Every age produces its own brand of oligarchs – feudal lords, banking gnomes, captains of industry. Our age has its own incipient ruling class, the tech oligarchs.
The ascendency of these new hegemons is barely complete, and could conceivably be slowed or even reversed. But the tidal wave of new wealth, and even greater influence, will not be easily turned back. Six of the world’s 20 richest people are from tech or related industries like media and entertainment. In America, the media-tech sector in 2014 accounted for five of the top wealthiest people. Not surprisingly, most self-made billionaires are either quite old (the Koch Brothers, the Waltons, Warren Buffett) or got rich the traditional way: they inherited it. In contrast, virtually all self-made billionaires under 40 are techies.
The making of a new ruling class
With their massive, and early, accumulated wealth, the tech oligarchs will dominate us long after the inheritors have financed the last art museum or endowed the newest hospital. Two decades from now, many tech oligarchs will still be young enough to be counting their billions and thinking up new ways to ‘disrupt’ our lives – for our own good, of course.
This tech elite differs from the founding generation of Silicon Valley. The early leaders – Bob Packard, Bob Noyce, Andrew Grove, Jerry Sanders – tended to be centrist and pragmatic. After all, the early Valley was heavily subsidised by the military and NASA, and produced industrial products that faced enormous competition. They also managed vast organisations with large numbers of ordinary employees. Like other industrialists, they were concerned with low-cost power and water, reasonable labour regulation and the health of the overall manufacturing economy.
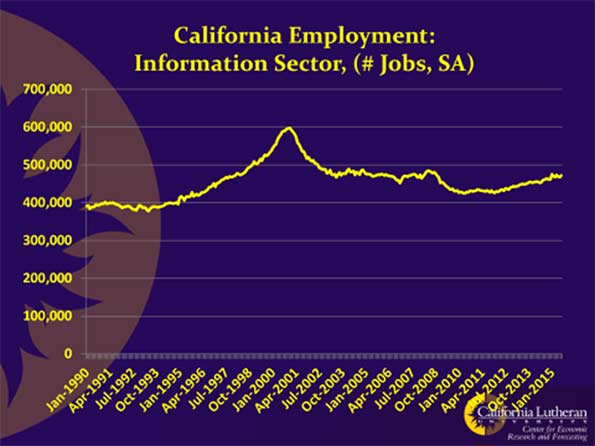
This changed when a combination of keen Asian competition and Californian regulation gradually shifted the chip and computer manufacturers out of Silicon Valley, which has lost roughly 80,000 manufacturing jobs since 2000. The new Valley is predominately post-industrial. For example, only 30 of about 16,000 production workers for the iPod are based in the US.
As Silicon Valley became software valley, tech firms no longer needed large numbers of semi-skilled workers and the network of small subcontractors to keep the industrial machine going. Those services, if needed, could be performed in India, China, Utah, Texas or North Carolina. ‘The job creation has changed’, notes long-time San Jose economic development official Leslie Parks. ‘We used to be the whole food chain and create all sorts of middle-class jobs. Now, increasingly, we don’t design the future – we just think about it. That makes some people rich, but not many.’
What has made ‘the sovereigns of cyberspace’, to quote author Rebecca MacKinnon, so wealthy is precisely what made John D Rockefeller so rich: control of markets. Google, for example, accounts for over 60 per cent of search, while, alongside Apple, it control almost 90 per cent of the operating systems forsmartphones. Similarly, over half of American and Canadian computer users use Facebook, making it easily the world’s dominant social-media site.
More important still, the tech oligarchs control portions of their companies that would make most oilmen or auto executives fantastically rich. Indeed, owners of only one energy-related firm, Koch Industries, have made it into the top 10 of the Forbes 400. The CEO and chairman of Exxon-Mobil, America’s largest oil company, Rex Tillerson, controls 0.04 per cent of Exxon stock, while Google’s Sergey Brin, Larry Page and Eric Schmidt control roughly two thirds of the company’s voting stock. Larry Ellison, the founder of Oracle, Bill Gates and Mark Zuckerberg also control outsized shares of their firms.
