Urban risk may be understood as a function of hazard, exposure, and vulnerability.1 In metro New Orleans, Katrina-like storm surges constitute the premier hazard (threat); the exposure variable entails human occupancy of hazard-prone spaces; and vulnerability implies the ability to respond resiliently and adaptively—which itself is a function of education, income, age, social capital, and other factors—after having been exposed to the hazard.
This essay measures the extent to which, after the catastrophic deluge triggered by Hurricane Katrina in 2005, residents of metro New Orleans have shifted their settlement patterns and how these movements may affect future urban risk.2 What comes to light is that, at least in terms of residential settlement geographies, the laissez faire rebuilding strategy for flooded neighborhoods proved to be exactly that.
“The Great Footprint Debate” of 2005-2006
An intense debate arose in late 2005 over whether low-lying subdivisions heavily damaged by Katrina’s floodwaters should be expropriated and converted to greenspace. Most citizens and nearly all elected officials decried that residents had a right to return to all neighborhoods. Planners and experts countered by explaining that a population living in higher density on higher ground and surrounded by a buffer of surge-absorbing wetlands would be less exposed to future storms, and would achieve a new level of long-term sustainability.
Despite its geophysical rationality, “shrinking the urban footprint” proved to be socially divisive, politically volatile, and ultimately unfunded. Officials thus had little choice but to abrogate the spatial oversight of the rebuilding effort to individual homeowners, who would return and rebuild where they wished based on their judgment of a neighborhood’s viability.
Federal programs nudged homeowners to return to status quo settlement patterns. Updated flood-zone maps from FEMA’s National Flood Insurance Program, for example, would provide actuarial encouragement to resettle in prediluvial spaces, while the federally funded, state-administered Louisiana Road Home Program’s “Option 1”—to rebuild in place, by far the most popular of the three options—provided grant money to do exactly that.
“Shrinking the urban footprint” became heresy; “greenspacing” took on sinister connotations; and rebuilding in flooded areas came to be valorized as a heroic civic statement. Actor Brad Pitt’s much-celebrated Make It Right Foundation, for example, pointedly positioned its housing initiative along a surge-prone canal, below sea level and immediately adjacent to the single worst Katrina levee breach, to illustrate that if a nonprofit “could build safe, sustainable homes in the most devastated part of New Orleans, [then it] would prove that high-quality, green housing could be built affordably everywhere.”3 Ignoring topography and hydrology gained currency in the discourse of community sustainability even as it flew in the face of environmental sustainability.
A Brief History of New Orleans’ Residential Settlement Patterns, 1718-2005
Topography and hydrology have played fundamental roles in determining where New Orleanians settled since the city’s founding in 1718. The entire region, lying at the heart of the dynamic deltaic plain of the Mississippi River, originally lay above sea level, ranging from a few inches along the marshy perimeter, to a few feet along an interior ridge system, to 8 to 12 feet along the natural levee abutting the Mississippi River.
From the 1700s to the early 1900s, the vast majority of New Orleanians lived on the higher ground closer to the Mississippi. Uninhabited low-lying backswamps, while reviled for their (largely apocryphal) association with disease, nonetheless provided a valuable ecological service for city dwellers, by storing excess river or rain water and safeguarding the city from storm surges. Even the worst of the Mississippi River floods, in 1816, 1849, and 1871, mostly accumulated harmlessly in empty swamplands and, in hindsight, bore more benefits than costs. New Orleanians during the 1700s-1900s were less exposed to the hazard of flooding because the limitations of their technology forced them to live on higher ground.4
Circumstances changed in the 1890s, when engineers began designing and installing a sophisticated municipal drainage system to enable urbanization to finally spread across the backswamp to the Gulf-connected brackish bay known as Lake Pontchartrain. A resounding success from a developmental standpoint, the system came with a largely unforeseen cost. As the pumps removed a major component of the local soil body—water— it opened up cavities, which in turn allowed organic matter (peat) to oxidize, shrink, and open up more cavities. Into those spaces settled finely textured clay, silt, and sand particles; the soil body thus compacted and dropped below sea level. Over the course of the twentieth century, former swamps and marshes in places like Lakeview, Gentilly, and New Orleans East sunk by 6-10 feet, while interior basins such as Broadmoor dropped to 5 feet below sea level. New levees were built along the lakefront, and later along the lateral flanks, were all that prevented outside water from pouring into the increasingly bowl-shaped metropolis.
Nevertheless, convinced that the natural factors constraining their residential options had now been neutralized, New Orleanians migrated enthusiastically out of older, higher neighborhoods and into lower, modern subdivisions. Between 1920 and 1930, nearly every lakeside census tract at least doubled in population; low-lying Lakeview increased by 350 percent, while parts of equally low Gentilly grew by 636 percent. Older neighborhoods on higher ground, meanwhile, lost residents: Tremé and Marigny dropped by 10 to 15 percent, and the French Quarter declined by one-quarter. The high-elevation Lee Circle area lost 43 percent of its residents, while low-elevation Gerttown increased by a whopping 1,512 percent.5
The 1960 census recorded the city’s peak of 627,525 residents, double the population from the beginning of the twentieth century. But while nearly all New Orleanians lived above sea level in 1900, only 48 percent remained there by 1960; fully 321,000 New Orleanians had vertically migrated from higher to lower ground, away from the Mississippi River and northwardly toward the lake as well as into the suburban parishes to the west, east, and south.6
Subsequent years saw additional tens of thousands of New Orleanians migrate in this pattern, motivated at first by school integration and later by a broader array of social and economic impetuses. By 2000, the Crescent City’s population had dropped by 23 percent since 1960, representing a net loss of 143,000 mostly middle-class white families to adjacent parishes. Of those that remained, only 38 percent lived above sea level.7
Meanwhile, beyond the metropolis, coastal wetlands eroded at a pace that would reach 10-35 square miles per year, due largely to two main factors: (1) the excavation through delicate marshes of thousands of miles of erosion-prone, salt-water-intruding navigation and oil-and-gas extraction canals, and (2) the leveeing of the Mississippi River, which prevented springtime floods but also starved the delta of new fresh water and vital sediment. Gulf waters crept closer to the metropolis’ floodwalls and levees, while inside that artificial perimeter of protection, land surfaces that once sloped gradually to the level of the sea now formed a series of topographic bowls straddling sea level.
When those floodwalls and levees breached on August 29, 2005, sea water poured in and became impounded within those topographic bowls, a deadly reminder that topography still mattered. Satellite images of the flood eerily matched the shape of the undeveloped backswamp in nineteenth-century maps, while those higher areas that were home to the historical city, quite naturally, remained dry.
But the stark geo-topographical history lesson could only go so far in convincing flood victims to move accordingly; after all, they still owned their low-lying properties, and real estate on higher terrain was anything but cheap and abundant. Besides, New Orleanians in general rightfully felt that they had been scandalously wronged by federal engineering failures, and anything short of full metropolitan reconstitution came to be seen as defeatist and unacceptable. Most post-Katrina advocacy thus focused on reinforcing the preexisting technological solutions that kept water out of the lowlands, rather than nudging people toward higher ground. “Shrink the urban footprint” got yelled off the table; “Make Levees, Not War” and “Category-5 Levees Now!” became popular bumper-sticker slogans; and “The Great Footprint Debate” became a bad memory.
Resettlement in Vertical Space
The early repopulation of post-Katrina New Orleans defied easy measure. Residents living “between” places as they rebuilt, plus temporarily broken-up families, peripatetic workers, and transient populations all conspired to make the city’s 2006-2009 demographics difficult to estimate, much less map. The 2010 Census finally provided a precise number: 343,829. By 2014, over 384,000 people lived in Orleans Parish, or eighty percent of the pre-Katrina figure. Of course, not all were here prior; one survey determined roughly 10 percent of the city’s postdiluvian population had not lived here before 2005.8
How had the new population resettled in terms of topographic elevation? We won’t know precisely until 2020, because only the decennial census provides actual headcounts aggregated at sufficiently high spatial resolution (the block level) for this sort of analysis; annual estimates from the American Community Survey do not suffice. Thus we must make do with the 2010 Census. While much has changed during 2010-2015, the macroscopic settlement geographies under investigation here had largely had fallen into place by 2010.
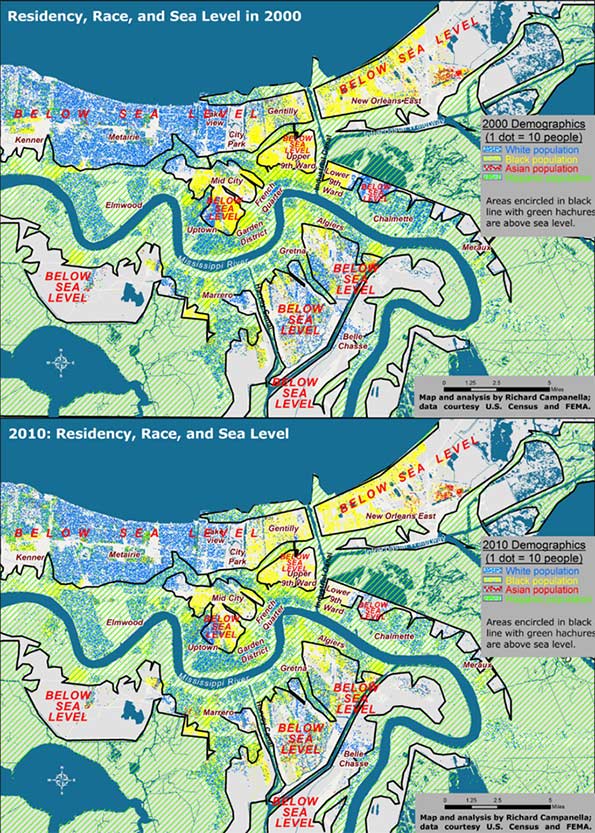
Figure 1. Residential settlement above and below sea level, 2000 and 2010; analysis and maps by Richard Campanella.
