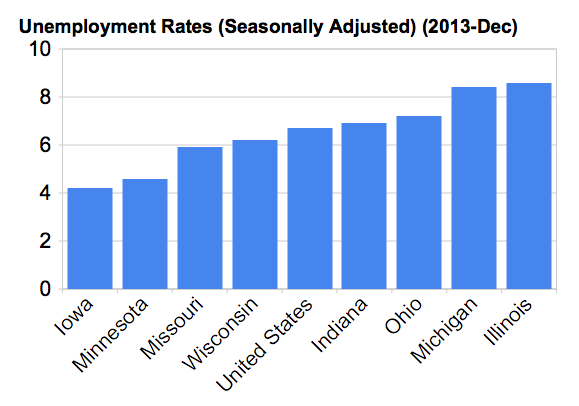
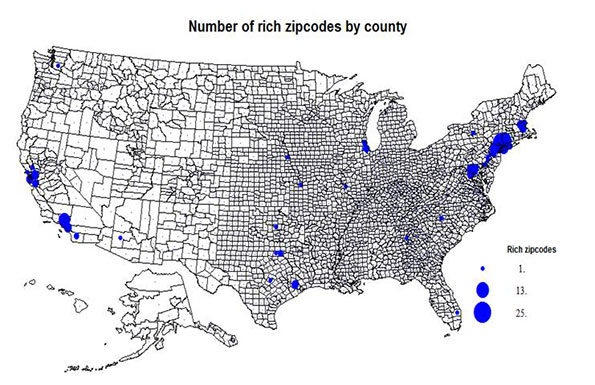
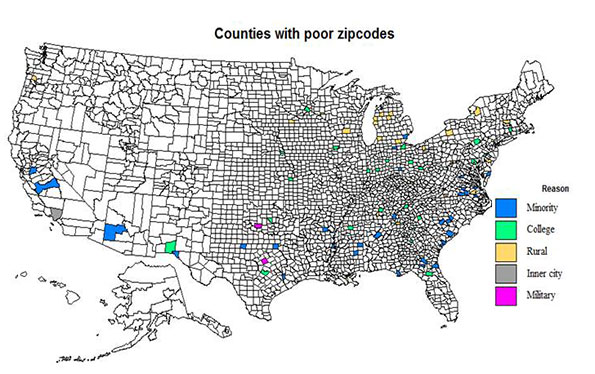
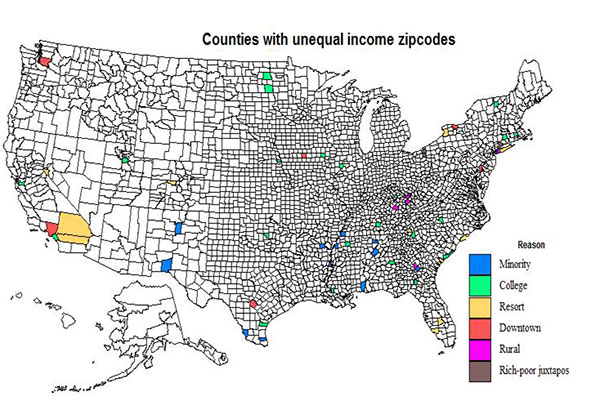
This is the executive summary from a new report Sustaining Prosperity: A Long Term Vision for the New Orleans Region, authored by Joel Kotkin for Greater New Orleans, Inc. Download the full report from GNO, Inc. here: gnoinc.org/sustainingprosperity
The recovery of greater New Orleans represents one of the great urban achievements of our era. After decades of slow economic, political and social decline, hurricane Katrina seemed a kind of coup de grâce, smothering the last embers of the region’s vitality. In the fall of 2005 it was entirely logical to see New Orleans as just a potential exemplar of failed urbanization, much as we might see in Detroit1, Cleveland, and a host of other once great cities – for example Naples, Lisbon, Antwerp and Osaka – that have tumbled from their once great importance.2
Yet in New Orleans’ case, disaster engendered not continued decline, but the revival of the entire region, its economy, and social and political institutions. Like Chicago after the great fire of 1871, San Francisco in the wake of the 1906 earthquake and fire, or New York following 9-ll, New Orleans has rebounded in ways that have defied expectations.