These firms are now so rich that they resemble countries. Besides General Electric, a classic conglomerate, Apple, Microsoft, Cisco, Oracle and Google often have more dollars on hand than the US government. And their influence can be felt in every office, home and phone through intrusive software that provides a trove of personal data that would make the old KGB turn from red to green with envy. As Google’s Eric Schmidt put it: ‘We know where you are. We know where you’ve been. We can more or less know what you’re thinking about.’
The politics of the intangible class
The liberation from the constraints of the tangible economy has inflamed the ambitions of the oligarchs. ‘Politics for me is the most obvious area [to be disrupted by the web]’, suggests former Facebook president Sean Parker. The success with which social media assisted President Obama’s re-election effort offers clear support to Parker’s assertion.
In allying with Obama, tech is moving in the opposite direction to much of the business community, particularly small business, which Gallup finds a hotbed of anti-Obama sentiment. Other traditional industries like oil and gas have also turned overwhelmingly to the right, as Obama has targeted them for their role in climate change. In 1990, energy firms gave out almost as much to Democrats as Republicans; in 2014 they gave over three times as much to the GOP.
In contrast, the oligarchs, as they have become ever richer, are clearly moving leftwards. In 2000, the communications and electronics sector was basically even in its donations; by 2012, it was better than two to one Democratic. Microsoft, Apple and Google – not to mention entertainment companies – all overwhelmingly lean to the Democrats with their donations.
The transformer and the disrupters
There seems a natural affinity between President Obama, who sees himself as a force for transformation, and the tech oligarchs, who love ‘disruption’. Each shares a high estimate of their basic intelligence and foresight; it is an alliance of those who feel they should own and shape the future.
‘We need to run the experiment, to show what a society run by Silicon Valley looks like’, venture capitalist Chamath Palihapitiya recently argued. This effort could appeal to a public that tends to regard the tech firms as better than more mundane businesses or the government. Indeed, when Steve Jobs, a 0.000001 per center worth $7 billion, and rugged capitalist of the classic type, passed away, protesters openly mourned his demise.
One critical PR advantage the tech firms enjoy is that most, with a notable exception of Amazon, don’t mistreat blue-collar workers, or unions, since they have few of either. This gets them a free pass from social-justice warriors unavailable to traditional firms. Andrew Carnegie and Henry Ford mostly exploited workers in Pittsburgh or Detroit, and paid a price; the exploitation of the oligarchs takes place far away in Chengdu, Guangzhou or India.
This alliance with the Democrats will not fade after Obama leaves office. Obama has enlisted several tech giants – including venture capitalist John Doerr, LinkedIn billionaire Reid Hoffman and Sun Microsystems co-founder Vinod Khosla – to help plan out his no doubt lavish and highly political retirement. Many former Obama aides have gone to work for tech firms. Uber, for example, uses Obama campaign manager David Plouffe to lead its PR team, while other former officials have descended to other tech firms such as AirBnB, Google, Twitter and Amazon.
What is the ideology of Silicon Valley?
Silicon Valley may be progressive in its social or environmental positions, but it has little interest in class politics, an issue being pushed by Vermont Senator Bernie Sanders in the Democratic primaries. ‘They don’t like [Bernie] Sanders at all’, notes San Francisco-based researcher Greg Ferenstein, who has been polling internet company founders for an upcoming book. Sanders’ emphasis on income redistribution, protecting union privileges and pensions hardly reflects the views of the tech elite. ‘He’s an egalitarian liberal’, Ferenstein explains, ‘these people are tech liberals. Equality is a non-issue in Silicon Valley.’
What are ‘tech liberals’? Ferenstein provides a picture of an unconscious elitism that runs through their worldview. Although their industry is overwhelmingly based in the San Francisco Peninsula’s suburban sprawl, the internet oligarchs, he claims, want ‘everyone’ to move to the urban centre, something not remotely practical for most middle- and working-class families. They also advocate for strict environmental laws and ever higher energy prices, which don’t threaten their lifestyles, but are often devastating to those below them.
