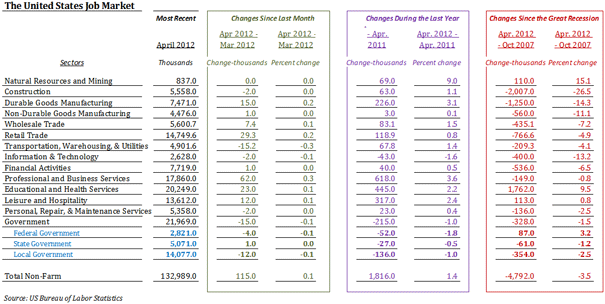
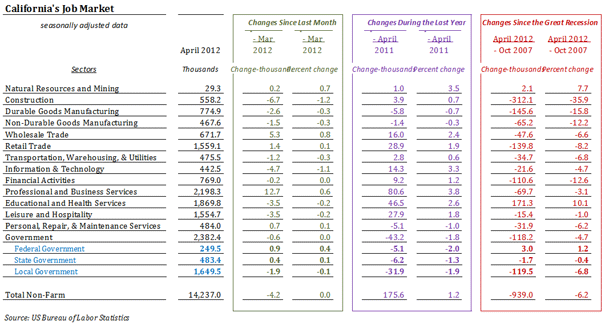
When we think of places with high salaries, big metro areas like New York, Los Angeles or San Francisco are usually the first to spring to mind. Or cities with the biggest concentrations of educated workers, such as Boston.
But wages are just one part of the equation — high prices in those East and West Coast cities mean the fat paychecks aren’t necessarily getting the locals ahead. When cost of living is factored in, most of the places that boast the highest effective pay turn out to be in the less celebrated and less expensive middle part of the country. My colleague Mark Schill of Praxis Strategy Group and I looked at the average annual wages in the nation’s 51 largest metropolitan statistical areas and adjusted incomes by the cost of living. The results were surprising and revealing.
In first place is Houston, where the average annual wage in 2011 was $59,838, eighth highest in the nation. What puts Houston at the top of the list is the region’s relatively low cost of living, which includes such things as consumer prices and services, utilities and transportation costs and, most importantly, housing prices: The ratio of the median home price to median annual household income in Houston is only 2.9, remarkably low for such a dynamic urban region; in San Francisco a house goes for 6.7 times the median local household income. Adjusted for cost of living, the average Houston wage of $59,838 is worth $66,933, tops in the nation.
Most of the rest of the top 10 are relatively buoyant economies with relatively low costs of living. These include Dallas-Fort Worth (fifth), Charlotte, N.C. (sixth), Cincinnati (seventh), Austin, Texas (eighth), and Columbus, Ohio (10th). These areas all also have housing affordability rates below 3.0 except for Austin, which clocks in at 3.5. Similar situations down the list include such mid-sized cities as Nashville, (11th), St.Louis (12th), Pittsburgh, (13th), Denver (15th) and New Orleans (16th).
One major surprise is the metro area in third place: Detroit-Warren-Livonia, Mich. This can be explained by the relatively high wages paid in the resurgent auto industry and, as we have reported earlier, a huge surge in well-paying STEM (science, technology, engineering and math-related) jobs. Combine this with some of the most affordable housing in the nation and sizable reductions in unemployment — down 5% in Michigan over the past two years, the largest such drop in the nation. This longtime sad sack region has reason to feel hopeful.
Only two expensive metro areas made our top 10 list. One is Silicon Valley (San Jose-Sunnyvale-Santa Clara), where the average annual wage last year of $92,556, the highest in the nation, makes up for its high costs, which includes the worst housing affordability among the 51 metro areas we considered: housing prices are nearly 7 times the local median income. Adjusted for cost of living, that $92,556 paycheck is worth $61,581, placing the Valley second on our list.
In ninth place is Seattle, which placed first on our lists of the cities leading the way in manufacturing and STEM employment growth. Housing costs, while high, are far less than in most coastal California or northeast metropolitan areas.
What about the places we usually associate with high wages and success? The high pay is offset by exceedingly high costs. Brain-rich Boston has the fifth-highest income of America’s largest metro areas but its high housing and other costs drive it down to 32nd on our list. San Francisco ranks third in average pay at just under $70,000, some $20,000 below San Jose, but has equally high costs. As a result, the metro area ranks a meager 39th on our list.
