Urban planning in Australia is lost in a dense fog of presumption and theory. What’s needed is to toss out the hype and to illuminate some of the common planning myths for what they really are: impediments to progress.
An example of planning hype occurred not long ago when ten urban academics loudly criticised the Victorian government’s decision to develop about 40,000 hectares of new land on Melbourne’s fringe, calling the decision short-sighted and unsustainable.
The best way to development Melbourne, they said, is to intensify redevelopment along tram and train lines and around existing activity centres, with such developments being more dense than the surrounding suburbs, but not necessarily high-rise. Their modelling suggests that the 600,000 new dwellings required by 2030 could be accommodated under four stories within the existing built-up area.
They did confess that not everyone wants or needs to live in an activity centre or on a rail/tramline, but were adamant that a sustainable city is “one where you can get there without a car”. The future, according to them, will be “fitter rather than fatter”; where we will “live with more amenity” and have more “choice of housing type”.
They concluded that this is a national issue because when we finally commit to a low-carbon economy, we will have these extra 40,000 undeveloped hectares which, one assumes, will act as some form of carbon sink.
Under normal circumstances, one might be tempted to dismiss the more extreme machinations of latte-left academia, but unfortunately, some serious decision makers are starting to listen to this type of questionable commentary.
Without doubt, a key challenge facing Australia’s major capitals is how to redevelop the middle-ring suburbs, but placing all of one’s development eggs in this basket is lunacy and is based on misguided presumptions and poor theory. In this light, it is pertinent to consider several urban myths.
But before our myth busting, it is worth stating that infill development is more expensive than many realise, in terms of site acquisition, approval processes, infrastructure provision, and combating NIMBYism. This is reflected in the high end prices of infill stock which, in short, costs more than twice as much as broadhectare product.
For example, the cost of a new infill dwelling (which is two bedroom/two bathroom and one car space) within five kilometres of the Brisbane CBD is $650,000. But a new detached house (around 20 kilometres from the GPO, comprises three bedrooms, study, two bathrooms, double garage and on a 500 sqm allotment) can cost $325,000. On a rate per square metre basis the infill product (including any land) is $8,000, the detached house (again including land) is around $2,000, sometimes less depending on who the builder is.
Low affordability makes the sale of infill product often slow, even in stronger economic times. In addition, there is often a large mismatch between the product type (and size) offered in infill locations and household demographics and, importantly, the market’s aspirations.
Our urban academics were somewhat correct on one point – not everyone wants to live in an infill development. Our experience is that demand for such product – and assuming the dwellings can be delivered at an economic price point – varies between 25% and 40% of overall demand, depending on the urban location in question. Under current conditions, the real demand, however, is around 15% at best. So from the get-go, delivering such an ambitious infill development target is extremely unlikely. In fact, it is impossible.
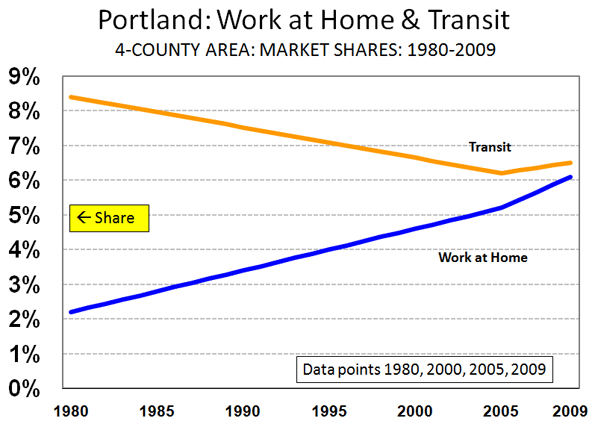
Myth – higher densities will mean less traffic
The theory is that higher densities around existing public transport networks will see a lift in public transport use and fewer cars on the road. Public transport accounts for about 10% of total trips in our major cities. Most urban metropolitan strategies aim to increase this to 20%. So, four-fifths of the trips will, at best, still be via private vehicle. Why? Because the car is much more convenient.
Without serious infrastructure commitments to repair and upgrade the public transport networks in our cities, cars will continue to dominate. In fact, under current conditions, and somewhat ironically, infill development would lead to more traffic congestion.
Most infill product built within Australian cities will not sell without a car space. The quality of our public infrastructure, especially outside of Melbourne, is not good enough for infill owners (or their tenants) to forgo the security of their cars. So, new infill development is increasing the number of cars on the road and often in areas which are already congested and are hard to improve from a traffic management perspective.
One could argue that it would be better to further decentralise employment and settlement around the edges of the metropolitan area, and most obviously upgrade the existing road network.
Academia, obviously, have never tried to sell a dwelling without a dedicated car parking space.
Myth – urban consolidation is better for the environment
This implicit assumption is now widespread among the media, the planning community, government agencies and in political circles. Yet the available evidence suggests the opposite.
- Comparison between suburban houses and infill product often overlooks the number of persons per household, which is much higher in the traditional suburban detached house.
