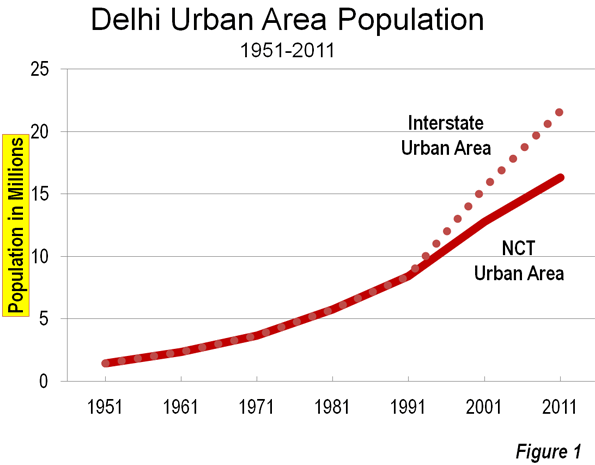
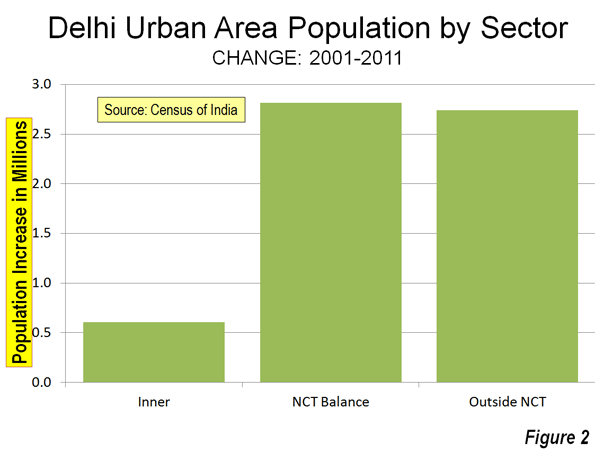
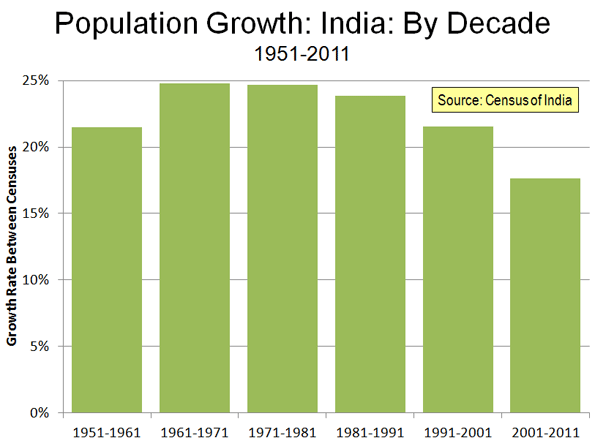
While many experts are pronouncing the demise of the American era and the rise of China, other East Asian nations complicate the picture. As America continues to participate and extend its influence in the dynamic Asian market, there may be no more suitable ally than its old antagonist, Vietnam.
In some senses, Vietnam has emerged as the un-China, a large, fast-growing country that provides an alternative for American companies seeking to tap the dynamism of East Asia but without enhancing the power of a potentially devastating global competitor. With 86 million people, Vietnam may not offer as large a market, but it has strong historical, cultural, and strategic reasons to lean towards America.
Why an un-China?
Vietnam has deep historical reasons for wanting to link closely with the United States and its other allies, such as Singapore, Thailand, South Korea, and Japan. Some of this has to do with the country’s unique history. While France, Japan, and the United States were at times deeply and bloodily entangled with the country, by far the biggest threat to Vietnam has always been its looming neighbor to the north.
France, Japan, and the United States intervened in Vietnam for comparatively short periods of time. In contrast, China has had an unrelenting interest in Vietnam and its 2,140-mile coastline ever since its nearly thousand-year rule over the country from 111 BC to 938 AD. The two countries have been embroiled in numerous territorial disputes over the years, with the most recent one involving the South China Sea, which has important shipping routes and is believed to contain rich oil and gas deposits.
Many Vietnamese see some of their former colonialist or “imperialist” powers as necessary allies in protecting themselves from escalating territorial threats from China. Opening Cam Ranh Bay naval base to foreign warships, notably to those from the United States, is an illustrative example of Vietnam’s defensive strategy during the unfolding geopolitical competition.