Much the same can be said about New York which, like San Francisco, is home to many of the richest Americans and best-paying jobs. The average paycheck clocks in at $69,029, fourth-highest in the country, but high costs, particularly for housing, eat up much of the locals’ pay: adjusted for cost of living, the average salary is worth $44,605. As a result, the Big Apple and its environs rank only 41st on our list.
Long associated with glitz and glitter, Los Angeles does particularly poorly, coming in 46th on our list. The L.A. metro area may include Beverly Hills, Hollywood and Malibu, but it also is home to South-Central Los Angeles, East L.A. and small, struggling industrial cities surrounding downtown. The relatively modest average paycheck of $55,000 annually, 12th on our list, is eaten up by a cost of living that is well above the national average. This creates an unpleasant reality for many non-celebrity Angelenos.
Many of the metro areas that rank highly on our list have enjoyed rapid population growth and strong domestic in-migration. Houston, Dallas-Fort Worth, and Austin all have been among the leaders the nation in both domestic migration and overall growth both in the last decade and so far in this one. In the past year, for example, Dallas led the nation with 40,000 net migrants while Austin’s population growth, 4 percent, was the highest rate among the large metropolitan areas.
In contrast, many of the cities toward the bottom of our list — notably the Los Angeles and New York areas — have led the country in domestic outmigration. Between 2000 and 2009, the nation’s cultural capitals lost a total of over 3 million people to other parts of the country. Although migration has slowed in the recession, the pattern has continued since 2010.
And how about the future? Income and salary growth has been so tepid recently that few large cities can claim to have made big gains over the past five years; there has been continued volatility as some regions that did worst in the past decade — for example San Francisco — pick up steam. Unfortunately any growth in such highly regulated areas also tends to increase costs rapidly, particularly for housing. In California, this is made much worse by both soaring taxes and a regulatory regime that drives up costs faster than income games.
Similarly these high prices seem to have the effect of driving out middle-class workers; places like New York, Los Angeles and San Francisco have extraordinary concentrations of both rich and poor workers but fewer in the middle. As we pointed out in our annual job and STEM rankings, many technology, manufacturing and business service jobs are heading not to the hotspots but more to the central part of the country.
Over time, it seems clear that, for the most part, the best prospects for the future lie in places that both experience income and employment gains but remain relatively affordable. These include some cities that didn’t crack the top 10 of our list but appear to be gaining ground, such as Nashville, Pittsburgh, St. Louis, San Antonio and New Orleans, a once beleaguered city that has experienced the nation’s fastest per capita personal income growth since 2005.
Maintaining affordability and a wide range of high-paying jobs many not be as glamorous a metric for success as the number of hip web startups or the concentration of educated people. But over time it is likely to be about as good a guide to future prospects as we have.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University, and contributing editor to the City Journal in New York. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050, released in February, 2010.
This piece originally appeared in Forbes.
Houston photo by BigStockPhoto.com.
Note: The table below was updated with 2012 data, so it may not match the narrative above discussing 2011 data. Contact Mark Schill at mark@praxissg.com.
