The political execution of Prime Minister Kevin Rudd by his own Australian Labor Party colleagues was extraordinary, the first time a prime minister has been denied a second chance to face the voters.
According to the consensus in Australia’s mostly progressive media establishment, Rudd fell victim to his “poor communication skills”, a somewhat Orwellian take since until recently he was hailed as a brilliant communicator. What went wrong?
Certainly, Rudd’s style of communication was a factor. Yet the media’s disjointed interpretations avoid what, for them, is an inconvenient truth. As much as any defects in the man himself, Rudd’s linguistic meltdown can be traced to deep socio-economic divisions wracking today’s Australian Labor Party.
Australia has its own version of the American red and blue state dichotomy. But with a much smaller, highly urbanised population, and only six states, the social fault line runs through major metropolitan regions rather than state boundaries. Left with a fractured support base, federal Labor often struggles to hold onto majority support. Rudd clearly underestimated the persisting social divide, and his obsession with a media driven solution was disastrous.
In Australia, post-war suburbanisation and gentrification played out differently than in the US. Since in the 1970s, Australian cities have experienced a broad geographic sorting along class lines. On the one hand, rising land values and car ownership dispersed the old industrial core, and its working class population, to the middle and outer suburbs. On the other, a booming generation of university graduates, many immersed in the counter-culture, and employed in expanding government agencies, flooded into inner-city tenements.
Lacking the racial frictions of some American cities, and typically adjacent to attractive harbour foreshores (Australia’s major cities are all coastal), these nineteenth century streetscapes were ripe for gentrification. Before long, all remnants of the old working class gave way to restaurants, upscale bars, coffee shops, cinemas, bookshops, art galleries and other favourite amenities of a new upper middle class.
Over time, urban polarisation has far-reaching political consequences. While the new professional class voted Labor, and transformed the Labor Party in their own image, they dominated only a handful of electorates (electoral districts). Most of these are in the inner precincts of Sydney and Melbourne. The overwhelming majority of electorates are suburban or regional, populated by blue-collar, routine white-collar and self-employed private sector workers. Whether former inner-city residents, or newly arrived migrants, they embraced the suburban ideal of reward for work, free-standing homes on a quarter acre block and the prospect of upward mobility, particularly for their children. Later, social commentators labelled them “aspirationals”.
Increasingly, inner-city elites and suburban aspirationals inhabited different worlds. By 1996, many aspirationals felt Labor had lost touch with their priorities. Apart from his poor record on inflation and interest rates, sensitive issues in the mortgage-belt, then Prime Minister Paul Keating became a champion of the elite’s obsession with race and gender. Having infiltrated Labor’s apparatus, progressives now seized control of the party’s policy agenda.
Ultimately, Labor’s historic bond with working people was severed at the 1996 election, when masses of aspirational voters defected to the conservative John Howard. Howard retained their support over four terms in office. During this time they acquired another label – “Howard Battlers” (an antipodean variant of Reagan Democrats).
Labor spent these years wavering between elite and aspirational programs, failing to reconcile their deep-seated differences. Successive leadership changes were a flop. Not until 2006, when Howard showed signs of running out of steam, was victory finally in sight. Leaving nothing to chance, the popular Rudd was installed as leader, and handed the task of herding both progressive and aspirational voters into Labor’s camp. Rudd’s strategy may have won him the election, but it bore the seeds of his destruction.
On sensitive issues, Rudd resorted to an elaborate form of doublespeak: headline rhetoric crafted for aspirationals with policy small print pitched at progressives. He was confident enough in his mastery over the media cycle to pull this off. And he assumed aspirationals were too unsophisticated to catch on. He was proved wrong on both counts, but only after winning office.
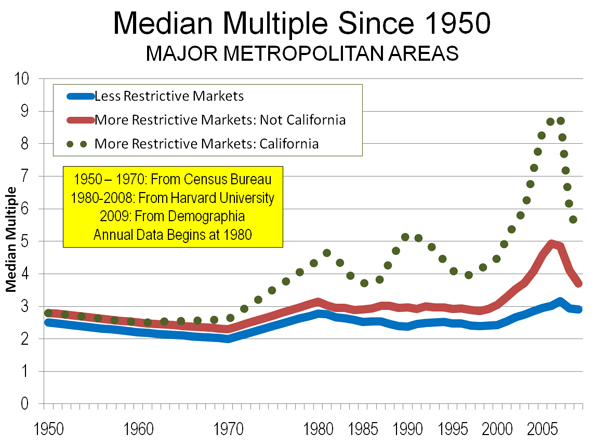
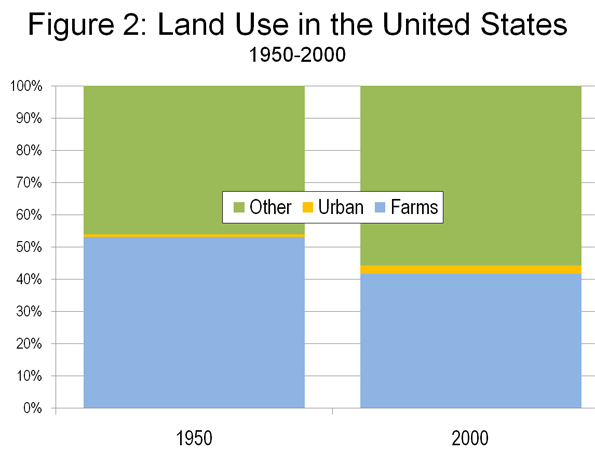
Take his handling of housing, transport and urban development. Housing affordability and traffic congestion loomed as hot topics in the 2007 election. Before the late 1990s, Australian cities had generally liberal approaches to land release and suburbanisation, and the motor vehicle was supreme. Urban planning was the province of state governments, which had long considered motorways the wave of the future, given the country’s increasingly dispersed patterns of residential, commercial and industrial development.
