One of the most ironic aspects of our putative “Age of Obama” is how little impact it has had on the nation’s urban geography. Although the administration remains dominated by boosters from traditional blue state cities–particularly the president’s political base of Chicago–the nation’s metropolitan growth continues to shift mostly toward a handful of Sunbelt red state metropolitan areas.
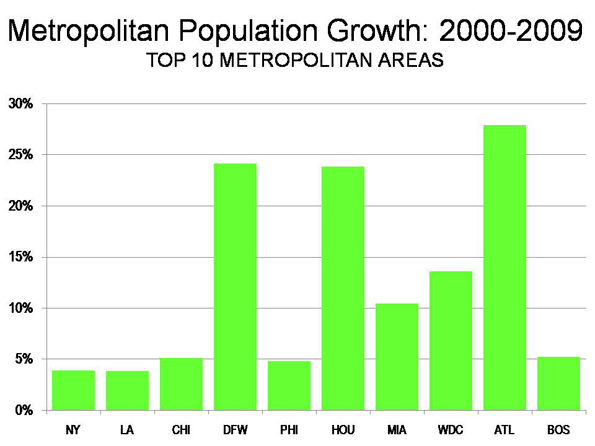
Our Urbanist in Chief may sit in the Oval Office, but Americans continue to vote with their feet for the adopted hometown of widely disdained former President George W. Bush. According to the most recent Census estimates, the Dallas and Ft. Worth, Texas, region added 146,000 people between 2008 and 2009–the most of any region in the country–a healthy 2.3% increase.
Other Texas cities also did well. Longtime rival Houston sat in second, with an additional 140,000 residents. Smaller Austin added 50,000–representing a remarkable 3% growth–while San Antonio grew by some 41,000 people.
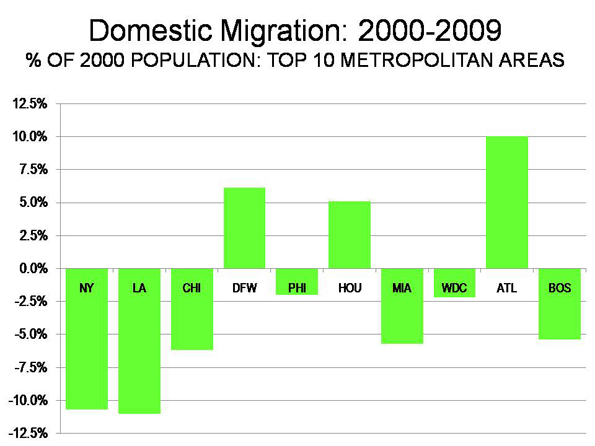
In contrast, most blue state mega cities–with the exception of Washington, D.C.–grew much more slowly. The New York City region’s rate of growth was just one-fifth that of Dallas or Houston, while Los Angeles barely reached one-third the level of the Texas cities.
These trends should continue: According to
This leads me to believe that the most dynamic future for America urbanism–and I believe there is one–lies in Texas’ growing urban centers. To reshape a city in a sustainable way, you need to have a growing population, a solid and expanding job base and a relatively efficient city administration.
None of these characteristics apply to places like President Obama’s hometown of Chicago, which continues to suffer from the downturn–but you would never know it based on media coverage of the Windy City.
The New Yorker, for example, recently published a lavish tribute to the city and its mayor, Richard Daley. But as long-time Chicago observer Steve Bartin points out, the story missed–or simply ignored–many critical facts. Mistaking Daley’s multi-term tenure as proof of effectiveness, it failed to recognize the region’s continued loss of jobs, decaying infrastructure, rampant corruption and continued out-migration of the area’s beleaguered middle class.
Generally speaking, as Urbanophile blogger Aaron Renn points out, the repeated reports of an urban renaissance in older northern cities should be viewed with skepticism. In the Midwest region over the past year the share of population growth enjoyed in core counties–an area usually much larger than the city boundary–actually declined in most major Midwestern metros, including Chicago.
Yet urbanists generally have not embraced the remarkable growth in the major Texas metropolitan areas. Only Austin gets some recognition, since, with its hip music scene and more liberal leanings, it’s the kind of place high-end journalists might actually find tolerable. The three other big Texas cities have become the Rodney Dangerfields of urban America–largely disdained despite their prodigious growth and increasingly vibrant urban cores.
Part of the problem stems from the fact that all Texas cities are sprawling, multi-polar regions, with many thriving employment centers. This seems to offend the tender sensibilities of urbanists who crave for the downtown-centric cities of yesteryear and reject the more dispersed model that has emerged in the past few decades.
Yet despite planners’ prejudices, places like Houston and Dallas are more than collections of pesky suburban infestations. They are expanding their footprints to the periphery and densifying at the same time.
Of course, like virtually all other regions, Houston and Dallas suffer excess capacity in both office buildings and urban lofts. But the real estate slowdown has not depressed Texans’ passion for inner city development. Indeed, over the past decade the central core of Houston–inside the boundaries of the 610 freeway loop–has experienced arguably the widest and most sustained densification in the country.
An analysis of building permit trends by Houston blogger Tory Gattis, for example, found that before the real estate crash, the Texas city was producing more high-density projects on a per-capita basis than the urbanist mecca of Portland. Significantly, as Gattis points out, the impetus for this growth has largely resulted not from planning but from infrastructure investment, job growth and entrepreneurial venturing.
This process is also evident in the Dallas area, which has experienced a surge in condo construction near its urban core and some very intriguing “town center” developments, such as the Legacy project in suburban Plano. In Big D, developers generally view densification not as an alternative to suburbia but another critical option needed in a growing region.
It’s widely understood there that many people move to places like Dallas, whether in closer areas or exurbs, largely to purchase affordable single-family homes. But as the population grows, there remains a strong and growing niche for an intensifying urban core as well.
Dallas and other Texas cities substitute the narrow notion of “or”–that is cities can grow only if the suburbs are sufficiently strangled–with a more inclusive notion of “and.” A bigger, wealthier, more important region will have room for all sorts of grand projects that will provide more density and urban amenities.
This approach can be seen in remarkable plans for developing “an urban forest” along the Trinity River, which runs through much of Dallas. The extent of the project–which includes reforestation, white water rafting and restorations of large natural areas–would provide the Dallas region with 10,000 acres of parkland right in the heart of the region. In comparison, New York City’s Central Park, arguably the country’s most iconic urban reserve, covers some 800 acres.
If it is completed within 10 years, as now planned, the Trinity River project will not only spawn a great recreational asset, but could revitalize many parts of the city that have languished over the past few decades. It could become a signature landmark in the urban development of 21st-century America.
As we look at the coming decades, this Texan vision may help define a new urban future for a nation that will grow by roughly 100 million people by 2050. To get a glimpse of that future, urbanists and planners need to get beyond their nostalgic quest to recreate the highly centralized 19th-century city. Instead they should hop a plane down to Dallas or Houston, where the outlines of the 21st-century American city are already being created and exuberantly imagined.
This article originally appeared at Forbes.com.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050
, released in Febuary, 2010.