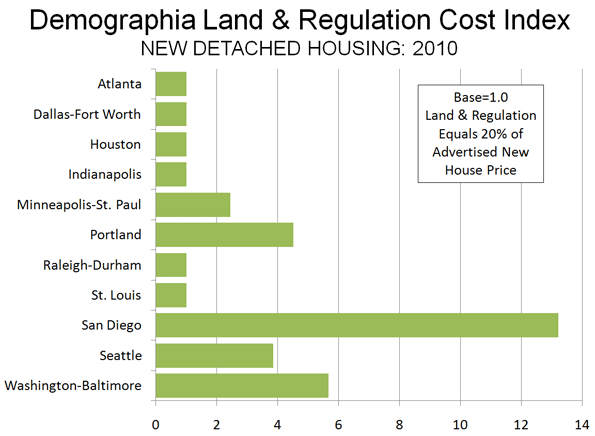
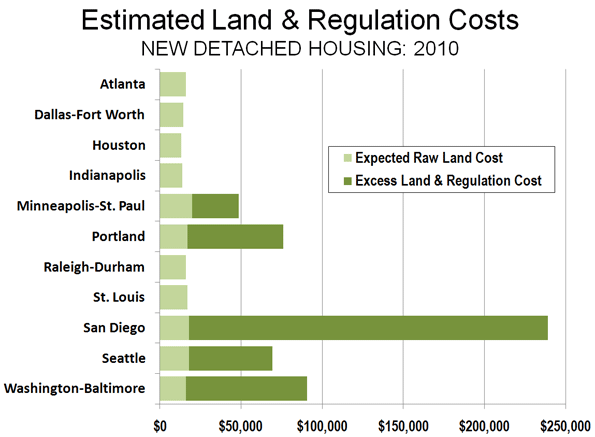
You know that something is up when a Washington Post editorial advises that the Obama Administration do a “reality check” on its plans for high speed rail. From the beginning, there was more slow-speed than high speed rail, however both components of the plan could be in trouble. The Onion joined the issue with a satirical video announcing a federal “high-speed bus” program that would replace the high-speed rail plans.
The Post criticized Secretary of Transportation Ray LaHood for not allowing Wisconsin and Ohio to use the federal money to make needed highway improvements instead:
“This blunt refusal to heed the fresh mandate of Ohio and Wisconsin’s voters seems hard to justify – especially since using the money for other infrastructure would have created jobs, just as building trains would have.”
Wisconsin and Ohio: This is vividly illustrated by recent election results, when successful gubernatorial candidates in two states vowed to kill two of the slower lines that had already received substantial federal funding. Wisconsin’s Scott Walker took aim at the Milwaukee to Madison line, which would average less than 60 miles per hour, despite reaching speeds of 110. Ohio’s John Kasich says that Ohio’s Cincinnati to Cleveland train is “dead” It could have been named the “Ohio Fast Mail,” because it would have averaged 50 miles per hour, about the same as the Fast Mail over the longer New York and Niagara Falls route — in 1877! These trains would have operated at average speeds from one-third to one-fourth those achieved by the Wuhan to Guangzhou trains in China.
Illinois: There are also problems in Illinois. That state received $1.1 billion from the federal government to ramp up Chicago to St. Louis speeds to 110 miles per hour and to make the trip in four hours. Yet, the state received only about one-third of the requested $3 billion from the federal government for this project. It is a fair question where the rest of the money is coming from. Illinois had proposed to contribute only one percent of the cost ($4 million), leaving the project still nearly $2 billion short, before the seemingly inevitable cost overruns (which are already an inflation adjusted 8 times earlier projections). Illinois, which by some accounts is in as bad shape fiscally as California, simply does not have the money to complete the job.
Incremental High Speed Rail? One of the most cynical myths about slower speed rail is that it is a “stepping stone” to genuine high speed rail, which is now being built in some countries to operate from 200 to 220 miles per hour. Such claims are patently misleading. The slower speed 110 mile per hour trains will run on tracks shared with freight trains and there will be some grade crossings (intersections with roads where trains, trucks and cars could conceivably collide). Genuine high speed rail requires starting all over.