When intersected with high-resolution LIDAR-based digital elevation models, the 2010 Census data show that residents of metro New Orleans shifted to higher ground by only 1 percent compared to 2000 (Figure 1). Whereas 38 percent of metro-area residents lived above sea level in 2000, 39 percent did so by 2010, and that differentiation generally held true for each racial and ethnic group. Whites shifted from 42 to 44 percent living above sea level; African Americans 33 to 34 percent, Hispanics from 30 to 29 percent, and Asians 20 to 22 percent.
Clearly, elevation did not exercise much influence in resettlement decisions, and people distributed themselves in vertical space in roughly the same proportions as before the flood. Yet there is one noteworthy angle to the fact that the above-sea-level percentage has risen, albeit barely (38 to 39 percent): it marked the first time in New Orleans history that the percent of people living below sea level has actually dropped.
What impact did the experience of flooding have on resettlement patterns? Whereas people shifted only slightly out of low-lying areas regardless of flooding, they moved significantly out of areas that actually flooded, regardless of elevation. Inundated areas lost 37 percent of their population between 2000 and 2010, with the vast majority departing after 2005. They lost 37 percent of their white populations, 40 percent of their black populations, and 10 percent of their Asian populations. Only Hispanics increased in the flooded zone, by 10 percent, in part because this population had grown dramatically region-wide, and because members of this population sometimes settled in neighborhoods they themselves helped rebuild.
The differing figures suggest that while low-lying elevation theoretically exposes residents to the hazard of flooding, the trauma of actually flooding proved to be, sadly, much more convincing.
Resettlement in Horizontal Space
Contrasting before-and-after residential patterns in horizontal space may be done through traditional methods such as comparative maps and demographic tables. What this investigation offers is a more singular and synoptical depiction of spatial shifts: by computing and comparing spatial central tendencies, or centroids.
A centroid is a theoretical center of balance of a given spatial distribution. A population centroid is that point around which people within a delimited area are evenly distributed.9
Centroids capture complex shifts of millions of data with a single point. But they do not tell the entire story. A centroid for a high-risk coastal area, for example, may shift inland not because people have moved away from the seashore, but because previous residents decided not to return there. It’s also worth noting it takes a lot to move a centroid, as micro-scale shifts in one area are usually offset by countervailing shifts elsewhere. Thus, apparent minor centroid movements can actually be significant. Following are the centroid shifts for metro New Orleans broken down by racial and ethnic groups (Figures 2 and 3).
In 2000, five years before the flood, there were 1,006,783 people living within the metro area as delineated for this particular study, of whom 512,696 identified their race as white; 435,353 as black; 25,941 as Asian; and 50,451 as Hispanic in ethnicity. Five years after the flood, these figures had changed to 817,748 total population, of whom 416,232 were white; 327,972 were black; 27,562 were Asian, and 75,397 were Hispanic.10 When their centroids are plotted, they show that metro residents as a whole, and each racial/ethnic sub-group, shifted westward and southward between 2000 and 2010, away from the location of most of the flooding and away from the source of most of the surge, which generally penetrated the eastern and northern (lakeside) flanks of the metropolis.
Did populations proactively move away from risk? Not quite. What accounts for these shifts is the fact that the eastern half of the metropolis bore the brunt of the Katrina flooding, and the ensuing destruction meant populations here were less likely to reconstitute by 2010, which thus nudged centroids westward. Additionally, flooding from Lake Pontchartrain through ruptures in two of the three outfalls (drainage) canals disproportionally damaged the northern tier of the city, namely Lakeview and Gentilly. Combined with robust return rates in the older, higher historical neighborhoods along the Mississippi, as well as the unflooded West Bank (which sit to the south and west of the worst-damaged areas), they abetted a southwestward shift of the centroids. In a purely empirical sense, this change means more people now live in less-exposed areas. But, as we saw with the vertical shifts, the movements are more a reflection of passive responses to flood damage than active decisions to avoid future flooding.
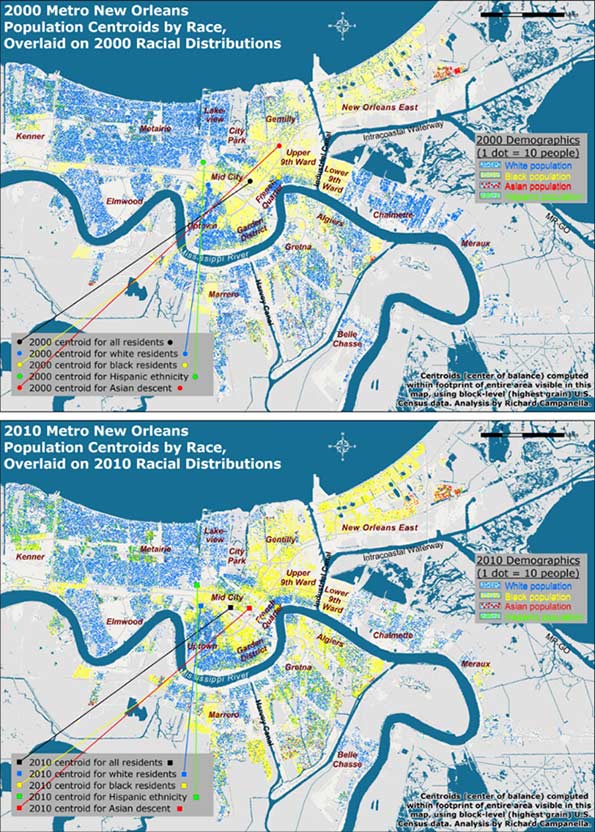
Figure 2. Population centroids by race and ethnicity for metro New Orleans, 2000-2010; see next figure for detailed view. Analysis and maps by Richard Campanella.
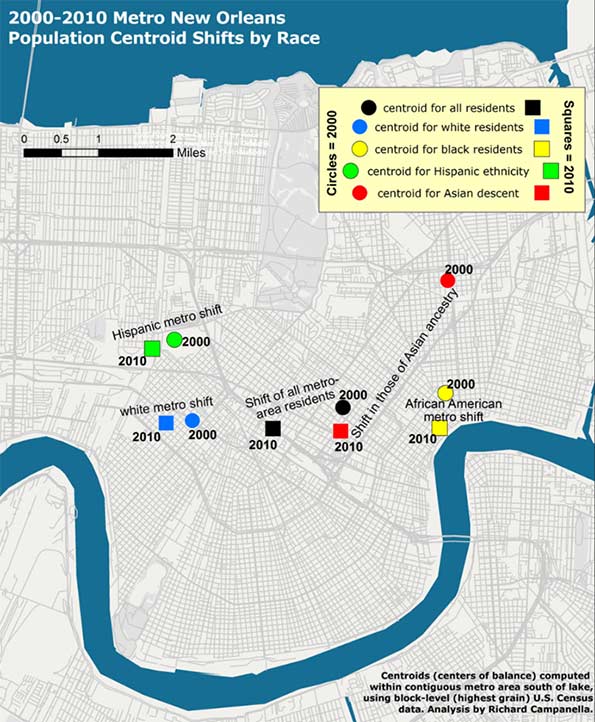
Figure 3. A closer look at the metro-area population centroid shifts by race and ethnicity, 2000-2010; analysis and map by Richard Campanella.
Reflections
Resettlement patterns in metro New Orleans have only marginally reduced residential exposure to the hazard of storm surge. In the vertical dimension, metro-area residents today occupy below-sea-level areas at only a slightly lower rate than before the deluge, 61 percent as opposed to 62 percent, although that change represents the first-ever reverse (decline) of the century-long drift into below-sea-level areas. Likewise, residents’ horizontal shifts, which were in southwestward directions, seemed to suggest a movement away from hazard, but these shifts were more a product of passive than active processes .
Metro New Orleans, it is important to note, has substantially reduced its overall risk—but mostly thanks to its new and improved federal Hurricane & Storm Damage Risk Reduction System (HSDRRS) rather than shifts in residences. No longer called a “protection” system, the Risk Reduction System is a $14.5 billion integrated network of raised levees, strengthened floodwalls, barriers, gates, and pumps built by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and its contractors to protect the metropolis from the surges accompanying storms with a 1-percent chance of occurring in any given year.11 The HSDRRD, which worked well during Hurricane Isaac’s surprisingly strong surge in 2012, has given the metropolis a new lease on life, at least for the next few decades. But all other risk drivers—the condition of the coastal wetlands, subsidence and sea level rise, social vulnerability, and, as evidenced in this paper, exposure—have either slightly worsened, only marginally improved, or generally remained constant.
