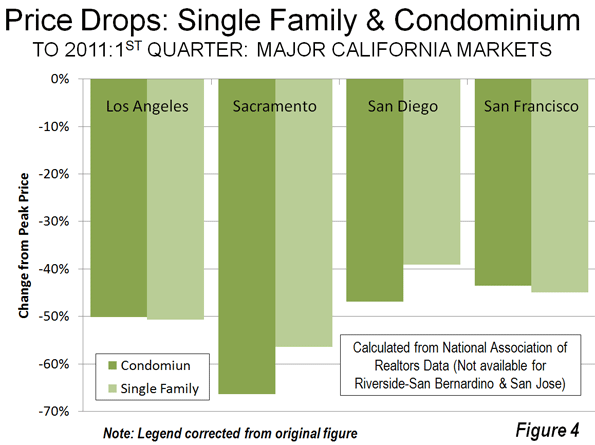
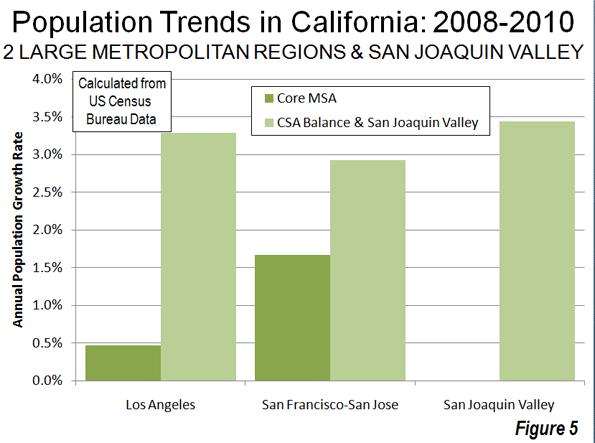
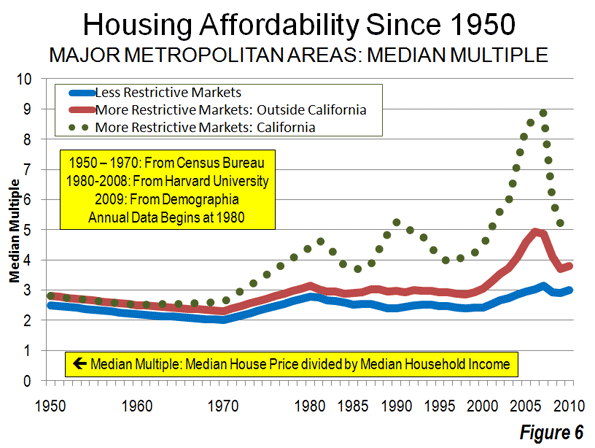
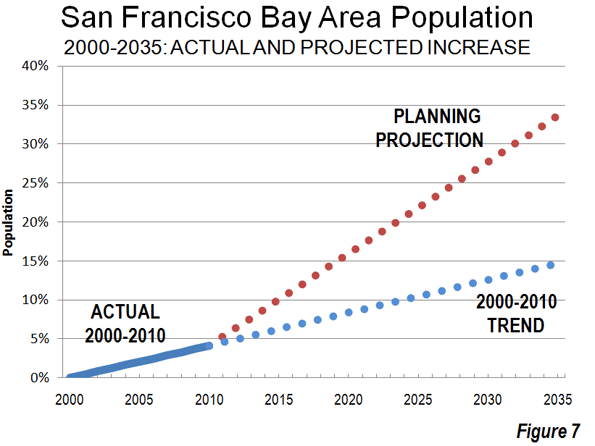
How can we prevent situations where environmental ‘solutions’ end up in failure? The tale of problems encountered with the misuse of pervious pavers (also known as porous or permeable pavers), used as an eco- friendly option, provides some answers.
Low impact sidewalk and street installations can become economic problems. Why? Because failed environmental solutions placed on public property are then replaced with conventional construction, using tax dollars. The EPA Section 438 mandating all owned and leased Federal Facilities be converted into low impact development promotes permeable pavement, that is, paving that allows rainwater to pour through it, instead of running off at high speed to an inlet and overloading the storm sewer system, taking pollutants downstream with the water, and eventually infecting our streams and oceans. To understand more about it, read reporter Dave Peterson’s exposés in the Minneapolis Star Tribune.
On the surface, permeable pavers seems logical: pavement that allows rain to fall through. But what happens after the rain falls through the pavement – where does the floodwater go? A sub-base is needed to support the pavement. The rainfall must fall not only through the pavers, but also through the ground below. If you were to place permeable pavers on your back yard patio, supporting the weight of people and furniture would require very little sub-structure. If your lot was made of sandy soil that allows rain to quickly filter through, better yet. But if the ground underneath is clay or rock, the water must be retained or piped off with a sub-drainage system. If this is starting to sound expensive, as we say in Minnesota, you betcha!
This sub-surface material must be sponge-like, and allow a conduit for water to either pass through to a piped system to be transported elsewhere, or have enough small void areas to retain the water until it can slowly be filtered through its lowest layer seeping back to the earth. To create a ‘base’ with properties that has ‘void spaces’, plenty of rock and large stone is used.