Amid the maritime tension between China and Vietnam regarding the oil-rich Spratly and Paracel islands in the South China Sea, the United States in 2010 successfully negotiated with Vietnam to reopen Cam Ranh Bay to foreign warships besides Russia. The bay will take approximately three years to rebuild and the primary foreign visitor is expected to be the United States. “The regular presence of U.S. warships at Cam Ranh Bay might make China think twice about using coercive military diplomacy against Vietnam,” noted Ian Storey, a fellow at the Institute of Southeast Asian Studies in Singapore.
The rise of the diaspora
Perhaps the greatest thing tying America to Vietnam is people. When the Communist government overran the former South Vietnam in 1975, several million Vietnamese fled the country. The Vietnamese eventually settled in 101 different countries and territories throughout the world, with the majority of them heading to the United States, France, Canada, and Australia. There are currently about 4 million Vietnamese living outside of Vietnam. Some settled in the former colonial ruler, France, and others in Australia, Canada, and Singapore. But the bulk—roughly 40 percent—moved to the United States, which is now by far the largest settlement of overseas Vietnamese. About 2 million Vietnamese are estimated to live in the United States (see map of “Overseas Vietnamese”).
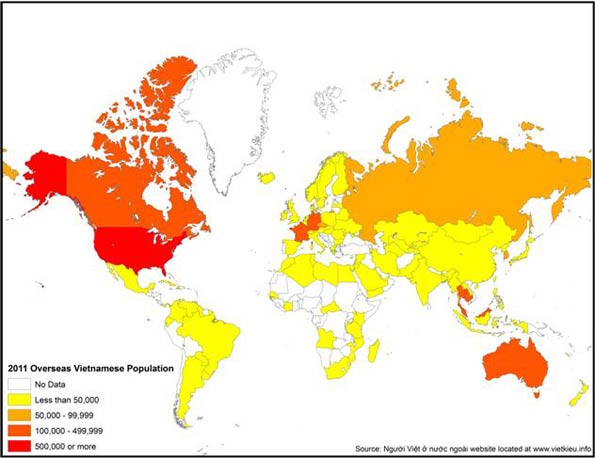
Hostile to the Communist regime, the overseas Vietnamese population turned away from their homeland , focusing instead on building new lives in their host countries. They flourished particularly in the United States, clustering in places such as Orange County and San Jose, California, as well as Houston and New Orleans. In 2009, they were enjoying levels of prosperity comparable to the national average, with a median family income of $59,129 and 64.6 percent owning homes. Vietnamese are also three times more likely to be in such fields as information technology, science, and engineering than other immigrants, and have one of the highest rates of naturalization—72.8 percent.
Contact between this dynamic diaspora and the homeland was constrained by the two governments for decades. After the Vietnam War, the United States had placed a strict embargo against Vietnam and prohibited any political or economic relations between the two countries. The Vietnamese refugees who sought to reconnect with their relatives in Vietnam had to rely on neutral third-party countries to act as an intermediary in sending various goods and money back to needy family members.
For their part, the Communist regime conducted stringent inspections of packages and letters sent to Vietnam. The Vietnamese government also imposed heavy taxation on financial remittances, which discouraged money transfers through official channels.
Desperate to help close relatives left behind in their impoverished homeland, many Vietnamese Americans were forced to invent creative alternatives to formal remittances. According to Yen Do, the creator of Nguoi Viet, the most prominent Vietnamese newspaper in the United States, overseas Vietnamese would hide American dollars inside pill bottles sent through either French or Canadian shipping companies.
With tens of millions of Vietnamese starving in Vietnam despite the clandestine remittances, the Vietnamese government eventually realized that they had to either change their economic strategy or suffer the debilitating consequences of a continually declining economy.
Remittances have played a critical role in reviving the economy. Last year alone the diaspora sent an estimated $7.2 billion into the country, according to the World Bank. This comprised about 7 percent of Vietnam’s overall GDP in 2010. A 2010 study conducted by Wade Donald Pfau and Giang Thanh Long revealed that 57.7 percent of all international remittances being sent to Vietnam in 1997-1998 came from the United States.