The exposure-related patterns reported here reflect who won the “Great Footprint Debate” ten years ago.12 Months after Katrina, when it became clear that no neighborhoods would be closed and the urban footprint would persist, decisions driving resettlement patterns in the flooded region effectively transferred from leaders to homeowners. Rather inevitably, the laissez faire rebuilding strategy proved to be exactly that, and people generally repopulated areas they had previously occupied, though at markedly varied densities.
Ten years later, the resulting patterns are a veritable Rorschach Test. Some observers look to the 75-90 percent repopulation rates of certain flooded neighborhoods and view them as heroically high, proof of New Orleanians’ resilience and love-of-place. Others point to the 25-50 percent rates of other areas and call them scandalously low, evidence of corruption and ineptitude. Still others might point to the thousands of scattered blighted properties and weedy lots and concede—as St. Bernard Parish President David Peralta admitted on the ninth anniversary of Hurricane Katrina—that “we probably should have shrunk the footprint of the parish at the very beginning.”13
As for the HSDRRS, continual subsidence and erosion vis-à-vis rising seas, coupled with costly and as-yet undetermined maintenance and certification responsibilities, will gradually diminish the safety dividend provided by this remarkable system. The nation’s willingness to pay for continued upkeep, meanwhile, may grow tenuous; indeed, it’s not even a safe bet locally. Voters in St. Bernard Parish, which suffered near-total inundation from Katrina, defeated not once but twice a tax to pay for drainage and levee maintenance, a move that may well increase flood insurance rates.14
Residents throughout the metropolis appear to be repeating the same mistakes they made during the twentieth century: of dismissing the importance of natural elevation, of over-relying on engineering solutions, of under-maintaining these structures in a milieu of scarce funds, and of developing a false sense of security about flood “protection.”
We need to recognize the limits of our ability to neutralize hazards—that is, to presume that levees will completely protect us from storm surges—while appreciating the benefits of reducing our exposure to them. Beyond the metropolis, this means aggressive coastal restoration using every means available as soon as possible, an effort that may well require some expropriations. Within the metropolis, it means living on higher ground or otherwise mitigating risk. In the words of University of New Orleans disaster expert Dr. Shirley Laska, “mitigation, primarily elevating houses, is [one] way to achieve the affordable flood insurance…. It is possible to remain in moderately at-risk areas using engineered mitigation efforts, combined with land use planning that restricts development in high-risk areas.”15
Planning that restricts development in high-risk areas: this was the same reasoning behind the “shrink the urban footprint” argument of late 2005—and anything but the laissez faire strategy that ensued.
Bio
Richard Campanella, a geographer with the Tulane School of Architecture, is the author of “Bienville’s Dilemma,” “Geographies of New Orleans,” “Delta Urbanism,” “Bourbon Street: A History,” and other books. His articles may be read at http://richcampanella.com , and he may be reached at rcampane@tulane.edu or @nolacampanella on Twitter.
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to thank Gulf of Mexico Program Officer Kristin Tracz of the Walton Family Foundation, Dr. Shirley Laska, and the Gulf Coast Restoration Fund at New Venture Fund, and Tulane School of Architecture, as well as Garry Cecchine, David Johnson, and Mark Davis for their reviews.
1 David Crichton, “The Risk Triangle,” in Natural Disaster Management, edited by J. Ingleton (Tudor Rose, London, 1999), pp. 102-103.
2 In this paper, “metro New Orleans” means the conurbation (contiguous urbanized area shown in the maps) of Orleans, Jefferson, western St. Bernard, and upper Plaquemines on the West Bank (Belle Chasse); it excludes the outlying rural areas of these parishes, such as Lake Catherine, Grand Island, and Hopedale, and does not include the North Shore or the river parishes.
4 Richard Campanella, Bienville’s Dilemma: A Historical Geography of New Orleans and Geographies of New Orleans (University of Louisiana Press, 2006, 2008); R. Campanella, Delta Urbanism: New Orleans (American Planning Association, 2010); R. Campanella, “The Katrina of the 1800s Was Called Sauve’s Crevasse,” Times-Picayune, June 13, 2014, and other prior works by the author.
5 H. W. Gilmore, Some Basic Census Tract Maps of New Orleans (New Orleans, 1937), map book stored at Tulane University Special Collections, C5-D10-F6.
6 Richard Campanella, Bienville’s Dilemma: A Historical Geography of New Orleans (University of Louisiana Press, 2008) and other prior works by the author.
7 Coincidently, 38 percent of all residents of the contiguous metropolis south of Lake Pontchartrain also lived above sea level in 2000. Thus, at both the city and metropolitan level, three out of every eight residents lived above sea level and the other five resided below sea level. All figures calculated by author using highest-grain available historical demographic data, usually from the U.S. Census, and LIDAR-based high-resolution elevation data captured in 1999-2000 by FEMA and the State of Louisiana.
9 Defining the study area is essential when reporting centroids. New Orleans proper, the contiguous metro area, and the Metropolitan Statistical Area, which includes St. Tammany and other outlying parishes, would all have different population centroids. This study uses the metro area south of the lake shown in the accompanying maps. It is also important to use the finest-grain—that is, highest spatial resolution—demographic data to compute centroids, as coarsely aggregated data carries with it a wider margin of error. This study uses block-level data from the decennial U.S. Census, the finest available.
10 Figures do not sum to totals because some people chose two or more racial categories while others declined the question, and because Hispanicism is viewed by the Census Bureau as an ethnicity and not a race.
12 Richard Campanella, Bienville’s Dilemma: A Historical Geography of New Orleans (University of Louisiana Press, 2008), pp. 344-355.
13 David Peralta, as quoted by Benjamin Alexander-Bloch, “Hurricane Katrina +9: Smaller St. Bernard Parish Grappling with Costs of Coming Back,” Times-Picayune/NOLA.COM, August 29, 2014.
14 Mark Schleifstein, “St. Bernard Tax Defeat Means Higher Flood Risk, Flood Insurance Rates, Levee Leaders Warn,” Times-Picayune/NOLA.COM, May 4, 2015, http://www.nola.com/environment/index.ssf/2015/05/st_bernard_tax_defeat_means_hi.html ; see also Richard Campanella, “The Great Footprint Debate, Updated,” Times-Picayune/NOLA.COM, May 31, 2015.
15 Shirley Laska, email communication with author, April 12, 2015.
It’s the best of times and the worst of times in Los Angeles.
Los Angeles is now attracting notice as a so-called “global city,” one of the world’s elite metropolises. It is ranked #6 in the world by AT Kearney and tied for 10th in a report by the Singapore Civil Service College that I contributed to. Yet it also has among the highest big city poverty rates in the nation, and was found to be one of the worst places in America for upward mobility among the poor. Newspaper columns are starting to refer to LA as a “third world city.”
Though the Bay Area gets the headlines, the LA region likes to boast it’s coming on strong in tech. With a diverse set of marquee names including Snapchat, Tinder, Oculus, and SpaceX, LA’s startup scene continues to grow. But tech growth overall has been middling, ranking 28th out of the country’s sixty-six largest region in information job growth, according to a recent Forbes survey.
More disturbing, job growth has also been slow, ranking 35th overall, at a time when it’s long time rivals in the Bay Area occupy the top job and tech rankings. Some of this reflects the loss of a key industry, aerospace, but also the departure of major corporations such as Lockheed, Northrup Grumman, Occidental Petroleum, and Toyota, which has left LA’s once vaunted corporate community but is a shell of its former self.
Yet LA’s glitz factor remains potent. The fashion industry has gained considerable recognition. Tom Ford set up shop and brought his runway show to the city. Locally grown brands like Rodarte have a major following. LA also is increasingly a global center of gravity in the art world.
Yet behind the glitz, in the city of Los Angeles, aging water mains regularly erupt and the streets and sidewalks decay, with the city’s own report estimating it has an $8.1 billion infrastructure repair backlog.
One report chronicles the flight of cash-strapped New York creatives fleeing to sunny, liberating, and less expensive LA. Another how high prices and the Southern California grind are sending those same creatives packing.
What’s going on here?
What we are witnessing is LA changing in the context of the two tier world —divided between rich and poor — that we live in. This has been made worse by a city that has excessively focused on glamour at the expense of broad based opportunity creation.
Los Angeles may be a creative capital and a great place to live as a creative worker, but it was always much more than that. It was also a great place to build the middle class American Dream or run a business that employed people at scale. For example, it was and still today remains the largest manufacturing center in the United States. Yet it has lost half of its manufacturing job base since 1990. That’s over half a million manufacturing jobs lost in the region since then, with over 300,000 of those just since 2000. Unlike Detroit, Houston, Nashville and even Portland, the region has not benefited at all from the resurgence of US manufacturing since 2009.
Manufacturing decline, of course, is hardly unique to LA, but the city’s problems are particularly acute because region is so huge and diverse, being both the second largest metro area in the country, and the most diverse major region in America. LA has a higher share of Hispanic population than any major metro apart from San Antonio – one twice as high as the Bay Area. The LA/Inland Empire’s 8.4 million Hispanics would by themselves be the fourth largest metro area in the country, and are more than the total number of people living in the Bay Area. The area also has over a million black residents.