Yet there is a danger that the issue of inequality could eventually affect the tech industry’s PR. Unlike the earlier products, such as computers or semiconductors, the products the tech industry now develop have provided little of value to the rest of society, whether in terms of jobs (outside of the Bay Area) or boostingproductivity. The social-media industry has made the likes of Mark Zuckerberg fantastically wealthy, but it’s difficult to maintain it has improved living conditions for most Americans.
At the same time, well-financed Valley ‘disruption’ can be seen as a threat to many businesses and individuals. These already include groups such as cab drivers, owners and workers at small hotels, realtors and travel agents, and newspaper scribblers, all of whom are being driven out of the middle class. The much-needed ‘sharing economy’ often offers these workers part-time employment without much in the way of benefits.
Even in the tech industry itself, American workers find themselves increasingly replaced by imported foreign workers. Oligarchs such as Mark Zuckerberg are anxious to expand H1B and other ‘guest-worker programmes’ that bring in low-cost indentured tech workers to the Valley, as well as to IT departments across corporate America.
Of course, this hardly makes the tech oligarchs unique – after all, capitalists have always sought out the cheapest source of labour, and understandably so. But it does mean that, in oligarchic America, where even getting a degree in computer science and software does not guarantee a bright future, the hip, PR-friendly ‘don’t be evil’ appearance of tech companies may soon be looking a little less cool.
Techies on the green team
Perhaps nothing separates the oligarchy from the rest of business than its support for Obama’s climate-change policies. Many industries see these policies as a direct threat to their very existence, but this means little to moguls, who can shift their energy needs to cheaper locales, such as the Pacific Northwest or the South. In California, such policies have less an impact on the temperate coast than in the less glamorous interior. As one recent study found, the summer electrical bills in rich, liberal and temperate Marin come to $250 monthly, while in impoverished, hotter Madera, the average is twice as high.
Not that there’s anything cynical about the tech oligarchy’s commitment to green policies. It is entirely sincere – the oligarchs really do believe, as do many liberal, Democratic types, that they are fighting the good fight. But that doesn’t mitigate the effects of their worldview.
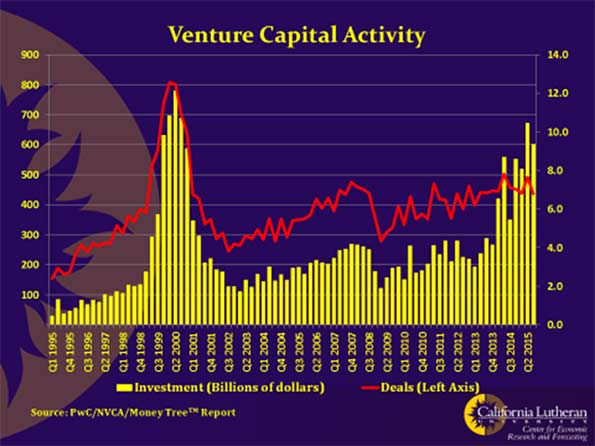
Still, the oligarch’s energy politics are not entirely based on the greater good. ForSilicon Valley and Wall Street supporters, there are also some business opportunities in the assault on fossil fuels. Cash-rich firms like Google and Apple, and many high-tech financiers and venture capitalists, have invested in subsidised green energy firms. Some, like Elon Musk, exist largely as creatures of subsidies. Neither SolarCity nor Tesla would be so attractive, or might not even exist, without generous handouts.
The brave new world of the oligarchs
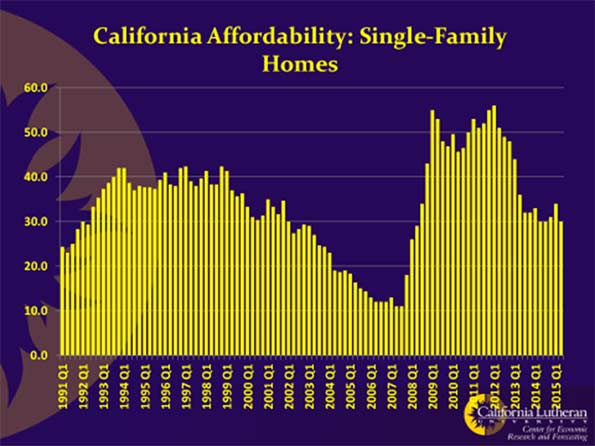
If we want to get some idea how an oligarch-dominated economy works, take a look at my adopted home state – of over 40 years – of California, the home of the most powerful oligarchs. The Golden State sees itself as the ‘brains’ of the tech culture and proof of the bountiful ingenuity of ‘the creative class’.
