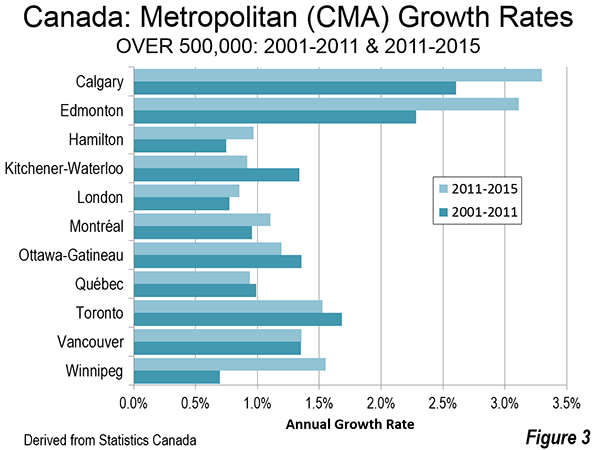
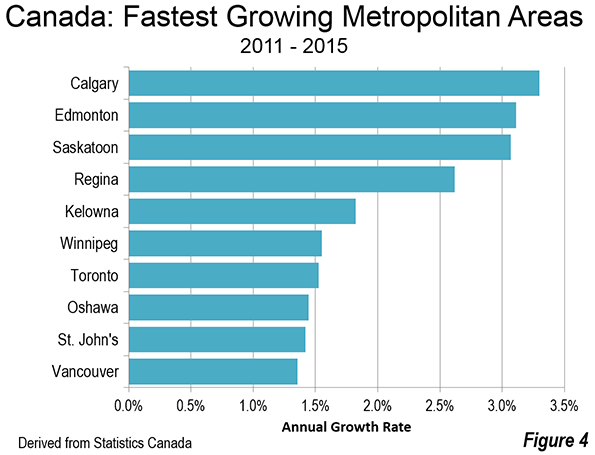
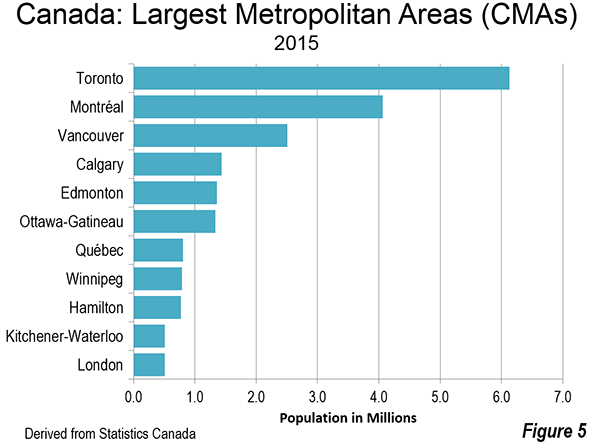
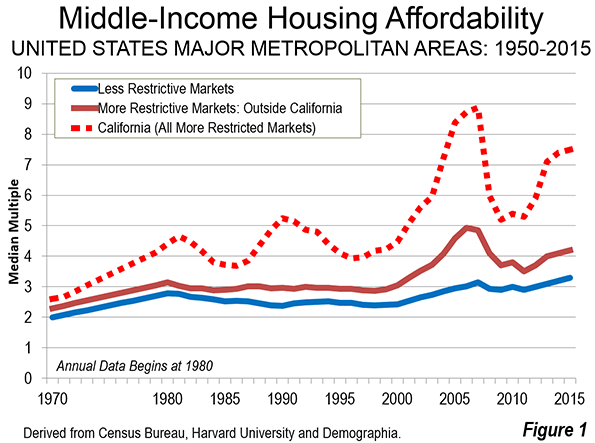
Some time back my brother recommended I watch the documentary film Medora, about a high school basketball team from rural Southern Indiana. I finally got around to doing it.
Someone described this film as an “inverse Hoosiers“, which is an apt description. Hoosiers is a fictional retelling of the Milan Miracle, the legendary story of how tiny Milan High School (enrollment 161) won the state’s then single-class basketball championship in 1954.
There’s no such happy ending in prospect in Medora (available on Netflix). The town’s basketball team had gone 0-22 the season before the film. The question is not whether they will win a championship or even the sectional, but if they can win just a single game.
The basketball team is a proxy for the community as a whole, a once proud town fallen on hard times. The town of Medora (pop ~700) and its surrounds, locals believe, used to be prosperous, socially cohesive, and have a great basketball team too.
This history is part mythological. I don’t doubt that these towns once had all the doctors and lawyers and such that people say they did. I’ve heard the same stories about where I grew up (two counties south). But that was a different era and I doubt there was ever real prosperity. Rural and small town life has always been tough in America.
But the social history certainly has much truth. Even in my own childhood I remember that people not only didn’t lock their houses, they left their keys in their cars. City water service, cable TV, garbage pickup, and even private telephone lines may not have been available, but it had its upsides too.
Today those Mayberry like characteristics are long gone.
In Medora we see not only poverty, but nearly complete social breakdown. I don’t recall a single player on the team raised in an intact family. Many of them lived in trailer parks. One kid had never even met his father. Others had mothers who themselves were alcoholics or barely functional individuals. They sometimes bounced around from home to home (grandmother, etc.) or dropped out of school to take care of a problematic mother.
