One hundred and fifty years after twin defeats at Gettysburg and Vicksburg destroyed the South’s quest for independence, the region is again on the rise. People and jobs are flowing there, and Northerners are perplexed by the resurgence of America’s home of the ignorant, the obese, the prejudiced and exploited, the religious and the undereducated. Responding to new census data showing the Lone Star State is now home to eight of America’s 15 fastest-growing cities, Gawker asked: “What is it that makes Texas so attractive? Is it the prisons? The racism? The deadly weather? The deadly animals? The deadly crime? The deadly political leadership? The costumed sex fetish conventions? The cannibal necromancers?”
The North and South have come to resemble a couple who, although married, dream very different dreams. The South, along with the Plains, is focused on growing its economy, getting rich, and catching up with the North’s cultural and financial hegemons. The Yankee nation, by contrast, is largely concerned with preserving its privileged economic and cultural position—with its elites pulling up the ladder behind themselves.
This schism between the old Confederacy and the Northeastern elites is far more relevant and historically grounded than the glib idea of “red” and “blue” Americas. The base of today’s Republican Party—once the party of the North—now lies in the former secessionist states, along with adjacent and culturally allied areas, such as Appalachia, the southern Great Plains, and parts of the Southwest, notably Arizona, largely settled by former Southerners.
“In almost every species of conceivable statistics having to do with wealth,” John Gunther wrote in 1946, “the South is at the bottom.” But even as Gunther was writing, the region had begun a gradual ascendancy, now in its seventh decade. That began with a belated post-WWII push to promote industrialization, much of it in relatively low-wage industries such as textiles. “Southerners don’t have any rich relatives. God was a Northerner,” the head of the pro-development Southern Regional Council told author Joel Garreau in 1980. “Without a heritage of anything except denial, Southerners, given a chance to improve their standard of living, are doing so.”
While the Northeast and Midwest have become increasingly expensive places for businesses to locate, and cool to most new businesses outside of high-tech, entertainment, and high-end financial services, the South tends to want it all—and is willing to sacrifice tax revenue and regulations to get it. A review of state business climates by CEO Magazine found that eight of the top 10 most business-friendly states, led by Texas, were from the former Confederacy; Unionist strongholds California, New York, Illinois, and Massachusetts sat at the bottom.
The South’s advantages come in no small part from decisions that many Northern liberals detest—lack of unions, lower wages, and less stringent environment laws. But for many Southerners, particularly in rural areas, a job at the Toyota plant with a $15-an-hour starting salary, and full medical benefits, is a vast improvement over a minimum-wage job at Wal-Mart, much less your father’s fate chopping cotton on a tenant farm.
And the business-friendly policies that keep costs down appeal to investors. Ten of the top 12 states for locating new plants are in the former confederacy, according to a recent study by Site Selection magazine. In 2011 the two largest capital investments in North America (PDF)—both tied to natural-gas production—were in Louisiana.
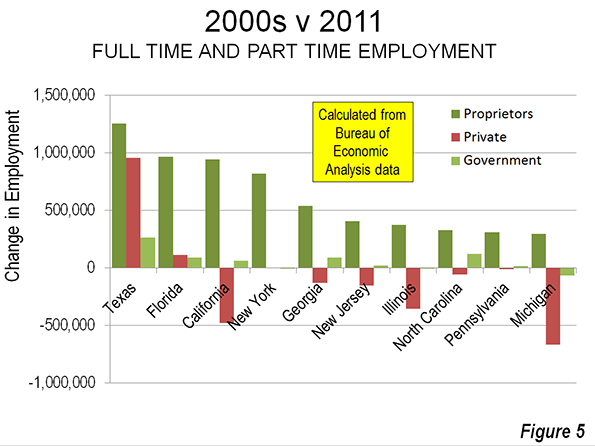
More recently, the region—led by Texas—has moved up the value-added chain, seizing a fast-growing share of the jobs in higher-wage fields such as auto and aircraft manufacturing, aerospace, technology, and energy. Southern economic growth has now outpaced the rest of the country for a generation and it now constitutes by far the largest economic region in the country. A recent analysis by Trulia projects the edge will widen over the rest of this decade, owing to factors including the region’s lower costs and warmer weather.
These developments are slowly reversing the increasingly outdated image of the South as hopelessly backward in high-value-added industries. Alabama and Kentucky are now among the top-five auto-producing states, while the Third Coast corridor between Louisiana and Florida ranks as the world’s fourth-largest aerospace hub, behind Toulouse, France; Seattle; and California.
Southern growth can also be seen in financial and other business services. The new owners of the New York Stock Exchange are based in Atlanta.
While the recession was tough on many Southern states, the area’s recovery generally has been stronger than that of Yankeedom: the unemployment rate in the region is now lower than in the West or the Northeast. The Confederacy no longer dominates the list of states with the highest share of people living in poverty; new census measurements (PDF), adjusted for regional cost of living, place the District of Columbia and California first and second. New York now has a higher real poverty rate than Mississippi.
Over the past five decades, the South has also gained in terms of population as Northern states, and more recently California, have lost momentum. Once a major exporter of people to the Union states, today the migration tide flows the other way. The hegira to the sunbelt continues, as last year the region accounted for six of the top eight states attracting domestic migrants—Texas, Florida, North Carolina, Tennessee, South Carolina, and Georgia. Texas and Florida each gained 250,000 net migrants. The top four losers were New York, Illinois, New Jersey, and California.
These trends suggest that the South will expand its dominance as the nation’s most populous region. In the 1950s, the Confederacy, the Northeast, and the Midwest all had about the same populations. Today the South is nearly as populous as the Northeast and the Midwest combined, and the Census projects the region will grow far more rapidly (PDF) in the years to come than its costlier Northern counterparts.