As the century drew to a close, however, sentiment in the planning profession, including state officials, many now religiously green, shifted from growth to consolidation (“smart growth“) and the revival of rail transport. More recently, the climate panic accelerated this trend. On the whole, state governments, mostly Labor in the decade to 2007, proved compliant. Considering that Australian cities were experiencing high rates of population growth, in part due to very high levels of immigration, land values and house prices soared and roads, particularly in the middle to outer suburbs, couldn’t cope with traffic volumes. These problems were especially bad in Sydney. For the first time, many Australians feared that their children would never achieve the dream of home ownership.
Leading up to the election, Rudd took to calling housing affordability “the ultimate barbeque stopper”, a subject on everyone’s lips. He convened a Housing Affordability Summit, and released a strategy paper. His campaign launch speech, weeks out from polling day, reminded voters that Labor had “put forward a national housing affordability strategy – so that we can keep alive the great Australian dream of one day owning your own home”. Rudd’s rhetoric on “infrastructure bottlenecks” was just as high-blown. “For 11 years”, he said repeatedly, “Mr Howard’s government has failed to provide leadership in developing our nation’s infrastructure”. References to traffic congestion were made in this context.
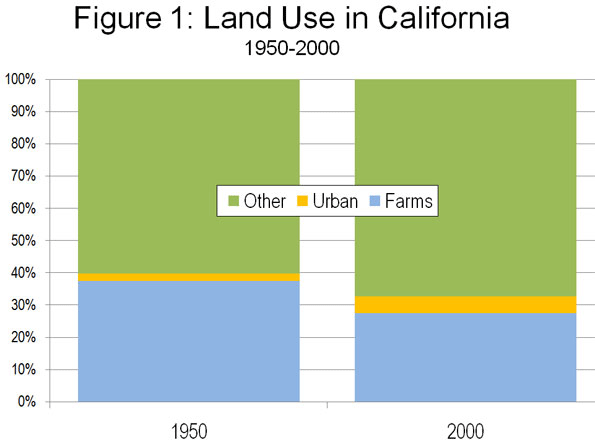
But the policies didn’t match the rhetoric. Since elite sentiment was, by this stage, in the grip of climate alarmism, there was little way Rudd would address the root causes of these problems. Restricted land supply and urban growth boundaries, to contain Australia’s “ecological footprint”, combined with population growth, were driving up land values and inducing developers to bank their land holdings rather than release them. Rudd’s plan just tinkered around the edges. There were to be tax breaks on capped home saver bank accounts, subsidised rental accommodation for low income earners, and a massive boost in social housing stock. Conceived by activists who saw housing as a welfare issue, these measures did little for the mass of aspirationals or their children. A later boost to the existing “first home buyer grant” probably inflated prices further. Far from saving the great Australian dream, Rudd cast it into the dustbin.
After the election, the small number of infrastructure projects selected for funding had limited potential to ease traffic congestion. In his landmark October 2009 speech on urban policy, Rudd had more to say on shifting motorists out of cars and onto trains than upgrading roads to improve traffic flows. For Sydney’s long-suffering commuters, there was no sign that “missing links” in the Orbital Motorway Network ring road would be completed.
Well into 2010, house prices had been escalating for over a year, and mortgage interest rates began to creep up again, having been slashed during the financial crisis. More and more Australians thought Rudd’s performance, on a broad range of policy fronts, was falling short of his elevated rhetoric. He was “all talk and no action”. When his opinion poll ratings plummeted, with no revival in sight, Labor Party power-brokers feared their government would be thrown out after just one term, a first since 1932. Either Rudd or the Labor government had to go. They chose Rudd.
John Muscat is a Sydney lawyer and co-editor of The New City (www.thenewcityjournal.net), a web journal of urban and political affairs.
 In 2006, the owner had refinanced the house with a $308,750 loan, indicating a value more than triple that of comparable housing in much of metropolitan America.
In 2006, the owner had refinanced the house with a $308,750 loan, indicating a value more than triple that of comparable housing in much of metropolitan America.