With their heavily well-educated populations the Bay Area and Boston can perhaps get away with operating as sort of luxury boutiques for upscale whites and Asians, however dubious a decision that may be. Not so LA.
The problem is that LA and California more broadly have adopted the luxury boutique mindset. Policies are made in ways that favor the glamorous industries like Hollywood, high tech, and the arts – industries that don’t employ a lot of aspiring middle class people, particularly Hispanics or blacks.
These policies include strongly anti-growth land use and environmental policies designed to produce the kind pristine playgrounds favored by glamour industries and creative elite. But they have rendered the region increasingly unaffordable to all but the highly affluent or those who were lucky enough to buy in long ago.
Tech firms and entertainment companies can afford to pay their key workers whatever they need to live in LA. That’s tougher for more workaday businesses. Ditto for business regulations, where many industries don’t have the margins to spend on things like a phalanx of compliance attorneys.
Now that high prices are starting to hurt younger hipsters who want to join the creative industries, this is starting to get attention. But if it’s a problem for young, educated Millennials, it’s a disaster for the working class.
LA does deserve credit for potentially opportunity expanding investments in transit. But if transit can be seen as a potential winner, most political leaders seem more concerned with finding ways to simply attempt to politically reallocate some money to those being squeezed by their policies, all at the expense of growth. The $15 minimum wage is Exhibit A. Like rent control, a high minimum wage benefits a few lucky winners while harming others and making it harder to justify business investment that would create more jobs and entry level opportunities onto the ladder of success, while raising consumer prices. The fact that nearly half of LA’s workers might be covered by the new minimum is a damning testament to the erosion of the region’s middle class job base.
The real measure of success for LA is not how many runway shows, startups, and elite rankings it can achieve, but whether it can recover its role as an engine of opportunity for its large and diverse population to achieve their American Dream. Local leaders would be better served looking for policies that will expand opportunity instead of the ones they are following that actually reduce it.
Aaron M. Renn is a Senior Fellow at the Manhattan Institute for Policy Research and a Contributing Editor at its magazine City Journal.
My latest piece is online in City Journal and is called “Chicago’s Financial Fire.” It’s a look at the ongoing financial crisis in that city, which has all of a sudden gotten very real thanks to a downgrade of the city’s credit rating to junk by Moody’s. Here’s an excerpt:
While some sort of refinancing may be required, the proposed debt issue contains maneuvers similar to those that helped get Chicago into trouble in the first place—including more scoop and toss deferrals, $75 million for police back pay, $62 million to pay a judgment related to the city’s lakefront parking-garage lease, and $35 million to pay debt on the acquisition of the former Michael Reese Hospital site (an architecturally significant complex Daley acquired and razed for an ill-fated Olympic bid). The debt-issue proposal also includes $170 million in so-called “capitalized interest” for the first two years. That is, Chicago is actually borrowing the money to pay the first two years of interest payments on these bonds. In true Chicago style, the proposal passed the city council on a 45-3 vote. Hey, at least the city is getting out of the swaps business.
Even with no further gimmicks, Emanuel will be six years into his mayoralty before the city can stop borrowing just to pay the interest on its debt. And without accounting for pensions, it will take the full eight years of both his terms to get the city to a balanced budget, where it can pay for the regular debt it has already accumulated.
Click through to read the whole thing.
Rahm donned a sweater during his reelection campaign and told the public he recognized he needed to change his ways, saying that he knows he “can rub people the wrong way.” The title of that ad was “Chicago’s Future.”
I decided to take him up on his new approach. When I was working on this piece, I tried to get some information of the mayor’s press office. I asked them such extremely hard hitting questions as, “Is there a consolidated location where all of the mayor’s most recent financial proposals can be seen in their current form?” I emailed them and got no response. So I followed up with a phone call. I was put on hold for a while then told the person I needed to talk to was away from her desk, but I should email her at a XYZ address. So I did. No response. This is the same pattern all previous inquiries I’ve made have followed, though I believe on occasion I’ve been put through to a voice mail from which I got no callback. Now, it’s not like I try to get stuff from these guys every day, but the message is pretty clear. I gather that this experience is not at all unusual when dealing with Rahm.
Having his press office simply refuse to respond at all to even basic inquiries from (the apparently many) people on his blacklist is naught put pettiness. Rahm takes people who could be friends and does his best to turn them into enemies. No wonder the Sun-Times titled a recent about him, “Rahm’s troubles plentiful, allies scarce.”
Thus it is that Chicago, a city of grand and expansive history and ambition, a city so big it overflows the page, comes to have a mayor with a certain smallness of spirit.
Aaron M. Renn is a senior fellow at the Manhattan Institute and a Contributing Editor at City Journal. He writes at The Urbanophile, where this piece first appeared.
Chicago photo by Bigstock.
Recent setbacks for social conservative ideals – most particularly on same-sex marriage – have led some to suggest that traditional values are passé. Indeed, some conservatives, in Pat Buchanan’s phrase, are in “a long retreat,” deserted by mainstream corporate America sporting rainbow logos. Some social conservatives are so despondent that they speak about retreating from the public space and into their homes and churches, rediscovering “the monastic temperament” prevalent during the Dark Ages.
This response would be a tragedy for society. For all its limitations, the fundamental values cherished by the religious – notably, family – have never been more important, and more in need of moral assistance. The current progressive cultural wave may itself begin to “overreach” as it moves from the certainty of liberal sentiment to ever more repressive attempts to limit alternative views of the world, including those of the religious.
In the next few years, social conservatives need to engage, but in ways that transcend doctrinal concerns about homosexuality, or even abortion. It has to be made clear that, on its current pace, Western civilization and, increasingly, much of East Asia are headed toward a demographic meltdown as people eschew family formation for the pleasures of singleness or childlessness.
Read the entire piece at The Orange County Register.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and Roger Hobbs Distinguished Fellow in Urban Studies at Chapman University, and a member of the editorial board of the Orange County Register. He is also executive director of the Houston-based Center for Opportunity Urbanism. His newest book, The New Class Conflict is now available at Amazon and Telos Press. He is also author of The City: A Global History and The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050. He lives in Orange County, CA.
Baby photo by Bigstock.
The next culture war will not be about issues like gay marriage or abortion, but about something more fundamental: how Americans choose to live. In the crosshairs now will not be just recalcitrant Christians or crazed billionaire racists, but the vast majority of Americans who either live in suburban-style housing or aspire to do so in the future. Roughly four in five home buyers prefer a single-family home, but much of the political class increasingly wants them to live differently.
Theoretically, the suburbs should be the dominant politically force in America. Some 44 million Americans live in the core cities of America’s 51 major metropolitan areas, while nearly 122 million Americans live in the suburbs. In other words, nearly three-quarters of metropolitan Americans live in suburbs.
Yet it has been decided, mostly by self-described progressives, that suburban living is too unecological, not mention too uncool, and even too white for their future America. Density is their new holy grail, for both the world and the U.S. Across the country efforts are now being mounted—through HUD, the EPA, and scores of local agencies—to impede suburban home-building, or to raise its cost. Notably in coastal California, but other places, too, suburban housing is increasingly relegated to the affluent.
The obstacles being erected include incentives for density, urban growth boundaries, attempts to alter the race and class makeup of communities, and mounting environmental efforts to reduce sprawl. The EPA wants to designate even small, seasonal puddles as “wetlands,” creating a barrier to developers of middle-class housing, particularly in fast-growing communities in the Southwest. Denizens of free-market-oriented Texas could soon be experiencing what those in California, Oregon and other progressive bastions have long endured: environmental laws that make suburban development all but impossible, or impossibly expensive. Suburban family favorites like cul-de-sacs are being banned under pressure from planners.
Some conservatives rightly criticize such intrusive moves, but they generally ignore how Wall Street interests and some developers see forced densification as opportunities for greater profits, often sweetened by public subsidies. Overall, suburban interests are poorly organized, particularly compared to well-connected density lobbies such as the developer-funded Urban Land Institute (ULI), which have opposed suburbanization for nearly 80 years.
The New Political Logic
The progressives’ assault on suburbia reflects a profound change in the base of the Democratic Party. As recently as 2008, Democrats were competitive in suburbs, as their program represented no direct threat to residents’ interests. But with the election of Barack Obama, and the continued evolution of urban centers as places with little in the way of middle-class families, the left has become increasingly oriented towards dense cities, almost entirely ruled by liberal Democrats.
Obama’s urban policies are of a piece with those of “smart growth” advocates who want to curb suburban growth and make sure that all future development is as dense as possible. Some advocate radical measures such as siphoning tax revenues from suburbs to keep them from “cannibalizing” jobs and retail sales. Some even fantasize about carving up the suburban carcass, envisioning three-car garages “subdivided into rental units with street front cafés, shops and other local businesses” while abandoned pools would become skateboard parks.
At the end of this particular progressive rainbow, what will we find? Perhaps something more like one sees in European cities, where the rich and elite cluster in the center of town, while the suburbs become the “new slums” that urban elites pass over on the way to their summer cottages.
