The world press has been fixated on the “Beijing” traffic jam that lasted for nearly two weeks. There is a potential lesson here for the United States, which is that if traffic is allowed to far exceed roadway capacity, unprecedented traffic jams can occur.
The Inner Mongolia Traffic Jam: First we need to understand that this was not a “Beijing” traffic jam at all,or even on the outskirts of Beijing. The traffic jam came no closer to Beijing than 150 miles (250 kilometers) away, beyond the border of the city/province of Beijing, through the province of Hebei and nearly to the border of Inner Mongolia. The traffic jam then extended for more than 60 miles (100 kilometers) from near the Inner Mongolia border to Jingxi, in the region/city of Ulanqab. In reality this would be like calling a New York City traffic jam something that originated from Springfield, Massachusetts to Boston’s I-495 beltway (Figure 1).
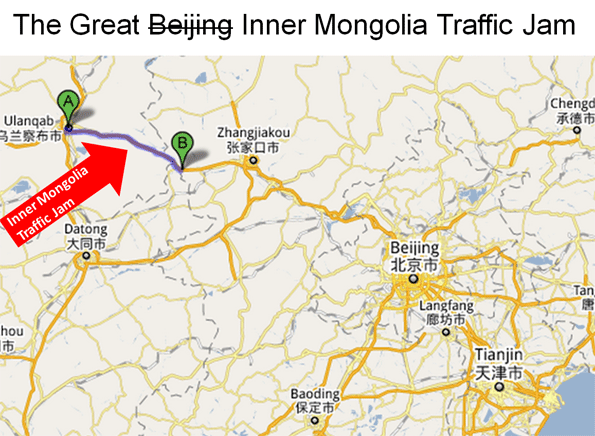
However, even the New York City example understates the complexity of the Chinese traffic jam. Beijing, China’s national capital, is one of the world’s largest urban areas (with a population of nearly 14 million). The city is situated at the northwestern limit of the densely populated part of China (which is called “China Proper”) that runs from Manchuria in the north to Yunnan in the south.
Beijing’s urbanization ends at the mountains less than 30 miles from the Forbidden City, Beijing’s core. The area beyond the mountains, through which the Great Wall runs, possesses only intermittent and generally minor urbanization. The area is dominated by grassland, and some rice farming. In this environment, it is not surprising that there were few alternatives for traffic to the G-110 Expressway (freeway), just as there would be few alternatives for traveling between Casper and Cheyenne, Wyoming on Interstate 25.
Continuing the I-25 comparison, the Inner Mongolian traffic jam more closely resembled traffic destined for Denver, with the congestion stretching from north of Cheyenne for another 60 miles, not far from the south end of the Powder River Basin, America’s largest coal producing region. This is a particularly appropriate comparison, because the type of traffic that caused the Inner Mongolian jam, coal trucks, would similarly jam I-25, were it not for the high-capacity freight rail system that moves most of the coal from the Powder River Basin to the nation’s electricity generation plants in the Midwest, East and South.
Like Interstate 25, the G-110 Expressway is a high quality divided and grade separated four lane road. As with Wyoming’s I-25, Inner Mongolia has an old 2-lane road (National Route 110) that parallels the G-110 for much of the way. This is not a viable alternative for the truck traffic volumes that are needed to supply the megacity of Beijing with its electric power.
Beijing’s First World Traffic: The Beijing city commission has announced that traffic flows continue to slow in Beijing. In the first half of 2010, the average speed dropped to 14 miles per hour (24 kilometers per hour). This is despite the fact that the urban area has a world class expressway system, with a fifth ring expressway (beltway) mostly completed (Note 1) and radial expressways feeding the inner areas. The surface arterial system in the inner area consists of a dense network of wide streets, providing capacity that certainly exceeds that of the city of Chicago or the four highly urbanized boroughs of New York, Manhattan, Brooklyn, the Bronx, and Queens (Note 2).
Beijing’s inner area traffic congestion is like that of New York City. The population density is 30,000 people per square mile (the approximate density also of the four New York boroughs), too high to move the volume of traffic over a freeway and expressway system. Higher population densities are associated with greater traffic congestion, slower speeds, stop and go traffic and more intense pollution. Beijing and New York share all of these conditions.
