST-1950 CITY/COUNTIES | (4,119) | 20,179 |
| Indianapolis | (3,401) | 5,341 |
| Jacksonville | (1,485) | 4,396 |
| Louisville | 18 | 1,868 |
| Nashville | 749 | 8,574 |
| NOT CLASSIFIED (Due to Hurricane Katrina) | ||
| New Orleans | 10,243 | (90) |
| TOTAL | (49,317) | (1,217) |
- Among the seven combined city/counties formed before 1950 (excluding New Orleans), the historical core municipalities had a net domestic migration loss of 55,000, while the suburban areas had a smaller net domestic loss of 21,000. In four cases, the historical core municipalities had domestic migration losses. In the three cases in which cities had domestic migration gains, there were also domestic migration gains in the suburbs. In this group, New York had a domestic migration loss of 57,000 despite having an overall population gain of 55,000 (the gain resulting from international migration and natural growth)
- Among the four combined city/counties formed after 1950, the historical core municipalities had a net domestic migration loss of 4,000, while the suburban areas had a net domestic migration gain of 20,000. In two cases, the historical core municipalities had domestic migration losses. In the two cases in which cities had domestic migration gains, there were also domestic migration gains in the suburbs.
- New Orleans is a special case, by virtue of the fact that it is "still rebounding from the effects of Hurricane Katrina," according to the Bureau of the Census and remains 20 percent below its 2005 population. New Orleans is the only case that meets the requirement of historical core net domestic migration gain and suburban net domestic migration loss to demonstrate the likelihood of movement from the suburbs to the city. The historical core municipality had a net gain of 10,000 domestic migrants, while the suburbs lost 90, which could indicate that a very small number of people moved to the city from the suburbs (Note 3).
Moreover, the county data indicates that in 25 of the 49 metropolitan areas with suburban counties, core counties lost domestic migrants between 2010 and 2011.
The Effect of "Staying Put"
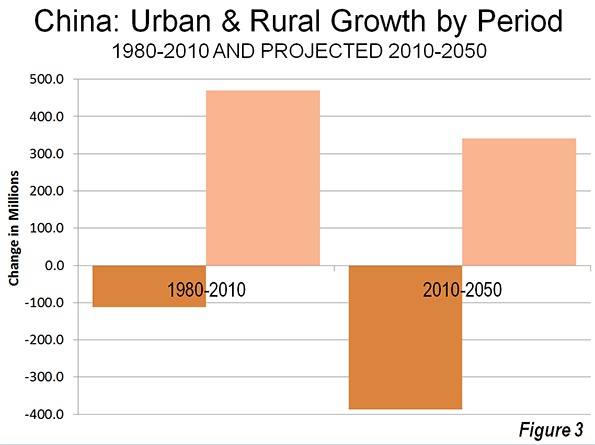
As with the previously released county population estimates, the city data that is available indicates that Americans are staying put in the difficult economy. Domestic migration has fallen substantially. Over the past year, 590,000 people moved between the nation’s counties. This domestic migration compares to an annual average of 1,080,000 between the 2000 and 2009 (Figure 1). This reduction in domestic migration has made international migration and natural growth more prevalent, and as a result, core growth has been stronger.
Note 1: An article in this morning’s Wall Street Journal contains information different from this article. The Wall Street Journal article classifies some cities as urban core that this article defines as suburbs (such as Fort Lauderdale [Miami], Aurora [Denver] and Arden-Arcade [Sacramento]). This article defines urban cores as historical core municipalities.
Note 2: All historical core municipalities are principally in one county, except for New York (city), which is five counties.
Note 3: The Bureau of the Census domestic migration data is limited to a net number for each county, so it is not possible to determine where people are moving to or moving from.