Political Dangers
The abandonment of the American Dream of suburban housing and ownership represents a repudiation of what Democrats once embraced and for which millions, including many minorities, continue to seek out. “A nation of homeowners,” Franklin D. Roosevelt asserted, “of people who own a real share in their land, is unconquerable.”
This rhetoric was backed up by action. It was FDR, and then Harry Truman, who backed the funding mechanisms—loans for veterans, for example—that sparked suburbia’s growth. Unlike today’s progressives, the old school thought it good politics to favor those things that most people aspire to achieve. Democrats gained ground in the suburbs, which before 1945 had been reliably and overwhelmingly Republican.
Even into the 1980s and beyond, suburbanites functioned less as a core GOP constituency than as the ultimate swing voters. As urban cores became increasingly lock-step liberal, and rural Democrats slowlyfaded towards extinction, the suburbs became the ultimate contested territory. In 2006, for example, Democrats won the majority of suburban voters. In 2012, President Obama did less well than in 2008, but still carried most inner and mature suburbs while Romney trounced him in the farther out exurbs. Overall Romney eked out a small suburban margin.
Yet by 2014, as the Democratic Party shifted further left and more urban in its policy prescriptions, these patterns began to turn. In the 2014 congressional elections, the GOP boosted its suburban edge to 12 percentage points. The result was a thorough shellacking of the Democrats from top to bottom.
Will demographics lead suburbs to the Democrats?
Progressive theory today holds that the 2014 midterm results were a blast from the suburban past, and that the key groups that will shape the metropolitan future—millennials and minorities—will embrace ever-denser, more urbanized environments. Yet in the last decennial accounting, inner cores gained 206,000 people, while communities 10 miles and more from the core gained approximately 15 million people.
Some suggest that the trends of the first decade of this century already are passé, and that more Americans are becoming born-again urbanistas. Yet after a brief period of slightly more rapid urban growth immediately following the recession, U.S. suburban growth rates began to again surpass those of urban cores. An analysis by Jed Kolko, chief economist at the real estate website Trulia, reports that between 2011 and 2012 less-dense-than-average Zip codes grew at double the rate of more-dense-than-average Zip codes in the 50 largest metropolitan areas. Americans, he wrote, “still love the suburbs.”
What is also missed by the Obama administration and its allies is the suburbs’ growing diversity. If HUD wants to start attacking these communities, many of their targets will not be whites, but minorities, particularly successful ones, who have been flocking to suburbs for well over a decade.
This undermines absurd claims that the suburbs need to be changed in order to challenge the much detested reign of “white privilege.” In reality, African-Americans have been deserting core cities for years, largely of their own accord and through their own efforts: Today, only 16 percent of the Detroit area’s blacks live within the city limits.
These trends can also be seen in the largely immigrant ethnic groups. Roughly 60 percent of Hispanics and Asians, notes the Brooking Institution, already live in suburbs. Between the years 2000 and 2012, the Asian population in suburban areas of the nation’s 52 biggest metro areas grew by 66 percent, while that in the core cities expanded by 35 percent. Of the top 20 areas with over 50,000 in Asian population, all but two are suburbs.
Left to market forces and natural demographic trends, suburbs are becoming far more diverse than many cities, meaning that in turning on suburbia, progressives are actually stomping on the aspirations not just of privileged whites but those of many minorities who have worked hard to get there.
Another huge misreading of trends relates to another key Democratic constituency, the millennial generation. Some progressives have embraced the dubious notion that millennials won’t buy cars or houses, and certainly won’t migrate to the suburbs as they marry and have families. But those notions are rapidly dissolving as millennials do all those things. They are even—horror of horrors!—shopping atWal-Mart, and in greater percentages than older cohorts.
Moreover, notes Kolko, millennials are not moving to the denser inner ring suburban areas. They are moving to the “suburbiest” communities, largely on the periphery, where homes are cheaper, and often schools are better. When asked where their “ideal place to live,” according to a survey by Frank Magid and Associates, more millennials identified suburbs than previous generations. Another survey in the same year, this one by the Demand Institute, showed similar proclivities.
Stirrings of Rebellion
So if the American Dream is not dead among the citizens, is trying to kill it good politics? It’s clear that Democratic constituencies, notably millennials, immigrants and minorities, and increasingly gays—particularly gay couples—are flocking to suburbs. This is true even in metropolitan San Francisco, where 40 percent of same-sex couples live outside the city limits.
One has to wonder how enthusiastic these constituents will be when their new communities are “transformed” by federal social engineers. One particularly troubling group may be affluent liberals in strongholds such as Marin County, north of San Francisco, long a reliable bastion of progressive ideology.
Forced densification–the ultimate goal of the “smart growth” movement—also has inspired opposition in Los Angeles, where densification is being opposed in many neighborhoods, as well as traditionally more conservative Orange Country. Similar opposition has arisen in Northern Virginia suburbs, another key Democratic stronghold.
These objections may be dismissed as self-interested NIMBYism, but this misses the very point about why people move to suburbs in the first place. They do so precisely in to avoid living in crowded places. This is not anti-social, as is alleged, but an attempt—natural in any democracy—to achieve a degree of self-determination, notes historian Nicole Stelle Garrett.
Aroused by what they perceive as threats to their preferred way of life, these modern pilgrims can prove politically effective. They’ve shown this muscle while opposing plans not only to increase the density in suburbs, and also balking at the shift of transportation funding from roads, which suburbanites use heavily, to rail transit. This was seen in Atlanta in 2012 when suburban voters rejected a mass transit plan being pushed by downtown elites and their planning allies. Opposition to expanding rail service has also surfaced in the Maryland suburbs of Washington.
Suburbs and 2016 Election
To justify their actions against how Americans prefer to live, progressives will increasingly cite the environment. Climate change has become the “killer app” in the smart growth agenda and you can expect the drumbeat to get ever louder towards the Paris climate change conference this summer.
Yet the connection between suburbs and climate is not as clear as the smart growth crowd suggests. McKinsey and other studies found no need to change housing patterns to reduce greenhouse gases, particularly given improvements in both home and auto efficiency. Yet so great is their animus that many anti-suburban activists seem to prefer stomping on suburban aspirations rather seeking ways to make them more environmental friendly.
As for the drive to undermine suburbs for reasons of class, in many ways the assault on suburbia is, in reality, a direct assault on our most egalitarian geography. An examination of American Community Survey Data for 2012 by the University of Washington’s Richard Morrill indicates that the less dense suburban areas tended to have “generally less inequality” than the denser core cities; Riverside-San Bernardino, for example, is far less unequal than Los Angeles; likewise, inequality is less pronounced in Sacramento than San Francisco. Within the 51 metropolitan areas with more than 1 million people, notes demographer Wendell Cox, suburban areas were less unequal (measured by the GINI Coefficient) than the core cities in 46 cases.
In the coming year, suburbanites should demand more respect from Washington, D.C., from the media, the political class and from the planning community. If people choose to move into the city, or favor density in their community, fine. But the notion that it is the government’s job to require only one form of development contradicts basic democratic principles and, in effect, turns even the most local zoning decision into an exercise in social engineering.
As America’s majority, suburbanites should be able to deliver a counterpunch to those who seem determined to destroy their way of life. Irrespective of race or generation, those who live in the suburbs—or who long to do so—need to understand the mounting threat to their aspirations Once they do, they could spark a political firestorm that could reshape American politics for decades to come.
This piece first appeared at Real Clear Politics.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and Roger Hobbs Distinguished Fellow in Urban Studies at Chapman University, and a member of the editorial board of the Orange County Register. He is also executive director of the Houston-based Center for Opportunity Urbanism. His newest book, The New Class Conflict is now available at Amazon and Telos Press. He is also author of The City: A Global History and The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050. He lives in Orange County, CA.
Suburbs photo courtesy of BigStockPhoto.com.
The Minneapolis-St. Paul Metropolitan Council is gambling $8.7 million on a project to alleviate pedestrian congestion that might exist in 5 to 10 years if we’re somehow able to build two additional light rail lines and they are operating at full capacity for 10 days a year.
That’s like buying flood insurance on the house you have yet to buy.
The below $8.7 million piece of public infrastructure is intended to create a more safe passageway for travelers at the Downtown East station during Vikings home games. It’ll serve west and northbound train passengers and other pedestrians looking to enter a new football stadium. It is deemed this will be an important pedestrian overpass once all four major light rail lines completed.
Download the Downtown East Plan Met Council PowerPoint here [PDF].
Those reading this should have at least two questions:
- How did this come to be a thing?
- Why is it all of a sudden getting $8.7 million?
I pay particularly close attention to local projects. I read blogs, forums and newspapers daily. I know and follow local decision-makers on social media, track development proposals, and pay attention to those boring committees few care about. I also work in the industry and talk to other people who work and follow the industry across related professions. It’s fair to say that I have a very good idea of what’s going on in the Twin Cities and the transportation and development needs of the community.
Never once have I heard of this project until a few days ago. And now, out of the blue, we’re dropping $8.7 million on a bridge that’ll be needed 10 days a year starting in 2019.