Illinois provides an example. The unfunded $3 billion slower speed line is not enough. The state has also sought federal funding to plan a genuine high speed rail line that would cost an additional $12 billion, according to a Midwest High Speed Association report. However, this amount would rise substantially, since it does not include rail-cars, maintenance facilities, stations and, of course, cost overruns. There is nothing incremental about building one line and then abandoning it to build another.
California and Genuine High Speed Rail? Maybe Not: Meanwhile, the news is not encouraging to proponents of the nation’s two genuine high speed rail lines, in California and Florida.
For two years, the California High Speed Rail Authority has been concentrating its attention on planning for the two most expensive sections of its proposed $43 billion (before cost-overruns) line from Los Angeles (Anaheim) to San Francisco. Plans that some claim would create a Berlin Wall across the largely affluent cites of the Peninsula led to a “boondoggle rally” attended by 500 people in Palo Alto. Community concerns have also been raised about the line through Orange County and southeastern Los Angeles County.
Now, however, the federal government has virtually steered all of promised money to the San Joaquin Valley, requiring that it be spent between Merced and Bakersfield. The provisions of the high speed bond issue will require that state funding to be spent where the federal money is spent.
The federal department of transportation has not indicated its rationale for this decision, but the new strategy could indicate that a modicum of sanity may be at work. Clearly the state of California does not have the money to build the system. Joe Vranich and I raised this issue in our Due Diligence report on the system, published by the Reason Foundation. We noted that the proposed 2:40 travel time from San Francisco to Los Angeles Union Station would more likely erode to 3:40, because the trains will not be able to travel as fast as planned in the urban areas, and they are not likely to attain their aggressive planned speeds on other portions of the route. We also suggested the likelihood that only part of the system would be built, with trains operating at conventional speeds over conventional tracks for the final 60 or more miles into San Francisco and Los Angeles. With insufficient money, there could be pressure to cut the genuine high speed rail portion of the system back even more than that, given the federal requirement for confining construction to the San Joaquin Valley, which now barely supports minimal air service and has largely traffic-free freeways.
Proponents have been mouthing fairy tales about French, Chinese or Japanese investment in the system. Can they be so naive to believe that French or Japanese taxpayers will pay for high speed rail system in California? In fact, any such “investment” would be loans and would have to be paid back. Around the world, virtually all private investment for high speed rail has been either lost or bailed out by taxpayers.
Perhaps the best that proponents can hope for is that some 220 mile per hour track will be built on the flat-as-Kansas agricultural land in the San Joaquin Valley. Trains could continue from the northern terminus (Merced) to San Francisco and from the southern terminus (Bakersfield) to Los Angeles and Anaheim on upgraded conventional rail tracks. This would bring the now discarded slower speed rail vision of Ohio and Wisconsin to California. Trains might well average 70 miles per hour or somewhat more.
It could be even worse. Californians Advocating Responsible Rail Design (CARRD) reveals that the California High Speed Rail Authority has revealed “Plan B.” Its October 2009 application to the US Department of Transportation indicated that “In the event of significant delays or abandonment of the HST program, the Merced/Fresno Program would have created rail crossing benefits, as well as provided the potential for significant improvement to the existing San Joaquin intercity passenger service operated by Amtrak and underwritten in part by the state.”
Florida: People were also having second thoughts about the genuine high-speed line between Orlando and Tampa. The two cities are so close together than even if the train reached the speed of light, given waiting in a rental car line and driving to and from the stations, car travel could be faster.
Congressman John Mica, who seems likely to be Chair of the House Infrastructure and Public Works Committee in the next congress, has suggested that the line be truncated to a local operation between Orlando International Airport and Disneyworld. Governor Elect Rick Scott is now reviewing the project.
International: The international news is barely any better. The Chinese government is now reviewing the wisdom of its huge expenditures on high speed rail, as a result of a critical report from the Chinese Academy of Sciences. And, as in California, communities are resisting along a proposed high speed rail line in England. Moreover, cost overruns have been routine, as have been revenue and ridership shortfalls relative to the always rosy projections.
At least in the United States, the high-speed rail “low-ball express” remains stuck in the station. The actual costs, however, will certainly rise well above the low-ball estimates.
Photo: The Fast Mail (1877 Average Speed Equal to Cancelled Ohio High Speed Rail Train): Harper’s Weekly, 1877.
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris and the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life”