Critical to making New Orleans a resilient city has been the transformation of the civic culture. This has much to do with the commitment of New Orleanians to their city – like Chicagoans, New Yorkers and San Franciscans in the past. “A city,” notes urban historian Kevin Lynch,” is hard to kill if it possesses unique cultural appeal, geographic assets and people who are determined to save the city they love.”3
New Orleans resiliency since Katrina constitutes much more than improved levees or better evacuation procedures; more than new brick and mortar applied to what had been an aging, deteriorating region. New Orleans has made enormous progress in cleaning up its famously corrupt political system, and also made huge strides in improving its educational infrastructure. Once considered one of the worst places to do business, the region, and the state of Louisiana, has undergone a marked improvement to its reputation. It has emerged as a good place for commerce – something of a “Cinderella” in economic development terms.4 Allison Plyer of the Greater New Orleans Community Data Center put it, “Greater New Orleans is in some ways rebuilding better than before”.5
Our analysis shows this progress in a host of indicators. Once a below-average job producer, the region has expanded its employment since the 2007 recession far faster than the national average. It recovered all the jobs lost in the recession by 2012 – and then some – while the nation remained three percent below its pre-recession level. Entrepreneurial activity also has grown faster than the national average by a wide margin.6
More important still, the region finally began to reverse a demographic decline that, for a generation or more, saw young, educated people and families depart for other locales to seek out a better life. The concentration of 25 to 35 year olds has increased far more quickly in the region than it has in the nation as a whole. Indeed since 2007, New Orleans region has experienced the fastest growth in educated population in the nation.7
Many economic trends favor the region’s continued ascendency. These include the still nascent US energy boom, which represents arguably the greatest shift in global economic power since the end of the Cold War and the rise of China; the massive flow of investment, domestic and foreign, into lower-cost locales and most particularly into the Third Coast, the burgeoning region around the Gulf of Mexico; and finally the expansion of US trade with Latin America and the Caribbean basin.
To these powerful forces we can also add demographic and social factors that work to the region’s advantage. One key is a relatively low cost of living, which, in effect, gives area residents and businesses a leg up on their East and West coast rivals. This is critical in attracting net migration from those regions, with their storehouse of educated residents and skilled workers.8 Another force is the breadth of skills that can be easily found in the region, including higher paid skilled professionals experienced in transportation and material moving, installation, maintenance and repair, construction, manufacturing and energy.
A future scenario can be constructed where greater New Orleans emerges as one of the brightest spots in the North American economy. Not only does the region have natural advantages in terms of energy resources and transportation, it can claim primary sources of higher-wage employment. It also possesses a cultural cachet that attracts educated workers, but in a cost and regulatory environment that appeals to business investors.
This is most notable in the growth of the region’s rapidly evolving information industry, including software, videogames and an expanding film/television industry. Over the past five years, New Orleans has come to enjoy a locational concentration equal to that of New York, and has emerged as a major player in this sector.
Challenges Ahead: Economic, Social and Environmental
As the region moves further from the immediate post-Katrina crisis, the great momentum of the last five years is clearly slowing down. Job creation remains positive, but has gradually fallen towards national norms. Indeed, since 2010, after years of running ahead, the region’s job growth rate actually trailed the national average. This could be simply a sign that, after recovering more slowly, the rest of the country is now catching up. But the slowdown relative to other cities should be taken seriously, as it could represent a loss of critical momentum.
“Concert Of Economic Forces” That Can Make Recovery Permanent
To overcome its legacy of poverty and inequality, the New Orleans region needs to focus not on just one sector but on five critical ones. In a highly competitive national and global economy, regions need to work on their unique strengths, establishing advantages that can lead to more, and better, job creation. Most particularly, the region needs to develop a broad, but still highly selective, base of industries that can create the higher-wage jobs necessary for the uplift not of a few New Orleanians, but for the many.
1. The first, and most evident, is the region’s cultural legacy, which serves as a major source of jobs for local people as well as a lure for talented people from elsewhere. This, of course, includes the still very important tourism industry, but also encompasses generally higher-wage professions in film, television, video game software and even medical research.
The growth in information sector employment, something relatively new to the region, represents a clear breakthrough. It allows the region to take advantage of its essential cultural assets, by attracting companies and highly skilled workers. Although it is unlikely that the New Orleans region will ever become as tech-dependent as, say, Silicon Valley — which may prove a good thing, given that industry’s volatility — New Orleans can look forward to a sustained increase in high-paying, and high-visibility, employment. Perhaps most critically, it has an excellent opportunity to make itself the cultural capital of the Third Coast, the burgeoning region around the Gulf, something the region desperately needs and a role that New Orleans is uniquely positioned to fulfill.
Yet although these industries are important, they alone cannot sustain a long-term, broad recovery. Wages in the tourism industry and the arts tend to be low – one reason for the city’s persistently poor income distribution in the past – and higher-wage jobs, except in engineering services and entertainment, remain below national norms in total jobs and will take many years to reach true critical mass. Perhaps most critically, these industries alone cannot produce enough high-wage skilled jobs for the region’s working class population.9
2. The river system. Its location at the shipping terminus of the Mississippi River, across the regions the region’s ports – New Orleans, South Louisiana, St. Bernard, Manchac, Plaquemines and Grand Isle Port – is the historic reason for the region’s existence and one of the key factors in its future success. The region needs to work to compete successfully with its Third Coast rivals, notably Houston, as well as Mobile and Tampa. Growing trade with the Caribbean and the completion of the Panama Canal expansion project increase the opportunities for expanded logistics and cargo handling. In addition, the river provides an ideal spur to new industrial production, such as the Nucor Steel plant in St. James Parish, which some see as the precursor of a new zone, akin to Germany’s Ruhr Valley, that could emerge between New Orleans and Baton Rouge.