The growing symbiosis of Vietnam with its diaspora, particularly in the United States, will shape the rapid development of the country. Nowhere will this impact be felt more than in major cities such as Hanoi, Danang, and especially Ho Chi Minh City (the former Saigon). “We are seeing more of the expatriates here, and they are bringing management skill and capital through their family networks,” notes economist Le Dang. “They are a key part of the changes here.”
The rise of a new dragon
Aware of the enormous progress being made in China with its liberalization, in 1986 the Vietnamese government made the crucial decision to begin the Renovation Process—also known as Doi Moi—and reform the closed communist economy. It was the first official step that Vietnam had made towards opening its economic doors to the rest of the world.
With the collapse of the Berlin Wall in 1989 and the subsequent fall of other communist powers in the world, the United States eventually responded to the improved political relations with Vietnam by lifting the 20-year-old embargo against its former foe in 1995. This put Vietnam on the fast track toward economic liberalization and ultimately helped it transition from a developing country to a middle-income country with a GDP per capita of more than $1,000. The International Monetary Fund estimated Vietnam’s GDP per capita as $1,155 for the 2010 fiscal year.
Yet, in sharp contrast to China—where the largest sources of capital came from Chinese diaspora havens such Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Singapore—most of the money that revived the economy came from outside Southeast Asia. In particular, the biggest investor turned out to be the old arch-enemy, the United States, followed by another former “imperialist” power, Japan. China, now the world’s fourth-largest foreign investor, lagged behind much smaller regional economies, including South Korea, Thailand, and Malaysia, as well as the Netherlands (see map of “FDI by Registered Capital”).
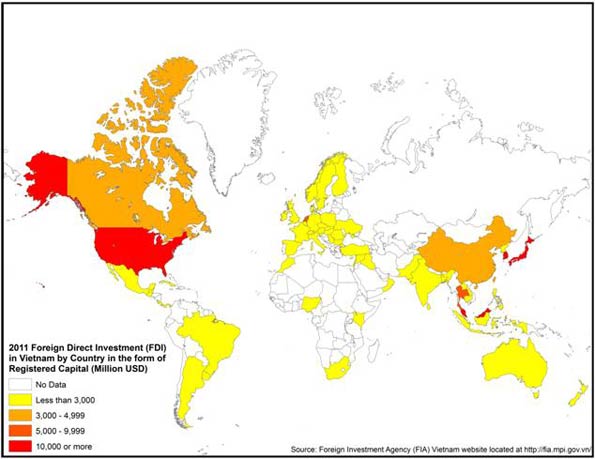
This is all the more remarkable given China’s huge expansion of investment with other developing countries. Over the past decade, China has expanded its capital flows both into other parts of Southeast Asia, including Laos and other Mekong Delta nations, as well as resource rich regions of the Middle East, Latin America, and Australia. Yet Vietnam, with its rich agriculture, fisheries, and developing energy industry, has stayed largely outside the emerging Sinosphere.
Trade winds
The tilt in investment is also borne out by trade patterns. Vietnam has seen, like most countries, a flood of Chinese goods, but it has also developed a strong appetite for exports from other countries, notably Japan, South Korea, and the United States (see map of “Exports to Vietnam”).
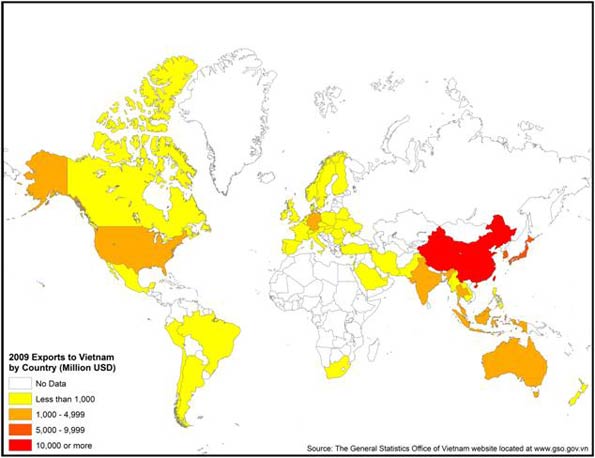
But perhaps the best measure of Vietnam’s emergence as an un-China can be seen in its own burgeoning exports, which increased from about $5 billion to over $70 billion over the past three decades. The United States has emerged as by far Vietnam’s largest market, with more than $10 billion in annual trade. Japan ranked a strong second, with China lagging behind.