These kids are also remarkably unsophisticated about the world. Once we see someone drive to Louisville – to pick his mother up from a rehab center – and another time one kid visits a seminary, but otherwise there’s no indication that these kids have spent much time or in some cases ever left Medora. One flirts with enlisting in the military. Another with what appears to be a for-profit technical college. But all of these are clearly unable to apply an independent knowledge or critical thought to what the sales reps for these entities are telling them.
Much of what structure exists in the town and the kids lives appears to be imported. Both the coach and one assistant coach appear to be from Bedford – 30 miles away. Neither really seems equipped to deal with these troubled kids.
Nothing indicates that these kids have much prospect of success in life.
Yet we see that there’s also little motivation on the part of the people in the town to actually change that. They are steeped in nostalgia and cling to a idealized vision of a past community that they surely know can never be reclaimed, yet insist on grasping until it is physically pried from their grip.
Medora is one of the last unconsolidated small town high schools left in Indiana. (I attended a small school, but one that was already consolidated, with the uninspiring name of South Central High School). It’s clearly not really viable as an independent school – it’s facing a major budget shortfall during the film – yet they steadfastly refuse to consider consolidation.
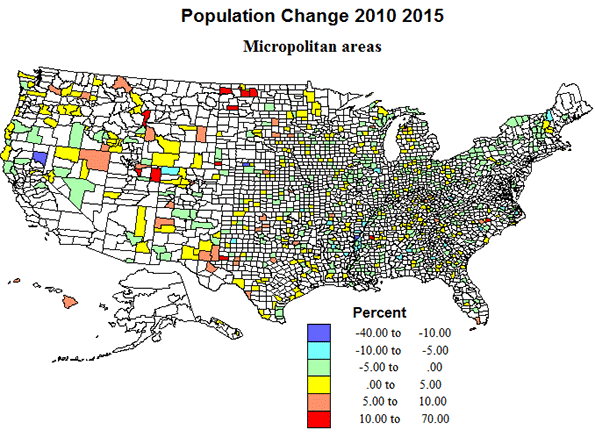
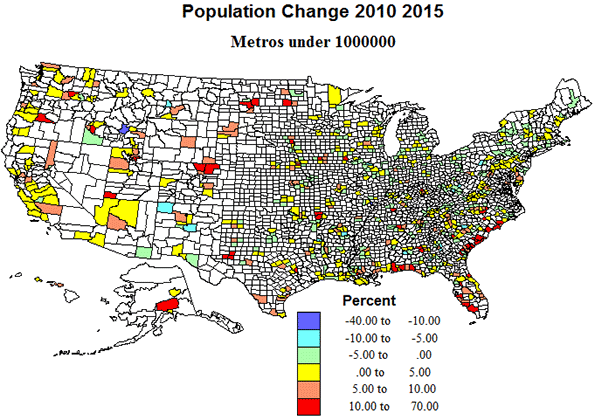
The town residents believe that the loss of the school would be the death knell of their community. They aren’t wrong about that. Merging the school would destroy the locus of identity. But the cold reality is that the modern world doesn’t need towns like Medora anymore. Always changing is the future as they say, but it’s hard to imagine anything that would sustainably restore the town. America is full of towns like Medoras. Some of them may experience a miracle. Most won’t, and will slowly bleed away to a dysfunctional rump community. (Interesting, Medora’s population grew by 23% during the 2000s, something worthy of further investigation).
The residents of Medora refuse to surrender their town and resolutely refuse to leave. In that they are not unlike the handful of people hanging on in depopulated Detroit neighborhoods who will accept planned shrinkage only over their dead bodies. It’s irrational to those of us who have no such attachment to a place, but it is clearly a sentiment that animates many such people all over the world.
The National Review’s Kevin Williamson blames the residents of these towns for their own demise. This is manifestly false. The people in these communities did not change the structure of the economy to render their homes obsolete. They did not invent the technology that destroyed the need for agricultural labor. They did not create the divorce revolution. They did not invent Oxycontin. These towns have always been belated, sometimes unwilling consumers of what is created elsewhere.
Yet the fact that outside forces acted on them does not absolve them from taking action now. Williamson is right about that. Much of the rural Midwest was settled by homesteaders who ventured off into the risky unknown, or German immigrants like the Renn family. These places were created by people who embodied different values than those who live there now, people who had no choice but to do something desperate in response to desperate conditions.
I chose to leave my hometown. Many other chose to stay. I know that many people there think it is God’s country and can’t imagine anyone ever leaving. I don’t want to claim that their attachment to place is less valid than my lack of it. Even in the city, to the extent that no one is attached to the place, to their neighborhood, for anything other than immediate self-interest, that’s not a good sign for the long term. I see today the consequences of viewing places purely as a mechanism for extracting personal or corporate profit in the now.
Yet the reality is that to the extent that people do choose to stay in the Medoras of this world, their future prospects aren’t good. Nor are those of their children. But if they leave their towns will die, along with a way of life. This isn’t a pleasant choice. They didn’t ask to be faced with it. But it’s the choice they face nevertheless.
Aaron M. Renn is a senior fellow at the Manhattan Institute, a contributing editor of City Journal, and an economic development columnist for Governing magazine. He focuses on ways to help America’s cities thrive in an ever more complex, competitive, globalized, and diverse twenty-first century. During Renn’s 15-year career in management and technology consulting, he was a partner at Accenture and held several technology strategy roles and directed multimillion-dollar global technology implementations. He has contributed to The Guardian, Forbes.com, and numerous other publications. Renn holds a B.S. from Indiana University, where he coauthored an early social-networking platform in 1991. His personal urban affairs website is Urbanophile, where this piece originally appeared.