I wrote a blog post last year titled The Politics of Dumb Infrastructure. It was well received, and is even being used as required reading in an undergrad planning course in California. In the article I theorize as to why we make bad decisions when it comes to receiving other people’s money on transit projects;
It’s the orderly, but dumb system that makes planners and politicians play to a bureaucratic equation that is supposed to guide officials towards the best alternative. Only it never actually works out that way and it usually forces smart people into making highly compromised and less-than-ideal decisions.
The pedestrian bridge is different. It may deal with Federal grants, but is also come from local and regional coffers. Regardless, this project is being pushed forward. According to the Star Tribune,
“The transit agency will likely devote $6 millon from its coffers for the project (this figure could be offset by federal grants), with the Minnesota Sports Facilities Authority (which oversees stadium construction) ponying up $2 million, and the rest coming from bonds issues by the Met Council.”
Before we go any further, I think we need to ask a complex question.
How Did We Get Here?
The new $1 billion Green Line is done and the $1.1 billion Vikings Stadium is underway. They combine to represent over $2 billion of investment. Our local leaders are concerned, as they should be, that these pieces of infrastructure be as perfect as possible.
To quote a former Governor (one who wasn’t a professional wrestler),
“All too often, the human tendency is to compound one big mistake with a series of additional mistakes in the hope that somehow the results will improve. This appears to be the case with the Vikings stadium.”
Politicians are attracted to big, transformitive projects, so it seems only natural that our leaders, who have expelled a great amount of political capital, want to see every inch of it succeed. Even if that means throwing good money after bad.
How We Justify It All
An engineer at the Met Council, likely under much political pressure, noticed something: based on 2019 projections, during peak hours on Minnesota Vikings game days, there will be only a 120 second headway between trains. This will likely not be enough time to manage safe pedestrian crossings. The proposed solution is the bridge.

Please note the skyway attached to the State-mandated parking structure.
The pedestrian bridge makes some sense. Based on the projections, there will be long lines and delays during this period; and building a bridge for pedestrians certainly isn’t an unreasonable response. The Met Council’s Transportation Committee appears to be interested in the idea.
Let’s look at these assumptions: they assume that there will be two additional light rail lines in full operation, both of which have not yet even been either fully allocated money or constructed. Basically, the Met Council is gambling $8.7 million that there might be a problem in 5 years if we’re somehow able to build two additional light rail lines and they are operating at full capacity for 10 days a year.
To reiterate: Four (4) LRT lines being in operation (Blue, Green, SW & Bottentieu) and that Vikings game attendees hitting a 40% transit mode share. All of things don’t currently exist. It also assumes, more importantly, that if there is congestion people will not find an alternative route or change their travel behavior. This isn’t to say we can’t plan ahead. We should. But, we should be more realistic in our projections and our priorities.
Where Are Our Priorities?
Why did this project get fast-tracked while other smaller, more “everyday” projects never see the light of day? And, when smaller projects get the public’s attention, why do they struggle to find funding? These are merely a question of priorities.
As Nick Magrino (at streets.mn) has asked so often, “why are we embarrassed by the bus?” He writes,
“… I can’t shake the feeling that many of the expensive transit improvements we get in the Twin Cities are thought up by people who don’t actually use transit. Which is why we end up with Northstar, the Red Line, and so on.”
A bridge like this seems like such a low priority, especially when we have legitimate transportation needs. For example, THIS is a bus stop on a heavily used transit line near the center of Minneapolis.
It’s not that a pedestrian bridge is a terrible idea. Under the projections, at some point in the future, it seems maybe reasonable. But, why is the Met Council prioritizing and fast-tracking this, whereas things like bike lanes, bus shelters, and potholes get ignored? I say this because you could build 40 miles of protected bike lanes for the same price tag.
Projects can take on a life of their own. There is no traditional process to getting things done. In this pedestrian overpass, you have the right person with the right slideshow presenting it to the right people at the right time. From here, you have the Met Council employees and political-appointed representatives who have monies at their disposal. The proposal, while not perfect, seems reasonable enough. And, we’ve just spent $2 billion on infrastructure, so we need to make it right. The presentation looks good, so why not go for it?
What Would Your City Do With $8.7 Million?
Imagine if the City of Minneapolis was given $8.7 million that could only be used on downtown pedestrian and/or transit projects. What would they do? The answer is: not a pedestrian bridge to be used during 10 sports games a year.
So, why are we doing it?
The answer is that we can get money from elsewhere to do the things we don’t need to do. But, when it comes to doing the simple things that we need to do, well, that money isn’t available from elsewhere. The pedestrian bridge is a bad idea (right now) that’s made worse when you think of the countless thousands of more useful public investments we could be making.
The truth is that the people and the City of Minneapolis don’t even care about it. It’s not on their radar. It’s the people who control infrastructure and transportation dollars who care about this. If given the opportunity to allocate these dollars elsewhere, it’s fair to say thatliterally everyone locally would divert them elsewhere.
Our priorities get skewed and we misallocate resources most when our funding comes from elsewhere. In fact, it is precisely why Minneapolis has the below. All of which the City of Minneapolis will be tearing down in 30 years …

Note: This is also next to a proposed park called “The Yard” that neither the City of Minneapolis nor it’s Park Board want to maintain. Yet, somehow it’s still a thing.
This post originally appeared in Strong Towns on September 9, 2014. Content licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License.
Find more from Nathaniel M. Hood at his blog: nathanielhood.com
Some future historian, searching for the origins of a second Middle Ages, might fix on the summer of 2015 as its starting point. Here occurred the marriage of seemingly irreconcilable world views—that of the Catholic Church and official science—into one new green faith.
As Pope Francis has embraced the direst notions of climate change, one Canadian commentator compared Francis’s bleak take on the environment, technology, and the market system to that of the Unabomber. “Doomsday predictions,” the Pope wrote in his recent encyclical “Laudato Si,” “can no longer be met with irony or disdain.”
With Francis’s pontifical blessing , the greens have now found a spiritual hook that goes beyond the familiar bastions of the academy, bureaucracy, and the media and reaches right into the homes and hearts of more than a billion practicing Catholics. No potential coalition of interests threatened by a seeming tsunami of regulation—from suburban homeowners and energy firms to Main Street businesses—can hope to easily resist this alliance of the unlikely.
Historical U-Turn?
There are of course historical parallels to this kind of game-changing alliance. In the late Roman Empire and then throughout the first Middle Ages, church ideology melded with aristocratic and kingly power to assure the rise of a feudal system. Issuing indulgences for the well-heeled, the Church fought against the culture of hedonism and unrestrained individualism that Francis has so roundly denounced. The Church also concerned itself with the poor, but seemed not willing to challenge the very economic and social order that often served to keep them that way.
Historically Medievalism represented a “steady state” approach to human development, seeking stability over change. Coming after the achievements of the classical age—with its magnificent engineering feats as well as an often cruel, highly competitive culture—the Middle Ages ushered in centuries of slow growth, with cities in decline and poverty universal for all but a few.
To be sure, the Church played an important, if difficult role, in preserving classical culture and, in the Renaissance, often nurtured a resurgence in some classical values of human self-improvement, science and inquiry, and individual enterprise. But ultimately, as Max Weber noted, it could not compete with a Protestantism that fit more easily with the emerging capitalist spirit. Protestant countries—the Netherlands, northern German, Britain, and America—took the lead in the development of the modern world.
Capitalism, particularly during the early industrial revolution, often abused human dignity and engendered huge poverty. This still happens today, as the Pope suggests, but this system has also been responsible for lifting hundreds of millions of people—most recently in China and East Asia—out of poverty. Without the resources derived from capitalist enterprise, there would have been insufficient funds to drive the great improvements in sanitation, housing, and education that have created huge pockets of relative affluence across the planet.
The Coalition for Anti-Growth
What makes the Pope’s position so important—after all, the world is rejecting his views on such things as gay marriage and abortion—is how it jibes with the world view of some of the secular world’s best-funded, influential, and powerful forces. In contrast to both Socialist and capitalist thought, both the Pope and the greens are suspicious about economic growth itself, and seem to regard material progress as aggression against the health of the planet.
The origins of this world view back to the ’40s. An influential group of scientists, planners, and top executives voiced concern about the impact of an exploding population on food stocks, raw materials, and the global political order. In 1948, environmental theorist William Vogt argued that population was outstripping resources and would lead to the mass starvation predicted in the early 19th century by Thomas Malthus.
The legacy of Malthus, himself a Protestant clergymen, dominates environmental thinking. As historian Edward Barbier notes, Malthusianism presumes that a culture or society lacks all “access to new sources of land and resources or is unable to innovate,” thus is “vulnerable to collapse.” In his seminal 1968 book,The Population Bomb, Paul Ehrlich predicted imminent mass starvation in much of the world and espoused draconian steps to limit fertility, which he saw being imposed by a “relatively small group” of enlightened individuals. He even raised the possibility of placing “sterilants” in the water supply and advocated tax policies that discouraged child-bearing.
Ehrlich’s dire predictions proved widely off the mark—food production soared, and starvation declined—but this appears not to have dissuaded the Church from embracing Ehrlich’s contemporary acolytes. This is not to say that environmentalism has not achieved much in terms of cleaning the air and water, restoring wildlife and expanding open space. Yet these triumphs are not seen as sources of inspiration by a movement that seems to live off pointing to a doomsday clock.