- In traditional suburban detached homes, larger household numbers share various facilities – the refrigerator; television; washing machine; dishwasher etc., and even the lighting needed to light a room. The per capita energy, and even water consumption, is more efficient in suburbia than in more central urban locations. The “average” household size within an infill development across Australia is around 1.6 people, in detached housing it is 3.2. In most cases infill product have as many appliances as are in a detached house, yet the number of occupants living in infill product is about half that living in detached suburban homes.
- The nature of infill housing is, in itself, prejudicial to positive environmental outcomes due to things like clothes driers (lack of outdoor drying areas), air conditioners, lifts and the need to service (lights and air-conditioning) common areas. Also, suburban development allows for wider footpaths and private yards, which in turn provide space for trees to grow. There is less opportunity for greenery – a key producer of carbon offsets – in higher density urban development.
Not withstanding anything about the actual built form, the greatest correlation between energy and water use (and hence, environmental impact) is based on per capita income. Wealthy people consume more energy/water and thus have a bigger environmental impact. The better off are the only ones who can afford to live in infill housing.
Research in 2007 by the Australian Conservation Foundation found that in almost all Australian cities, higher-density, infill housing produced higher per capita greenhouse emissions and had larger eco footprints than outer suburbs, notwithstanding the greater access to public transport.
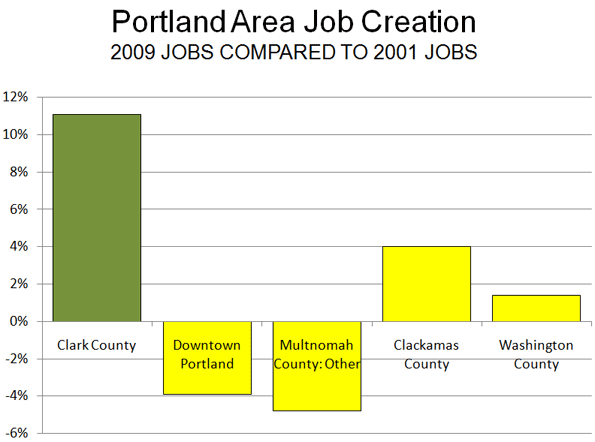
Myth – most jobs are downtown
There is also a widespread presumption that central business districts and their immediate fringes contain the majority of jobs in a city’s economy, and are therefore the major generators of traffic. Developing housing further from the downtown area, the argument goes will only mean more congestion as commuters try to get into and out off the downtown area.
It is easy to understand how this myth developed: the CBD/fringe holds the tallest buildings; the seat of government is often located there; so, too, are many cultural facilities; they are the hub of train/tram networks and the focus of much of our angst about traffic congestion.
But downtown is home to around 20% of all jobs in a city’s metropolitan area (just 10%, when looking at the CBD alone. According to the latest Australian census (2006) the proportion of employment in our major CBDs (Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide) ranges from 9% to 11% – thus 10% is pretty consistent). So 80% of our jobs are actually outside of the downtown area. The implications of this are profound. Our ten friends from academia are proposing a policy based on a myth: that urban dispersal of housing will mean longer commutes to work.
The facts are that most commutes (over 90%) within a city are across suburbs and not downtown. Unfortunately, this type of travel (and the nature of the work involved) makes it impossible to service efficiently via public transport.
So in truth, more housing on the urban fringe will not in itself lead to more inner-city congestion, but will produce more suburb-to-suburb work trips. Perhaps as a priority (and in concert with more decentralisation and suburban development), we should build better ring-road systems (and more river crossings in a city like Brisbane, for example), rather than advocating mostly infill redevelopment and heavy urban infrastructure spending.
Michael Matusik is a qualified town planner and director of independent residential development advisory firm, Matusik Property Insights, based in the Brisbane region in Australia.
Photo by Onlygoneanddoneit – Suziflooze & Stuart
 Locating new satellite towns far enough to make commuting infeasible will be a real problem for Beijing. There just is not enough territory in the provincial level municipality. That means the new towns would have to be in the province Hebei, which along with the province level municipality of Tianjin surrounds Beijing.
Locating new satellite towns far enough to make commuting infeasible will be a real problem for Beijing. There just is not enough territory in the provincial level municipality. That means the new towns would have to be in the province Hebei, which along with the province level municipality of Tianjin surrounds Beijing. Recently (February), I examined tax assessment records for all parcels in Portland’s Washington County that abut the urban growth boundary to see if value differences exist. The properties had to be 5 or more acres and be undeveloped. Research was conducted based upon Internet information in February 2010. Property along 25 miles of the urban growth boundary from Cedar Hills to Hillsboro to southwest Beaverton was included in the analysis.
Recently (February), I examined tax assessment records for all parcels in Portland’s Washington County that abut the urban growth boundary to see if value differences exist. The properties had to be 5 or more acres and be undeveloped. Research was conducted based upon Internet information in February 2010. Property along 25 miles of the urban growth boundary from Cedar Hills to Hillsboro to southwest Beaverton was included in the analysis.