Given the devastation of the region’s unique ecological environment, the river presents unique challenges to be addressed. At the same time, the river offers the region new opportunities to develop yet another nascent sector: environmental remediation. The RESTORE Act funds will bring billions to the Gulf help alleviate the region’s own environmental issues, but could also support the unique expertise and skills related to the profound challenges of maintaining coastal regions. This can be seen already in the over $210 million that has flowed to expert Louisiana companies as a result of Hurricane Sandy.10
3. The energy revolution. Perhaps no sector has more potential to generate higher wage jobs across the region, particularly for working class residents, than the current energy revolution. This is rapidly shifting economic power to North America, and it’s a shift for which the region has a front row seat. Louisiana and the greater New Orleans area boast enormous oil and gas reserves, but the region has not kept up with Houston or even smaller cities in terms of energy-related jobs. Yet there has been continued growth in many upstream services, such as petro-industrial development and exploration, even if headquarters employment has dropped. With the resolution of the BP disaster, it is hoped that the region will recover more employment in this high-wage sector.
4. Environmental remediation. This is both a major challenge and an opportunity for economic development. Simply put, there is no long-term future for the region if the environment that supports it collapses. Katrina, after all, was not the first ecological disaster to hit the region, and it won’t be the last. Finding ways to restore coastal wetlands and manage the river and other water resources in a sustainable manner not only preserves the environment that New Orleanians cherish, but could also create significant business opportunities down the road; More than 4% of Dutch GDP is related to water management, and more than 50% of that is related to international projects and the export of water expertise and services.11
The region has already received $1.3 billion from various BP criminal settlements that will be applied to river diversion and barrier island restoration projects. Over $600 million is already budgeted for projects being let in 2014 alone, signifying great potential to expand the region’s expertise and capacity in this sector.12
5. The construction of infrastructure. New industries require new or improved roads, better freight and harbor access, reliable, inexpensive electricity, and improved air service. The region is moving ahead on many of these fronts, from the expansion of the airport to major port improvements and the development of a new biomedical district along the Canal Street corridor. A region that has historically lagged in forward-looking improvements is showing clear signs of determination to catch up with competitors in the country and around the world.13
Yet all these efforts must be done in conjunction with a long-term commitment to preserve the very environment that New Orleanians treasure. This is the ultimate challenge to sustaining and expanding regional prosperity in the era ahead.
This concert of economic forces is critical to driving down poverty rates and raising incomes across class and racial lines. This can only be realized if there is a conscious effort to promote broad-based, sustainable growth in a diversity of industries. This requires placing a greater emphasis, among other things, on higher education, particularly on engineering and the biosciences, and, perhaps even more, on community colleges, technical schools and certificate training. The area may now be attracting more college-educated workers, but it still lags behind the national average, reflecting a legacy of out-migration of skilled workers over the past few decades.14
This is the executive summary from a new report Sustaining Prosperity: A Long Term Vision for the New Orleans Region, authored by Joel Kotkin for Greater New Orleans, Inc. Download the full report from GNO, Inc. here: gnoinc.org/sustainingprosperity
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and Distinguished Presidential Fellow in Urban Futures at Chapman University, and a member of the editorial board of the Orange County Register. He is author of The City: A Global History and The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050. His most recent study, The Rise of Postfamilialism, has been widely discussed and distributed internationally. He lives in Los Angeles, CA.
Endnotes
1 http://www.newgeography.com/content/003897-root-causes-detroit-s-decline-should-not-go-ignored
2 http://www.theatlantic.com/business/archive/2012/01/the-10-fastest-growing-and-fastest-declining-cities-in-the-world/251602/#slide16
3 Lawrence J. Vale and Thomas J. Campanella, “Conclusion: Axioms of Resilience”, in The Resilient City, editors, Lawrence J. Vale and Thomas J. Campanella, Oxford University Press, (New York: 2005), pp.335-353
4 http://chiefexecutive.net/best-worst-states-for-business-2012
5 The New Orleans Index, by Allison Player, 2013
6 Allison Plyer, Elaine Ortiz, Ben Horwitz and George Hobor, The New Orleans Index at Eight: Measuring Greater New Orleans Progress Towards Prosperity, Greater New Orleans Community Data Center August 13, 2013, p.6-7
7 newgeography.com/content/002044-americas-biggest-brain-magnets
8 http://www.newgeography.com/content/002950-the-cities-where-a-paycheck-stretches-the-furthest
9 Author’s analysis of data from EMSI, Inc.
10 http://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/sustainability/environment/managing-our-impact-on-the-environment/complying-with-regulations/clean-water-act-provision.html; http://www.restorethegulf.gov/council/about-gulf-coast-ecosystem-restoration-council
11 Dale Morris, Senior Economist, Royal Netherlands Embassy
12 http://www.nfwf.org/gulf/Pages/home.aspx;
13 http://biodistrictneworleans.org/
14 Plyer, etal, op. cit., p.12