Given their lack of faith in markets or people, the green movement has become ever less adept at adjusting to the demographic, economic, and technological changes that have occurred since the ’70s. Huge increases in agricultural productivity and the recent explosion in fossil fuel energy resources have been largely ignored or downplayed; the writ remains that humanity has entered an irreversible “era of ecological scarcity” that requires strong steps to promote “sustainability.”
The green movement’s views on population represent the most difficult contradiction in the new alliance. Many environmental organizations and pundits favor strong steps to discourage people from having children. The Church and Francis are now allied to the likes of Peter Kareiva, chief scientist for the U.S.-based Nature Conservancy, who has concluded that not having children is the most effective way for an individual in the developed world to reduce emissions, although he adds that he himself is a father. In the United Kingdom, Jonathan Porritt, an environmental advisor to Prince Charles, has claimed that having even two children is “irresponsible,” and has advocated for the island nation to reduce its population by half in order, in large part, to reduce emissions.
The Poor will always be with us. But they might not go along with the plan.
Another flash point between papal concerns and those of their new best friends lies in addressing poverty. The Pope is correct in identifying inequality and poverty as major concerns, but it’s hard to say how green strategies—particularly when they make energy, housing, and industry far more expensive—actually alleviate the plight of the poor or the middle class.
Ultimately the green platform seeks not to increase living standards as we currently understand them (particularly in high income countries) but to purposely lower them. This can be seen in the calls for “de-development,” a phrase employed by President Obama’s science advisor John Holdren for all “overdeveloped” advanced countries, in part to discourage developing countries from following a similar path. This way of thinking is more mainstream among European activists who seek to promote what is called “de-growth,” which seeks to limit fossil fuels, suburban development, and replace the current capitalist system with a highly regulated economy that would make up for less wealth through redistribution.
We are not talking here about not socialism, as some right-wingers suggest. Marxism, for all its manifest flaws, justified itself by promising to improve living standards; it was passionate about technology, which is one reason Marx called it “scientific socialism.” Instead, Francis seems closer to Peronism, the dominant state ideology of his native Argentina. Even before his most recentpronunciamento, Francis widely disparaged capitalism, which he equated with the cronyism dominant throughout South America.
Peron himself may have battled the Church of his day, but Francis’s relations with the current Peronist regime have warmed considerably, particularly since his ascension. As the Guardian reports, when he was named pontiff, posters quickly appeared around Buenos Aires with the image of Francis over the words “Argentine and Peronist.” Peronism embraces the ideal of an economy where justice is mandated through the state’s redistribution of wealth.
This is not reassuring. Since the last century, Argentina has been one of the world’s greatest economic failures, a country that despite a talented and educated populace and huge natural resources, has tumbled from rich country status to a second or third world country. In essence, replacing the American dream with an Argentinian one sounds less than appealing.
Trying to sell anti-growth green ideology may prove a tougher in the developing world. Not surprising then that, no matter what the rhetoric that is adopted by the climate conference to be held in Paris this month, critical figures like India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi will not restrict building new coal plants—the country has tripled coal imports three fold since 2008. In the sweltering cities of the subcontinent, moves to ban air conditioning are simply not good politics. And Chinese President Xi Jinping, the leader of the world’s largest carbon emitter and user of coal, clearly has no real intention of reversing rapid development, based in large part fossil fuels, till 2030, when reasonably priced alternatives may well be generally available.
In contrast, many greens now seem to embrace ever continuing poverty for emerging countries. Prince Charles, for example, embraces the “intuitive grammar” of ultra-dense slums such as Mumbai’s Dharavi, which, he claims, have perfected more “durable ways of living” than those in the suburbanized west. Similarly, the influential environmental group Friends of the Earth applauds recycling in Dharavi as an “inspiration” for the urban future. California’s Stewart Brand openly endorses the notion “Save the Slums” because they will save the planet.
Given the reluctance of still poor countries to further impoverish themselves, the burden of the Catholic-green alliance will necessarily fall on the middle and working classes. As we can already see in California (the state with the most draconian environment laws), long-term economic growth has been tepid, despite the occasional tech and property bubbles. At the same time, the state suffers not only among the highest unemployment rates in the country, but the highest level of poverty, when cost of living is addressed, and has become home to one-third of the nation’s welfare recipients.
Overcoming the “Poverty of Ambition”
Architect Austin Williams suggests that sustainability, the new prayer word of spiritual greenism, “is an insidiously dangerous concept, masquerading as progress.” It poses an agenda that restricts industry, housing and incomes in a manner that severely undermines social aspiration. Indeed, Williams argues, greens and their allies—now including the world’s most important church—have created “a poverty of ambition.” Williams suggests the common green view is that humanity is “destructive and in need of reduction” rather than “a source of innovation, creativity, imagination and socialization.”
What matters little to the green movement are the economic ramification of their preferred policies, such as forcing a large percentage of the population into “fuel poverty.” Loss of jobs in trucking and manufacturing would hit blue-collar workers and neighborhoods hardest, according to most studies. How this jibes with meeting the high welfare and retirement costs with an urban population increasingly dominated by immigrants, their offspring, and other poor children, seems problematical at least.
The new feudal order that is being proposed, like the original, is based as much on powerful self-interest as fulsome good intentions. Tech oligarchs love a regime where they can invest in renewables with the guarantee of public subsidy. The Trustifarians promote subsidies and renewable use through their foundations and feel personally vindicated for their efforts. The media can celebrate the enlightening shift towards sustainable power. Academics receive grants and churn out studies in support. And the lawyers and the upper bureaucracy achieve ever greater job security to administer the entire program. The Church, by embracing the strongest intellectual current, gets a shot at renewed relevance, and even “hipness.”
This confluence of private interest, public power and the clerical class is suggestive of a new feudal epoch. Bankrolled by inherited money, including from the oil-rich Rockefellers as well as Silicon Valley, the green alliance has already shown remarkable marketing savvy and media power to promote its agenda. Now that their approach is officially also the ideology of the world’s largest and most important church, discussion of climate change has become both secular and religious dogma at the same time.
What we seem to have forgotten is the historic ability of our species—and particularly the urbanized portion of it—to adjust to change, and overcome obstacles while improving life for the residents. After all, the earliest cities of Mesopotamia and Egypt arose, in part, from a change in climate that turned marshes into solid land, which could then be used for intensive, irrigated agriculture.
Similarly, pollution and haze that covered most cities in the high income world—St. Louis, Pittsburgh, Dusseldorf, Osaka, Los Angeles—only a few decades ago has greatly improved, mostly through the introduction of new technology and, to some extent, deindustrialization. In recent decades, many waterways, dumping grounds for manufacturers since the onset of the industrial revolution and once considered hopelessly polluted, have come back to life.
This notion that people can indeed address the most serious environmental issues is critical. We should not take, as Francis does, every claim of the climate lobby, or follow their prescriptions without considerations of impacts on people or alternative ways to address these issues. As we have seen over the past few decades, many of the assertions of environmental lobbyists have turned out to be grossly exaggerated. Similarly, concerns over “sprawl” in the high-income world, for example, have focused on such things as the disappearance of forests, yet, with enlightened policies, both green spaces and forest lands have expanded. Similarly, “sprawl” has not impinged much on farmland or harmed food stocks; indeed both the European Union and the United States continue to produce vast surpluses of food. Rather than suffering from “peak oil,” we are awash in oil and gas.
At the same time, new technologies like low emission cars, solarizing homes, more efficient monitoring of energy use and some intelligent planning—for example, dispersing work or planting trees—make the draconian steps being proposed by many greens and their allies moot. There is simply no reason, as a recent McKinsey study has shown, for a shift to denser urban housing, a critical element in contemporary climate change thinking.
The key issue may be how Catholics embrace his views, and how willing they are to work with environmentalists whose views on family, fecundity, abortion, and gay marriage are polar opposites of church dogma. As one influential lay Catholic explained, many do not look to the Church for scientific and political direction but for spiritual and moral leadership. “The Church speaks with moral authority, at least to me,” this prominent Catholic suggested, “but it does not possess a special scientific authority—a fact well established by its history (see Galileo).”
Certainly the Church that built so many of the world’s great hospitals, universities, and charities could contribute greatly to grassroots environmental efforts that do not depress the prospects for the poor. In seeking to improve conditions for its flock, the Church needs to make sure that they also don’t get fleeced and driven further into poverty. Social justice may be an important value, but it is dubious that the Church’s credibility will be well served by a neo-feudal alliance dominated by those who abhor the Church’s other core values such as family, the sanctity of human life and some degree of social prudence.
The Church, as well as those of us outside of it, would do better to develop morehumane, and less hysterical, responses to climate-related issues, and in ways that do not stomp on human aspiration. We should avoid the march full-speed backward in time, to the glorious elitism, mass poverty, and class stagnation of the Medieval era. The world’s people, and Francis’s flock, deserve better than that.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and Roger Hobbs Distinguished Fellow in Urban Studies at Chapman University, and a member of the editorial board of the Orange County Register. He is also executive director of the Houston-based Center for Opportunity Urbanism. His newest book, The New Class Conflict is now available at Amazon and Telos Press. He is also author of The City: A Global History and The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050. He lives in Orange County, CA.