Of course this means digging a very deep channel under the proposed pavement, moving (removing) the old soil and hauling in this sub-base material. A 100 foot long 30 foot wide road would require a five foot deep excavation with 555 cubic yards of soil to be removed, and almost the same in sub-base to be hauled in. Since a large dump truck holds up to 20 cubic yards (typically less), that small section of street would require at least 27 trips to and from the destination with 27 truckloads of rock, no doubt consuming massive amounts of petroleum.
Anybody who has been in Minnesota in the winter knows that during, those seven months of freezing weather, cold is redefined. Water expands about nine percent as it freezes, so 555 cubic yards of water would increase about 50 cubic yards. Where does the water go? Up! Water pressure can lift pavers and cause havoc in the winter, so before cold weather sets in it is recommended that the liquid be vacuumed out of the sub-surface and hauled away. Now how much energy does that take?
People and patio furniture are not that heavy, certainly not as heavy as a bus, which weighs somewhere between 26 and 40 thousand pounds transferred to the tires, depending upon the size and how many it is carrying. This weight is then transferred to the pavement, which is on top of rocks and stone that are intentionally ‘loose,’ to hold water.
There is another problem with permeable pavement in some applications: water settles to a level surface. A few years ago we designed a low-impact, clustered neighborhood in Minnesota. At the ‘consultants’ meeting with the developer, the young engineer pushed the permeable paver idea. We had designed the neighborhood by harnessing the natural grade, embracing the heavily wooded site’s natural drainage to save most of the existing trees on the steep slopes. In other words, we planned to use what nature provided, eliminating much of the grading, costs and environmental impacts. On this site there were some fairly steep grades, in many cases exceeding a five foot drop in its length along private drives.
The engineer aggressively insisted on permeable pavers. His idea was to create a five foot deep sub-base under the private drives (26’ wide) and run the gutters of the roofs underground to the sub-surface drainage system. In such meetings it is not polite to scream, “Are you out of your mind?” Instead, after the meeting I told the developer to kill the idea for being far too expensive. The developer did not heed my advice, and when the economics of the engineering was done, the cost escalated out of control. Several months of the engineer trying to (unsuccessfully) convince the city that the permeable pavers was a great solution caused the project to be delayed. By the time it was approved (with the natural drainage solution), the recession was in full swing and the development went dormant.
From a personal experience, when I built my Green Certified home in 2008, MNGreenstar provided points for permeable pavement but only if the underlying base held the storm water underneath. The soil of my lot is sandy, and could have quickly absorbed the rainwater, allowing a fairly cheap sub-base, but the ‘green’ certification did not allow for compromise. The green certification ‘all or nothing’ approach meant that my sub-surface would have added $5,000 to the construction to get a few green ‘points’ encouraging the ‘nothing’ side of the equation. So, instead of designing the driveway with permeable pavement, we used sculpted landscaped strips (like the driveways of yesterday) to reduce the paved surface area and the overall costs. It is not unusual to see people taking pictures of my ‘low impact’ driveway, which adds curb appeal and value, however, we gained no green points for this logical solution.
Why the motivation to push permeable pavement? In many cases it might indeed make sense. One reason is profitability, not by those selling the pavement alternatives, but by the consulting industry that specifies materials charging fees based upon a percentage of the construction cost. Permeable pavers and other ‘green’ alternatives can add a considerable amount to costs, and to the profitability of a consulting firm. If all bids were based upon rewarding solutions that cost less, with a penalty for solutions that cost more, consultants would truly deliver on the promise of sustainability; development costs and future maintenance burdens would plummet, while the environment would benefit. If we rewarded engineers employed by government agencies by allowing them to share a percentage of the money they saved by introducing green solutions that are cost effective, it would bring about change overnight.
Can this be done? Absolutely. The technology and educational materials have been developed for this overhaul, but it would take effort and investment, since we’re currently in an economy where up to 65% of the architectural and land consultants are unemployed, and those remaining are not exactly overloaded with work.
The EPA Section 438 is the Federal agenda to rebuild existing facilities and have all new construction (including all military bases) comply with low impact standards. On some new construction and redevelopment, permeable pavement could be effective, but it is unlikely to be cost effective where heavy loads, bad soils, and/or frigid weather occur.
The decreased pavement width of New Urbanism is a start in the right direction, as long as safety and functionality are maintained. Combined with the reduced ‘length’ of infrastructure in plans like Prefurbia, it is entirely possible to reduce the environmental impact of newly paved development by about 30%, and of re-developed areas (i.e. EPA Section 438) by more than 50%, while increasing function and value. Now that we have the knowledge to do so, isn’t it time to start reaping the benefits of design techniques that reduce pavement without harming function?
Photo by Mockney Rebel; “Pavement Archeology”
Rick Harrison is President of Rick Harrison Site Design Studio and Neighborhood Innovations, LLC. He is author of Prefurbia: Reinventing The Suburbs From Disdainable To Sustainable and creator of Performance Planning System. His websites are rhsdplanning.com and performanceplanningsystem.com.