Yankees tend to shrug off such numbers as largely the chaff drifting down. “The Feet are moving south and west,” The Atlantic’s Derek Thompson wrote in 2010, “while the Brains are moving toward coastal cities.”
To be sure, some Yankee bastions, such as Massachusetts and Connecticut, enjoy much higher percentages of educated people than the South. Every state in the Southeast falls below the national average of percentage of residents 25 and over with at least a bachelor’s degree—but virtually every major Southern metropolitan region has been gaining educated workers faster than their Northeastern counterparts. Over the past decade, greater Atlanta added over 300,000 residents with B.A.s, more than the larger Philadelphia region and almost 70,000 more than Boston.
The region—as recently as the 1970s defined by its often ugly biracial politics—has become increasingly diverse, as newly arrived Hispanics and Asians have shifted the racial dynamics. While the vast majority of 19th-century immigrants to America settled in the Northeast and Midwest, today the fastest-growing immigration destinations—including Nashville, Atlanta, and Charlotte—are in the old Confederacy. Houston ranked second in gaining new foreign-born residents in the past decade, just behind New York City, with nearly three times its size. And Houston and Dallas both now attract a higher rate of immigration than Boston, Chicago, Seattle, or Philadelphia.
These immigrants are drawn to the South for the same reasons as other Americans—more jobs, a more affordable cost of living and better entrepreneurial opportunities. A 2011 Forbes ranking of best cities for immigrant entrepreneurs—measuring rates of migration, business ownership, and income—found several Southeastern cities at the top of the list, with Atlanta in the top slot, and Nashville coming in third.
Then there’s the most critical determinant of future power: family formation. The South easily outstrips the Yankee states in growth in its 10-and-under population. Texas and North Carolina expanded their kiddie population by over 15 percent; and every Southern state gained kids except for Katrina-ravaged Louisiana. In contrast New York, Rhode Island, and Michigan lost children by a double-digit margin while every state in the Northeast as well as California suffered net losses.
The differences are most striking when looking at child-population growth among the nation’s 51 largest metropolitan areas. Eight of the top ten cities for growth in children under 15 were located in the old Confederacy—Raleigh-Cary, Austin, Charlotte, Dallas, Houston, Orlando, Atlanta, and Nashville. New York, Los Angeles, and Boston, along with several predictable rust-belt locals, ranked in the bottom 10.
Historically, regions with demographic and economic momentum tend to overwhelm those who lack it. Numbers mean more congressional seats and more electoral votes, and governors who command a large state budget and the national stage. Unless there is a major political change, the South’s demographic elevation will do little to help Democrats there, who, like Northern Republicans, appear to be an endangered species.
Pundits including the National Journal’s perceptive Ron Brownstein suggest that the GOP’s Southern dominance has “masked” the party’s decline in much of the rest of the country. Other, more partisan voices, like the New Yorker’s George Packer simply dismiss Southern conservatives as overmatched by the Obama coalition of minorities, the young, and the highly educated. The even more partisan Robert Shrum correctly points out that the Southern-dominated GOP is increasingly out of step with the rest of the country on a host of social and economic issues, from income inequality to support for gay marriage.
“A lot of sociologists have projected that the South will cease to exist because of things like the Internet and technology,” Jonathan Wells told Charlotte Magazine. An associate professor of history at UNCC and author of Entering the Fray: Gender, Culture, and Politics in the New South, Wells predicts the region “will lose its distinctive identity that it had in the past.”
It’s unlikely, though, that the South will emulate the North’s social model of an ever-expanding welfare state and ever more stringent “green” restrictions on business—which hardly constitutes a strong recipe for success for a developing economy. It’s difficult to argue, for example, that President Obama’s Chicago, broke and with 10 percent unemployment, represents the beacon of the economic future compared to faster-growing Houston, Dallas, Raleigh, or even Atlanta. People or businesses moving from Los Angeles, New York, or Chicago to these cities will no doubt carry their views on social issues with them, but it’s doubtful they will look north for economic role models.
Instead, you might see some political leaders, even Democrats, in states such as Pennsylvania, Ohio (a Civil War hotspot for pro-Southern Copperheads), and Michigan come to realize that pro-development policies, such as fracking, offer broader benefits than the head-in-the-sand “green” energy policy that slow growth in places like New York and California. The surviving Southern Democrats (by definition, a tough breed) like Houston Mayor Anise Parker have shown that you can blend social liberalism with “good old boy” pro-business policies.
Politicians like Parker, along with Republicans such as former Florida governor Jeb Bush, represent the real future of the states that once made up the Confederacy. As they look to compete with the Northeast and California for the culture, and high-test and financial-service firms that are forced to endure the high cost of the coasts, Southerners are likely to at least begin shrugging off their regressive—and costly—social views on issues like gay marriage.
Bluntly put, if the South can finally shake off the worst parts of its cultural baggage, the region’s eventual ascendancy over the North seems more than likely. High-tech entrepreneurs, movie-makers, and bankers appreciate lower taxes and more sensible regulation, just like manufacturers and energy companies. And people generally prefer affordable homes and family-friendly cities. Throwing in a little Southern hospitality, friendliness, and courtesy can’t hurt either.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University, and a member of the editorial board of the Orange County Register . He is author of The City: A Global History and The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050. His most recent study, The Rise of Postfamilialism, has been widely discussed and distributed internationally. He lives in Los Angeles, CA.
This piece originally appeared at The Daily Beast.
Photo by Belle of Louisville.