| Metropolitan Pay per Job 2012 – Adjusted for Cost of Living | |||||
| MSA Name | 2012 Avg. Annual Wage | Unadj. Rank | 2012 Adj Annual Wage | Adj. Rank | Rank Change |
| Houston-Sugar Land-Baytown, TX | $67,279 | 7 | $75,256 | 1 | 6 |
| San Jose-Sunnyvale-Santa Clara, CA | $107,515 | 1 | $71,534 | 2 | (1) |
| Detroit-Warren-Livonia, MI | $60,503 | 16 | $64,571 | 3 | 13 |
| Dallas-Fort Worth-Arlington, TX | $60,478 | 17 | $62,867 | 4 | 13 |
| Austin-Round Rock-San Marcos, TX | $58,103 | 19 | $62,679 | 5 | 14 |
| Memphis, TN-MS-AR | $53,069 | 36 | $61,780 | 6 | 30 |
| Charlotte-Gastonia-Rock Hill, NC-SC | $57,506 | 20 | $61,636 | 7 | 13 |
| Atlanta-Sandy Springs-Marietta, GA | $58,836 | 18 | $60,844 | 8 | 10 |
| Seattle-Tacoma-Bellevue, WA | $67,225 | 8 | $60,237 | 9 | (1) |
| Cincinnati-Middletown, OH-KY-IN | $54,683 | 26 | $59,828 | 10 | 16 |
| Nashville-Davidson–Murfreesboro–Franklin, TN | $53,928 | 30 | $59,787 | 11 | 19 |
| Birmingham-Hoover, AL | $52,773 | 37 | $59,563 | 12 | 25 |
| St. Louis, MO-IL | $54,112 | 29 | $59,398 | 13 | 16 |
| Columbus, OH | $53,634 | 33 | $59,395 | 14 | 19 |
| Denver-Aurora-Broomfield, CO | $62,021 | 11 | $59,068 | 15 | (4) |
| Washington-Arlington-Alexandria, DC-VA-MD-WV | $79,852 | 2 | $58,672 | 16 | (14) |
| Chicago-Joliet-Naperville, IL-IN-WI | $62,746 | 10 | $58,477 | 17 | (7) |
| Pittsburgh, PA | $55,004 | 24 | $58,021 | 18 | 6 |
| New Orleans-Metairie-Kenner, LA | $54,636 | 27 | $57,151 | 19 | 8 |
| Salt Lake City, UT | $53,901 | 31 | $56,978 | 20 | 11 |
| Raleigh-Cary, NC | $53,243 | 34 | $56,762 | 21 | 13 |
| Milwaukee-Waukesha-West Allis, WI | $55,434 | 22 | $55,825 | 22 | 0 |
| Phoenix-Mesa-Glendale, AZ | $53,835 | 32 | $55,788 | 23 | 9 |
| Minneapolis-St. Paul-Bloomington, MN-WI | $61,515 | 14 | $55,645 | 24 | (10) |
| Oklahoma City, OK | $50,641 | 42 | $55,345 | 25 | 17 |
| Jacksonville, FL | $51,763 | 40 | $55,126 | 26 | 14 |
| Richmond, VA | $55,065 | 23 | $55,010 | 27 | (4) |
| Tampa-St. Petersburg-Clearwater, FL | $50,462 | 43 | $54,969 | 28 | 15 |
| Louisville/Jefferson County, KY-IN | $50,385 | 44 | $54,945 | 29 | 15 |
| Hartford-West Hartford-East Hartford, CT | $67,826 | 6 | $54,787 | 30 | (24) |
| Kansas City, MO-KS | $54,378 | 28 | $54,706 | 31 | (3) |
| Philadelphia-Camden-Wilmington, PA-NJ-DE-MD | $63,615 | 9 | $54,372 | 32 | (23) |
| Cleveland-Elyria-Mentor, OH | $54,701 | 25 | $53,946 | 33 | (8) |
| Boston-Cambridge-Quincy, MA-NH | $73,267 | 5 | $53,363 | 34 | (29) |
| San Francisco-Oakland-Fremont, CA | $79,137 | 3 | $52,988 | 35 | (32) |
| San Antonio-New Braunfels, TX | $49,219 | 47 | $52,867 | 36 | 11 |
| Rochester, NY | $51,798 | 39 | $52,533 | 37 | 2 |
| Baltimore-Towson, MD | $61,542 | 13 | $51,759 | 38 | (25) |
| Buffalo-Niagara Falls, NY | $50,013 | 46 | $50,723 | 39 | 7 |
| Las Vegas-Paradise, NV | $50,378 | 45 | $50,328 | 40 | 5 |
| New York-Northern New Jersey-Long Island, NY-NJ-PA | $77,640 | 4 | $50,169 | 41 | (37) |
| Portland-Vancouver-Hillsboro, OR-WA | $56,134 | 21 | $49,414 | 42 | (21) |
| Virginia Beach-Norfolk-Newport News, VA-NC | $51,693 | 41 | $49,091 | 43 | (2) |
| Miami-Fort Lauderdale-Pompano Beach, FL | $52,357 | 38 | $48,012 | 44 | (6) |
| Orlando-Kissimmee-Sanford, FL | $46,481 | 48 | $47,771 | 45 | 3 |
| San Diego-Carlsbad-San Marcos, CA | $61,149 | 15 | $46,822 | 46 | (31) |
| Los Angeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana, CA | $61,634 | 12 | $46,411 | 47 | (35) |
| Providence-New Bedford-Fall River, RI-MA | $53,071 | 35 | $42,254 | 48 | (13) |
| Riverside-San Bernardino-Ontario, CA | $46,084 | 49 | $41,000 | 49 | 0 |
| Indianapolis-Carmel, IN | $53,839 | No data | |||
| Sacramento–Arden-Arcade–Roseville, CA | $59,200 | No data | |||
| 2012 wage data: EMSI Class of Worker, 2012.3 | |||||
| Cost of living data: C2ER | |||||