North America remains easily the most favored continent both by demography and resources. The political party that harnesses this reality will own the political future.
America cannot afford a prolonged period of slow economic growth. But neither Democrats nor Republicans are prepared to offer a robust growth agenda. Regardless of what happened in the November midterm elections, the party that can outline an economic expansion strategy suitable to this enormous continental nation will own the political future.
Economic expansion that barely exceeds the current 2 percent or less is woefully insufficient for the United States. Such meager growth could perhaps work in countries with very low birthrates and limited immigration, such as in much of Europe and Japan, but not in the demographically vibrant United States.
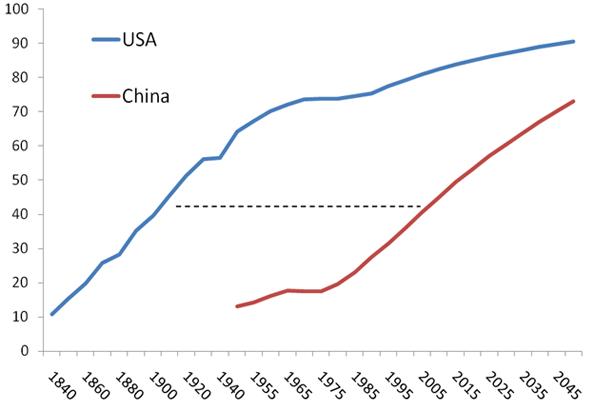
In the years between 2000 and 2050, Europe’s workforce will decline by 25 percent; Japan’s by 44 percent; China’s by 10 percent. In contrast, America’s workforce is expected to expand by more than 40 percent, adding millions of new entrants from an increasingly diverse population.
Given the growth in workforce, it is impossible to see how the country succeeds without rapid expansion not only of employment but also a broad-based wealth creation. Despite conservative attempts to dress up the numbers, the vast bulk of all the gains in wealth since 2000 have been achieved by the relatively small number of Americans with incomes significantly above the poverty level. Meantime many middle-tier educated and skilled workers have lost ground while the rate of upward mobility has stagnated.
The collapse of the housing bubble has eliminated the one way that middle class families took advantage of economic growth during the Bush years. Under Obama, virtually all the gains have been to the stock market (up 30 percent) and corporate profits (42 percent). Meanwhile, weekly earnings, jobs, and home sales price all stagnated or declined. But the biggest price may be paid by young people; even those with degrees have lagged behind in wage growth as they crowd into a labor market potentially far tougher than the one their boomer parents faced.
All this suggests an emerging “aspiration gap” that could define our politics for much of the next few decades. Today, belief in the achievability of the “American dream,” according to a recent survey by Strategy One, has dropped to the low 40s. Americans may still overwhelmingly believe in the ideal of upward mobility but, as individuals, now only a minority feel they can achieve it themselves.
The “aspiration gap” fundamentally does not advantage either party at the moment. Democrats are set for large losses in the 2010 election. But party identification and approval for the GOP remain low, particularly among the rising minority and millennial constituencies. Even in suburbia, amid rapidly rising middle class angst, the Republicans, according to a recent Hofstra University poll, have lost more support than the Democrats since 2008. Independents have been the big winner and constitute the largest faction of suburbanites—more than 36 percent, compared to just 30 percent two years ago.
Our Failing Parties: The Democrats
Let’s start with the Obamacized Democratic Party. Up through the 1990s, the Democrats still maintained strong links to small businesses, private sector unions, and the old Midwest industrial economy. This gave them reasons to favor growth-inducing policies that could close the “aspiration gap.”
But today the party has become captured largely by the coastally oriented alliance of public employees, their charges, greens, and the professiorate—what Fred Siegel calls an alliance of the “overeducated and the undereducated.” For the most part, these constituencies are largely detached from the private sector, and thus only tangentially interested in economic growth. Even high unemployment, unsurprisingly, was not the primary concern for an administration dominated by longtime public servants and tenured professors—people who rarely lose their jobs.
This indifference stems not so much from a traditional socialist agenda, as imagined by some conservatives, but by the nature of the party’s constituencies. It is more a dictatorship of the professoriate than that of the proletariat.
Further obscuring the growth agenda is the fact that some key advisors consider growth itself inherently evil. Take for instance the president’s science advisor John Holdren. A protégé of the Malthusian Paul Ehrlich, Holdren long has favored the planned “de-development” of Western economies in order to reduce consumption.
The “de-development” agenda has been bolstered by the growth of the climate change industry. Proposals for “cap and trade” rules or Environmental Protection Agency regulations on greenhouse gases represent profound threats to basic industries like manufacturing, housing, and agriculture. In contrast, they have proven boffo for university research grant-seekers and Silicon Valley venture capitalists, who increasingly focus on “clean” technologies subsidized by government grants and edicts favoring their technologies.
