Nearly a century and half since the United States last divided, a new “irrepressible conflict” is brewing between the states. It revolves around the expansion of federal power at the expense of state and local prerogatives. It also reflects a growing economic divide, arguably more important than the much discussed ideological one, between very different regional economies.
This conflict could grow in the coming years, particularly as the Obama administration seeks to impose a singular federal will against a generally more conservative set of state governments. The likely election of a more center-right Congress will exacerbate the problem. We may enter a golden age of critical court decisions over the true extent of federal or executive power.
Some states are already challenging the constitutionality of the Obama health care program. Indiana, North Dakota, Mississippi, Nevada and Arizona joined a suit on March 23 by Florida Attorney General Bill McCollum to overturn the law. And Arizona’s right to make its own pre-immigration regulations has gained support from nine other states: Texas, Alabama, Florida, Nebraska, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, South Dakota, Michigan and Virginia.
These may be just the opening salvos. If the Republicans and conservative Democrats gain effective control of Congress, the White House may choose to push its agenda through the ever expanding federal apparat. This would transform a policy dispute into something resembling a constitutional crisis.
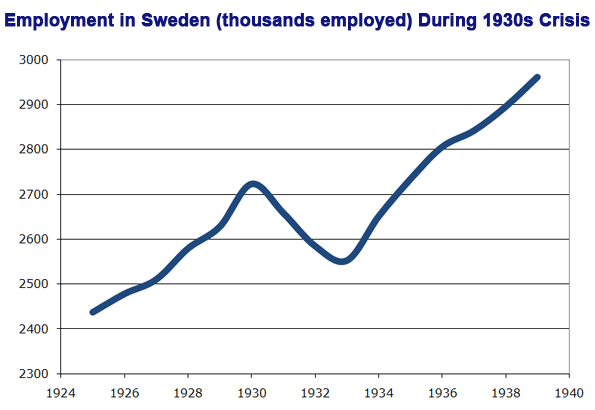
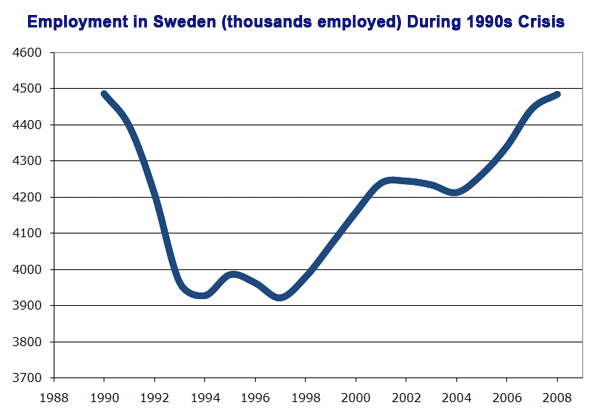
Such legal kerfuffles are unlikely to serve as precursors to armed conflict. But the political and rhetorical battles will certainly be heated. The federalistas can take heart from the the Civil War of a century and a half ago, which was decisively won by the union. They can also gain some encouragement from the ultimate success of the New Deal and of World War II.
The federal government’s greatest bragging right–ending the absolute evil of slavery–was secured during the last war between the states. While most Union soldiers may have gone to war for the Union, the final result was an end to slavery. The consolidation of that gain during the 1960s also rests on expanded federalism.
But the Civil War also was, as Karl Marx observed, a conflict between powerful economic interests. The Southern economy depended heavily on the export of commodities–primarily cotton, but also tobacco and other foodstuffs. It enjoyed profitable trading ties with the capitalistic superpower of the time, Great Britain. The North, in contrast, was an emerging industrial power for whom the British Empire represented the prime competitor.
After the war the industrial capitalists ran the country virtually unchallenged. They overcame the Southern commodity producers politically and burdened them with high tariffs. By the 1890s American manufacturing surpassed Great Britain. The North became relatively rich while the South and much of the West remained backwaters until the 1950s.
The economic map looks very different today. Generally speaking, states in relatively good economic shape are concentrated in an economic “zone of sanity” across the vast Great Plains. They are also in the least “fiscal peril,” according to a recent Pew study. Not surprisingly, these states see little reason to extend federal power and increase taxation in order to bail out their more profligate counterparts.
To a large extent these states, according to Pew, are also the ones willing to reform their pension and other spending to keep down costs. Significantly, strong pension reforms have been enacted in some hard-hit sunbelt states–such as Nevada, Georgia, New Mexico and Arizona–which appear to be following the fiscal model of the zone-of-sanity states.
In contrast those states most favorable to a more powerful Washington are often the ones suffering the worst fiscal situations. They also seem least willing to solve their structural budget issues. Free-spending, poorly managed states like New York, California, Michigan, Oregon and Illinois–all of which are controlled by the president’s political allies, need massive federal largesse to pay their bills without ruinous tax increases or painful cuts. Some localities in these states could become the Greeks of late 2010 as they head inexorably toward defaults.
The differences between the states, however, extend beyond budget items. Many of the worst-managed also benefit from more federal spending on academic and medical research, and from subsidies for their often expensive green energy policies. They can also argue, with some justification, that the zone-of-sanity states have benefited in the past from federal crop supports, military spending and highway funding. Now it’s their turn for disproportionate time at the trough.
Perhaps the most divisive issue will be the Obama administration’s proposed “cap and trade” legislation. For the most part, the strongest opposition comes from coal-dependent, industrial heartland states such as Indiana, whose governor, Mitch Daniels, has denounced the legislation as “imperialism” from Washington. Other keen opposition can be expected among members in both parties from energy-producing states like West Virginia, Texas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, North Dakota, Alaska and Wyoming.
In contrast “cap and trade” seems less of a problem to the rapidly deindustrializing coastal states. Many of these states pride themselves as exemplars of an emerging low-carbon “information economy” and seem determined to limit their gas-spewing sectors like agriculture, manufacturing and transportation. A strong federal mandate on carbon emissions also would diminish the competitive gap between states like California, burdened by draconian local climate change policies, and less restrictive places like Texas.
So who is likely to win the emerging new war between the states? Federal partisans might paint their opponents as the new “Confederates” fighting a protracted rear guard action, this time against science and social enlightenment. Certainly some demographic trends–youth attitudes on environmental issues, growing ethnic diversity and urbanization of “rural” states–favor the unionists.
Yet you can argue that the fiscally strong states will be better positioned for the future. In contrast to the mid-19th-century Confederates, whose population growth paled compared with the Northern states, many of today’s demographic trends favor the anti-federalists.
Over the past decade America’s population and enterprises have been shifting away from the unionist strongholds. Once depopulating states like Kentucky and the Dakotas are enjoying net in-migration from the rest of the country. Texas gradually threatens to supplant California as the leading destination for the young and ambitious.
This suggests that after the 2010 census we could see something of a neo-confederate majority in Congress. Historical patterns may be repeating themselves, but they could produce a very different final result.
This article originally appeared at Forbes.com.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050
, released in February, 2010.
Photo: Marxchivist