Yet behind the media glitz, California is increasingly a bifurcated state, divided between a glamorous software- and media-based economy concentrated in certain coastal areas, and a declining, and increasingly impoverished, interior. Overall, nearly a quarter of Californians live in poverty, the highest percentage of any state, including Mississippi, and, according to a recent United Way study, close to one in three people are barely able to pay their bills.
So how do the oligarchs make this work politically? One way is simply to make alliances – through contributions and media support – with politicians who are most hurt by California’s regulatory vice. This strategy is evident in the odd coupling of San Francisco hedge-fund billionaire, Tom Steyer, the biggest funder of climate-change hysteria, and his Latino sidekick, California Senator Kevin de Leon, who represents impoverished East Los Angeles.
The new political configuration works in classic medieval fashion, with the rich providing the necessities for the poor, without providing them opportunity for upward mobility or the chance, God forbid, to buy a house in the outer suburbs. With the fading of California’s once powerful industrial economy – Los Angeles has lost much of its manufacturing base over the past decade – its working classes now must be mollified by symbolic measures, such as energy rebates, subsidised housing and the ever illusive chimera of ‘green jobs’.
This ‘upstairs-downstairs’ California coalition could presage the country’s political future. Perhaps it’s best to think of it as a form of high-tech feudalism, in which the upper classes run the show, but bestow goodies on the struggling masses. This alliance will allow the present tech oligarchs to thrive without facing a populist challenge that could interfere with their profits and expansion into other markets.
In the oligarchic era, the bottom line is an increasing concentration of power in ever fewer hands. Romantic notions that the high-tech era would be marked by a surge of small, independent companies are belied by the market domination of a few firms and their expansion into ever more business areas. Companies like Google begin to morph into conglomerates, or American versions of Japan’skeiretsu, with interests in such businesses as health, media and autonomous vehicles.
Similar keiretsu are forming around companies such as Apple, Amazon and Facebook, which now can buy their way into what were once seen as unrelated markets. This is married to increased media power, which will allow them to set the agenda in coming decades. This is being accomplished both through the purchase of old media – the most important being the purchase by Amazon’s Jeff Bezos of the venerable Washington Post – or by new sites controlled by firms like Yahoo, the No1 news site in the US, with 110million monthly viewers, or Google’s news site with 65,000,000 users.
The intrusion of tech firms into media is likely to become even more pervasive as the millennial generation grows up and the older cohorts begin to die off. Among those over 50, only 15 per cent, according to a Pew report, get their news over the internet; among those under 30, the number rises to 65 per cent.
Ultimately the ambitions of the oligarchs are boundless. Firms like Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin, and Elon Musk’s Space X, seek to lead the world in space exploration. If NASA continues to retreat from many areas of space exploration, it is likely that, in the future, the heavens may end up belonging to the oligarchs as well.
When historians write the history of this age, their attention likely will focus on the rise of these oligarchies. They already control California, with its unparalleled creative and technical prowess, as well as the dominant cultural power centre in the English-speaking world. Tomorrow the new oligarchs will be looking to consolidate their power in Washington. And the day after that, maybe the world and galaxy as well.
This piece originally appeared at Spiked.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and Roger Hobbs Distinguished Fellow in Urban Studies at Chapman University, and a member of the editorial board of the Orange County Register. He is also executive director of the Houston-based Center for Opportunity Urbanism. His newest book, The New Class Conflict is now available at Amazon and Telos Press. He is also author of The City: A Global History and The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050. He lives in Orange County, CA.
Official White House Photo by Pete Souza.