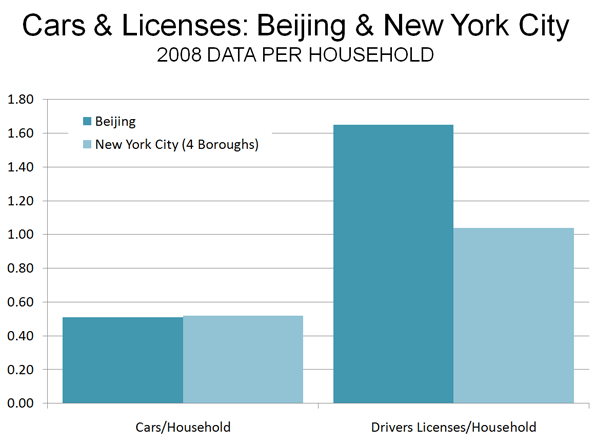
There is a perception that the traffic situation could become substantially worse in Beijing, and that could well be the case. However, it is surprising that the Bejing (the city/province) is already well along in private vehicle ownership and use. Beijing has achieved a car ownership rate almost equal to that of New York City’s dense boroughs. In 2008, the dense boroughs of New York City had 0.52 cars per household, while Beijing had achieved a 0.51 rate. One report now places Beijing’s car ownership one third higher than in 2008, which would place Beijing’s car ownership rate 20% above that of New York City.
By 2008, Beijing already had 1.5 times as many drivers per household as New York City’s dense boroughs (Figure 2). The difference appears to be in commercial drivers licenses, which account for nearly one-half of Beijing’s 9.4 million driver’s licenses. With the coal truck traffic and heavy truck traffic to the port of Tianjin, little more than 100 miles (160 kilometers) away, it is possible that trucks comprise a higher share of the traffic volume in Beijing than in New York City (Note 3).
Local authorities are seeking to reduce the traffic congestion problem by building one of the world’s largest Metro (subway) systems. By the middle of the decade, nearly 350 miles (561 kilometers) should be open. Some lines will extend to outside of the fifth ring road, where much of the population growth is occurring. The Beijing Metro, like that of Mexico City, has been designed to better serve the contemporary urban area. Both are characterized by a concentration of grid routes and less by radial routes. Beijing also has ring routes. This design is especially appropriate for Beijing, which as is typical for many large Asian urban areas and unlike New York, Chicago or Hong Kong, has a decentralized core. Large office buildings in the center are more sparsely spread around a larger area, larger than these concentrated central business districts. Yet, even with this appropriate route design, the decentralization of retail and office activity necessitates time-consuming transfers that can make cars faster, even in Beijing’s traffic.
China is also encouraging the use of electric cars, subsidizing buyers willing to switch from cars powered by fossil fuels. This will not ease traffic congestion, but it will reduce air pollution.
At the same time, a period review of traffic conditions on the Internet will show Beijing’s worst traffic congestion to be concentrated in the high density core while in the much less dense expanding suburbs, traffic conditions are considerably better. Additionally, there is discussion of a seventh ring road and Beijing officials continue to improve their roadway network. As in US urban areas, Beijing’s continued decentralization could allow traffic to eventually be managed. Economists Peter Gordon and Harry W. Richardson have found that “suburbanization has been the dominant and successful mechanism for reducing congestion.”
Clearing the Traffic: Meanwhile, there are reports that authorities have eased the traffic jam in Inner Mongolia. A longer term solution might be to add a couple of additional lanes in each direction. This should not be too difficult in a nation that by the end of the year will have nearly as many miles of freeway (43,000 or 70,000 kilometers) as the original US interstate system and will probably lead the world early in the next decade. This is a key to improving the competitiveness of Chinese urban areas. Sufficient roadway investment to handle growing travel demand will be just as important to maintain the competitiveness of US urban areas.
—-
Note 1: Beijing has six ring roads, however the first is the arterial road surrounding the Forbidden City, which is not an expressway.
Note 2: Staten Island is excluded because its urban form is principally that of a post-war suburb, with a much lower population density.
Note 3: This assumes comparability of data, which may not be fully reliable due to incomplete information.