This is all the more remarkable given that Vietnam possesses many things China needs and the two countries share both a border and obedience, at least nominally, to the same ideology. Vietnam seems to be making a choice to diversify itself away from China and avoid the semi-colonial status that many of China’s neighbors—notably Cambodia, Laos, and Myanmar—seem to have tacitly accepted (see map of “Vietnamese Exports”).
This rising engagement with the global economy has brought great benefits. According to the CIA World Factbook, the country’s poverty rate has dropped from 75 percent in the 1980s to 10.6 percent in 2010. In terms of economic output, a brief on Vietnam by the World Bank reported that between 1995 and 2005 real GDP increased by 7.3 percent annually and per capita income by 6.2 percent annually.
Why Vietnam matters to America
Hanoi today—and even more so Ho Chi Minh City, the former Saigon—recalls China in the 1980s. But there are crucial differences. State-owned companies in Vietnam lack the depth and critical mass of their Chinese counterparts and are thus less likely to pose an immediate competitive threat to the United States and other foreign countries.
Still, this is clearly a country on the way up. Many rural residents—still roughly 70 percent of the population—continue to pour into Hanoi and other cities, but without the same desperation that characterizes, for example, people moving from Bihar to New Delhi or Mumbai. There is nothing of the kind of criminal elements that fester in the favelas of Brazil or Mexico City’s colonias.
More important still are the “animal spirits” of the place. Adam Smith—or Jane Jacobs for that matter—would enjoy the very un-socialistic frenzy as motorcyclists barrel down the streets like possessed demons, with little regard to walking lanes or lights. Everyone not on the government payroll seems to be hustling something, or looking to. It reminds one of the Vietnamese outposts in Orange County, California, or in Los Angeles’ Chinatown, which is now largely dominated by Chinese from Vietnam.
Le Dang Doanh, one of the architects of Doi Moi, estimates that the private sector now accounts for 40 percent of the country’s GDP, up from virtually zero. But Le Dang also estimated that as much as 20 percent more occurs in the “underground” economy where cash—particularly U.S. dollars—is king.
“You see firms with as many as 300 workers that are not registered,” the sprightly, bespectacled 69-year-old economist explains. “The motive force is underground. You walk along the street. I followed an electrical cable once and it led me to a factory with 27 workers making Honda parts and it was totally off the system.”
This energy is in part a product of demographics. Most of the people you see in these unofficial workshops are in their 20s and 30s. And unlike what you see in China, these workers also have children. Vietnam may be modernizing and getting richer, but it also enjoys a growing population.
These trends have enormous long-term consequences. According to the CIA World Factbook, 69 percent of the approximately 86 million people in Vietnam are currently between the working ages of 15 and 64. In the next four decades the Vietnamese workforce is expected to expand rapidly; at the same time, it will contract dramatically in Japan, Taiwan, Singapore, South Korea, and China. As these countries amble into what demographer Nick Eberstadt has called a “fertility implosion” that will lead to a rapid aging of the workforce, Vietnam will remain relatively young.
Already this enormous source of cheap labor has compelled investors around the world to look toward Vietnam as a way to simultaneously cut costs and increase profits. But more important still is the rapid growth of education. The country enjoys nearly 95 percent literacy.
This combination of a growing and skilled workforce represents the same combination of factors that previously led to rapid growth in other Asian countries, from Japan in the 1960s to South Korea and Taiwan in the 1980s, and China more recently. One local investment house, Indochina Capital, estimates that by 2050 Vietnam’s economy will be the world’s 14th-largest—ahead of Canada, Italy, South Korea, and Spain.
Combined with the strong human ties and its aversion to domineering neighbors, these factors suggest that Vietnam may well prove itself as valuable an ally and trade partner to the United States as it was once an irrepressible enemy.
This piece originally appeared at The American.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University, and an adjunct fellow of the Legatum Institute in London. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050, released in February, 2010.
Jane Le Skaife is a doctoral candidate at the University of California, Davis. She is currently conducting her dissertation research involving a cross-national comparison of Vietnamese refugees in France and the United States.
Accompanying maps were prepared for Legatum Institute by Ali Modarres, chairman of the Geography Department, California State University at Los Angeles.
Photo courtesy of BigStockPhoto.com
.