The climate change agenda also distorts the administration’s approach to infrastructure. Instead of focusing on transportation bottlenecks effecting companies and commuters on a daily basis, the administration has favored massive boondoggles such as high-speed rail or sometimes poorly conceived light-rail systems. These are often too expensive compared to alternatives, and not well-suited to the needs of most American communities or companies.
Our Failing Parties: The Republicans
Today, with as many as 25 million Americans unemployed or underemployed, the Democratic Party still seems to be missing a coherent program to put them back to work. Sadly, much the same can be said of the Republicans, who benefit from populist outrage about the stimulus, but also lack an answer to the deepening aspirational gap.
The fundamental problem is obvious at the level of the Tea Party, the grassroots driving force behind today’s GOP. Tea partiers know what they are against—higher taxes and government spending—but have not developed much in the way of approaches to spur growth.
This is epitomized by the career of the movement’s patron saint, Sarah Palin. Celebrated by many in the “lower 48,” Palin is widely seen among Alaska’s predominately Republican business community as indifferent to economic growth. As governor, they maintain, she proved more interested in redistribution to the middle class—through larger checks from the state’s energy fund—than in investing in things like new infrastructure.
“She epitomizes the whole idea of we get a piece and no sense of planning for the future, about thinking about what we need to do,” notes Jim Egan executive director of Commonwealth North, a local think tank.
Long-term growth, in Alaska and elsewhere, Egan suggests, needs government to play a critical supporting role. The fact that the Obama administration missed its opportunity to focus on basic infrastructure in its bungled, politically driven stimulus does not mean that investing in the future is an inherently bad idea.
The Republican embrace of austerity represents good policy when it comes to reducing wasteful spending, notably on public employee pensions. But knee-jerk resistance to any government spending could prove detrimental in an increasingly competitive world.
Needed: A Continental Strategy
To promote economic growth, the country needs to develop a new national consensus around which I call “a continental strategy.” This would focus on taking advantage of the unique demographic and resource assets of this country as well as its North American neighbors, Mexico and Canada.
Today the United States faces formidable competitors, notably from China, India, and Brazil. These are proud, vast countries with considerable resources and an expanding middle class population. At least in the short run, they suffer neither the ruinous demography of Japan nor the elaborate welfare burdens of Western Europe.
Already these countries are investing in their basic infrastructure so that they can tie their vast landmass together and profit from it.
Hard as it is to imagine amid the wreckage of the stimulus, American history is replete with examples of how government can actually do good things. The public support for canals, railway lines, the New Deal engineering and construction projects, the Interstate Highway, and space programs all greatly benefited the country’s economy. They underpinned first American leadership in the industrial age, and then in the information economy. In recent decades, public investment in basic infrastructure construction and maintenance has declined, even in the face of considerable population growth.
“One looks back at that map ‘Landscape by Moses,’” writes the sociologist Nathan Glazer, about the legacy of New York City’s “master builder” Robert Moses, “and if one asks what has been added in the 50 years since Moses lost power, one has to say astonishingly: almost nothing.”
Restoring our priority towards binding together and improving our continental infrastructure remains critical to achieving greater economic growth. Rather than a policy of retrenchment, it would represent a return to an approach that sparked our original ascendency and could gain broad bipartisan support.
Even today, what makes a continental strategy so compelling lies with this often overlooked reality: North America remains easily the most favored continent both by demography and resources. It possesses the world’s second-largest oil reserves and massive, still largely untapped natural gas supplies.
North America also constitutes by far the world’s richest agricultural area, with the most arable land. This is a huge advantage as global food demands grow over the next few decades. Critically, the continent also boasts more than four times as much water per capita as either Asia or Europe.
Most important still, North America retains a unique demographic vitality among all advanced countries. It continues to lure upwardly mobile people from around the world: roughly half of the world’s educated migrants come to America, and a considerable number also head for Canada.
Ultimately a continental strategy meets the needs of large segments of the country—ranging from immigrants and their children to millennials—who will dominate our emerging job market. These same groups in the coming decades will also shape our political future.
The party that offers these new voters the greatest opportunities for work, raising a family, and buying a house will be the one that dominates the political future. As generational chroniclers Mike Hais and Morley Winograd, both committed Democrats, have pointed out, millennials are essentially nonideological; they will be attracted to those policies that work, both for society and for their young families.
Although this year’s political results may please conservative ideologues, they should recognize that this represents only the defeat of poorly executed Obamian statism. The future belongs to whichever party emerges as the true party of growth.
This article originally appeared at The American.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050
, released in February, 2010.