—-
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris and the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life”
Photo of Beijing Fourth Ring Road by archlife
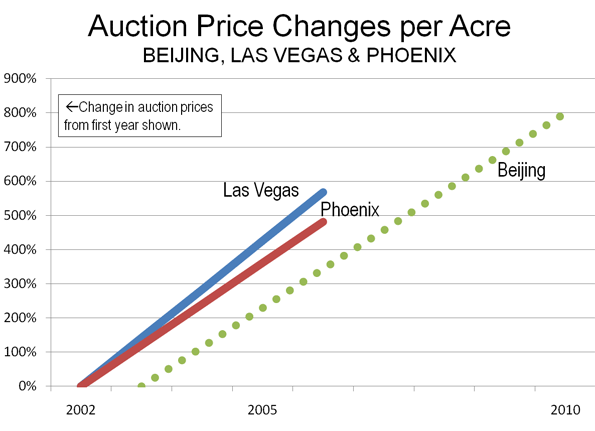
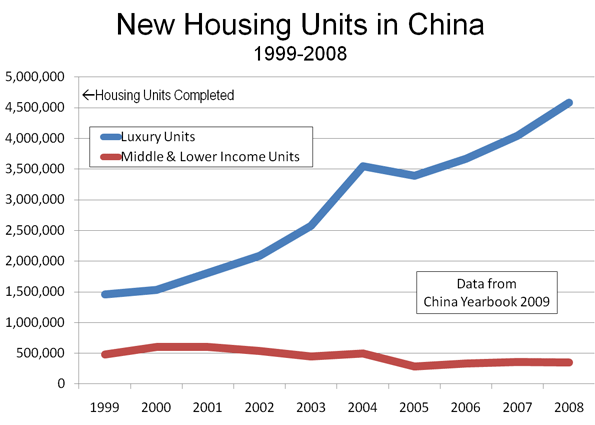
 The Coalition policy, however, represents the second significant development in recent weeks (Note). The first was an
The Coalition policy, however, represents the second significant development in recent weeks (Note). The first was an 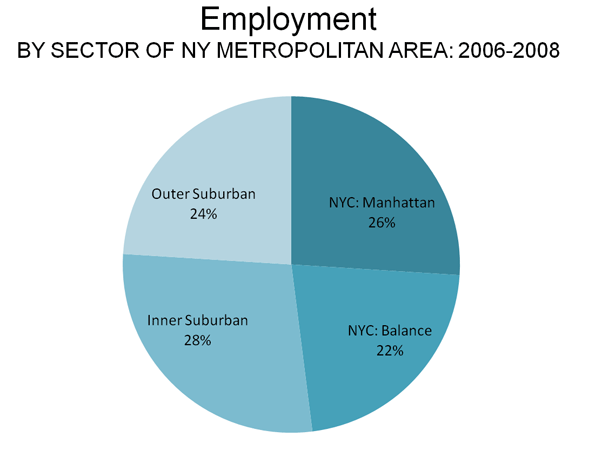
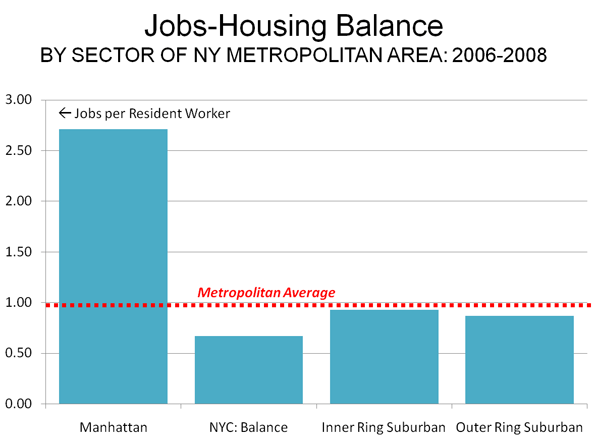
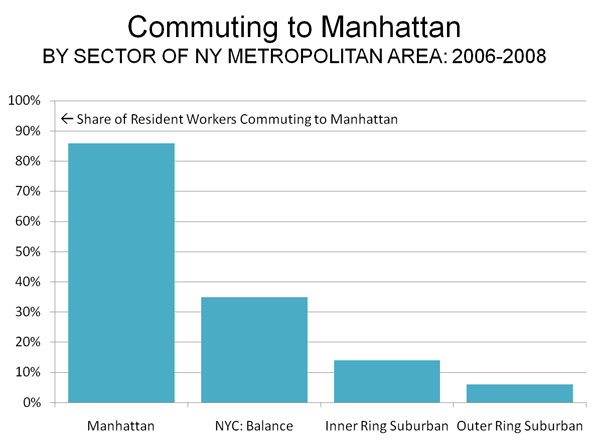
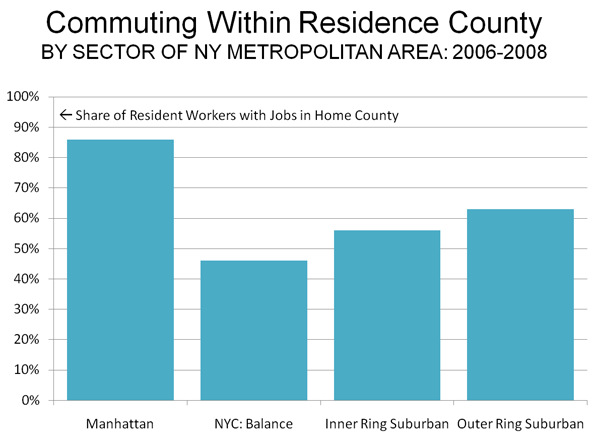
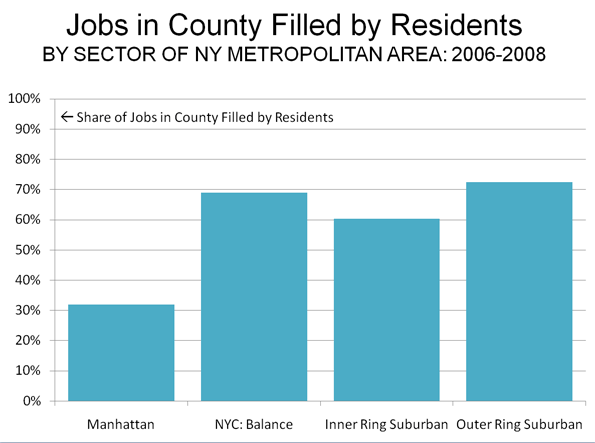
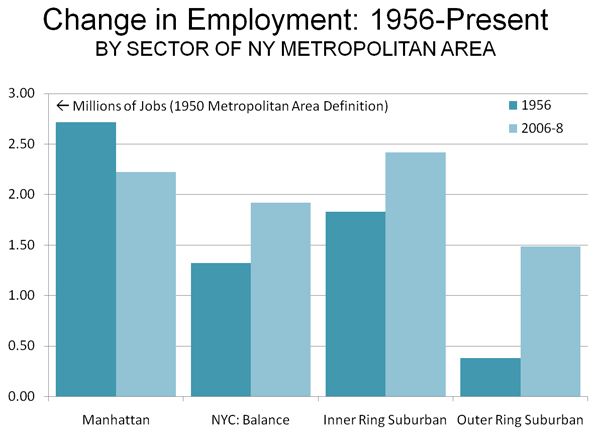
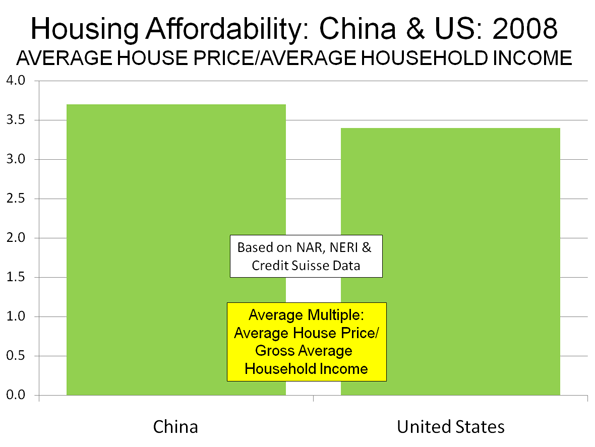
 At the same time, more liberal development regulations allowed a sufficient inventory of housing to meet the demand in high growth areas like Atlanta, Dallas-Fort Worth, Houston and Austin. In each of these places (and many others), the Median Multiple remained near or below the historic norm of 3.0, even with the heightened demand generated by a finance sector that had lost interest in credit-worthiness. As would be expected, speculators and flippers avoided the traditionally regulated markets, where an adequate supply of affordably priced housing continued to be produced.
At the same time, more liberal development regulations allowed a sufficient inventory of housing to meet the demand in high growth areas like Atlanta, Dallas-Fort Worth, Houston and Austin. In each of these places (and many others), the Median Multiple remained near or below the historic norm of 3.0, even with the heightened demand generated by a finance sector that had lost interest in credit-worthiness. As would be expected, speculators and flippers avoided the traditionally regulated markets, where an adequate supply of affordably priced housing continued to be produced.