Pope Francis photo by presidencia.gov.ar [CC BY-SA 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
Across federal, state, and local levels, Australian urban planning authorities have emphasized the need for policies that seek to limit urban fringe development and create densely-populated urban centers. This process is called ‘urban consolidation’ and has been a goal of Australian authorities for more than three decades. More specifically, urban consolidation is defined by efforts to concentrate housing, jobs, and amenities around “activity centers” such as a traditional downtown, satellite urban centers, and elongated strategic corridors. These high-density areas are to be separated by green belts of undeveloped land and connected by public transport links such as trains and light rail systems.
Australian planners’ efforts to establish a high-density urban form have been effective, at least from their point of view. From 1981 to 2011, housing stock in Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane saw a large shift towards high-density units. A net total of 640,000 new multi-unit dwellings were built during this time, representing an increase of over 115%. This surge forced the proportion of multi-unit housing to increase to nearly one-third of the total housing supply in cities that have historically been dominated by single-family dwellings.1
As Australia moves toward higher-density cities, what will be the result? Urban planners assert that their policy decisions are thoroughly researched and provide the “best” outcomes, but evidence from Australia’s largest cities tends to refute that claim. Among the numerous issues that arise due to consolidation ideology, perhaps the most disturbing are the severe impacts on housing affordability, poverty, and housing quality.
Urban consolidation policies, by definition, are aimed at choking the supply of new single-family detached housing by limiting urban fringe growth as a means of minimizing the urban footprint. This is intended to drive more and more of the urban population into compact living situations. Thus, by limiting the supply of single-family detached housing and pushing more households into the market for multi-family housing, urban consolidation causes home prices to rise in both markets. As Figures 1 through 5 show, this is exactly what has happened in cities that adopt consolidation ideology. The Australian Bureau of Statistics reports that “the price of established houses in the capital cities rose by almost half (46%) between 2002-03 and 2008-09, with prices increasing at an average of 6.5% per year.”2 From 2001 to 2011, the number of dwellings in Sydney costing less than AUD $275 in rent per week decreased by 52% while the number of dwellings costing more than $275 in weekly rent surged by 269%; in Melbourne, the number of dwellings that cost at least $650 per week in rent more than tripled. Homeowners in Sydney and Melbourne have also seen tremendous increases in mortgage payments. In the same ten-year period, there was a seven-fold increase in the number of households in Sydney and Melbourne paying more than $4,000 per month in mortgage payments, while the number of households paying less than $1,000 per month was cut in half.3 At a time when wages and income have been stagnant, this means a severe decrease in housing affordability, meaning fewer Australians are able to afford the highly sought-after stability of homeownership.
Given the profile of buyers and sellers, the market for dense multi-family housing is predominantly driven by investors, landlords, and institutional property owners.4 Thus the large majority of occupants are renters, not owner-occupiers, and there is no reason to infer that this ownership pattern will change. As Australian cities continue to densify, ownership demand – that is, the market for the purchase and sale of housing units – will be driven less by owner-occupiers and more by investors and landlords, who have historically been the dominant players in multi-unit dwelling markets. This latter group of owners responds to market conditions in a different way than the owner-occupier group, and the shift is likely to have a profound impact on economic and socio-political outcomes in the long-term.
In housing markets, there are two groups of consumers: investors, who intend to lease the units after buying, and owner-occupiers, who intend to live in the residences themselves. Owner-occupiers purchase homes for personal consumption; their decision about which home to buy is driven by the quality of the housing, access to transportation and employment, amenities in the surrounding area, and the sense of financial stability provided by owning one’s own home. Investors, on the other hand, are quite different. By definition, investors are driven by profit. They are seeking rental income from tenants as well as appreciation in the value of both the property and the underlying land. They evaluate properties based on the potential cash flows from renting and the price they can receive when they sell the property sometime in the future.
But investors’ motives may become distorted in Australia due to a policy known as ‘negative gearing.’ Negative gearing, in terms of real estate investment, allows any negative cash flow from a single property to be deducted from the investor’s total taxable income.5 This gives investors an incentive to purchase properties where the mortgage payments exceed rental income, especially if value of the property is appreciating. This pushes up the after-tax returns to investors which inflates housing prices even further. It also provides investors with greater incentive to make speculative purchases, which increases home price volatility and instability.
What happens when you throw urban consolidation policies into the mix? As urban planners continue to choke the supply of new land, the price of existing land continues to accelerate upward. When investor profits are increasingly driven by speculating on the land value rather than income from the tenants, investors are more inclined to purchase lower-value properties which require less maintenance and fewer capital expenditures yet enjoy the same increases in underlying land value. By this logic, we could expect that low-income housing would increase in value at a faster pace than higher-quality housing as investors bid up the prices, which is exactly what happened in Sydney’s last real estate boom.6 Low-value properties are also more likely to provide investors with the support of negative gearing since they typically provide the lowest rental revenues. But investors, looking primarily at tax advantages, are less likely to improve the properties or even maintain existing structures. Thus, we can see how more and more investors not only have the incentive to compete for low-value housing units, where there is already insufficient supply, but also neglect those units in the long-term. Such market pressures are already noticeable in Sydney and Melbourne, where urban consolidation has been occurring for a longer time, and will certainly arise in Brisbane, in the state of Queensland, as planners establish growth boundaries for its booming population.7
But it doesn’t stop there. This problem is exacerbated by the nature of Strata title plans, which have come to dominate the market for higher density housing in Australia. Essentially, strata titling comes from legislation passed in the 1960s whereby each apartment unit or flat on a parcel of land can be owned individually, and thus a mortgage could be taken out in order to purchase individual high-density housing units. This is similar to a condominium ownership structure in the United States, but with a few key shortcomings. Although strata titling allows a few individuals living in high-density areas to enjoy homeownership, it primarily benefits investors who now only have to purchase single units instead of entire multi-family buildings. Even worse, strata titling’s lack of consideration for common areas poses a serious issue in the long run for the maintenance of high-rise buildings and their surrounding neighborhoods, especially in areas of lower income. According to Bill Randolph, Director of the City Futures Research Center at the University of New South Wales, “the strata system may come badly unstuck in lower value areas where investor landlords have little incentive to reinvest in their property and home owners do not have the wherewithal to afford major repair costs.”8
Putting it all together, what can we expect to be the future for Australia? Urban consolidation policies continue to push more Australians out of suburban homes and into cramped apartments, where housing markets are dominated by investor-landlords instead of owner-occupiers. The consolidation policies will squeeze the supply of land and force dwelling prices to rise regardless of rental revenue, promoting speculative behavior among investors. Negative gearing and strata titling programs incentivize these investors to neglect their properties, causing high-density areas (especially low-income neighborhoods) to deteriorate. The end result is slum-like conditions, social tension, and perpetual poverty for the neighborhood’s inhabitants. Even in higher-value neighborhoods, a lack of necessary upkeep will erode housing quality, even as prices continue to inflate. This is the reality of urban consolidation; it takes ownership out of the hands of Australians and puts it in the hands of speculative and neglectful investor-landlords. It is nothing short of a recipe for urban decay.
Clinton Stiles-Schmidt graduated magna cum laude from Chapman University where he earned a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration (emphasis in Real Estate and Finance) and a Bachelor of Arts in Economics. His experience includes several internships in real estate investment and development as well as studying abroad in both Spain and Australia. Clinton recently joined Cushman & Wakefield as an Analyst in their Corporate Finance & Investment Banking Group.
Figure 1: Ratio of Housing Debt to Disposable Income in Australia9
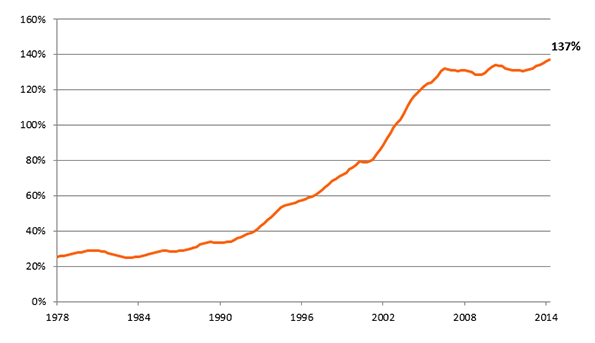
Figure 2: Weekly Rent Payments in Sydney10
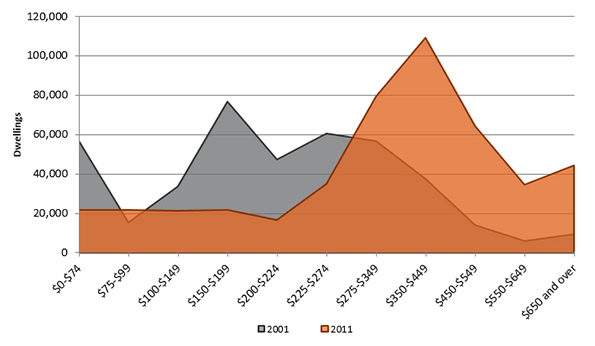
Figure 3: Monthly Mortgage Payments in Sydney11
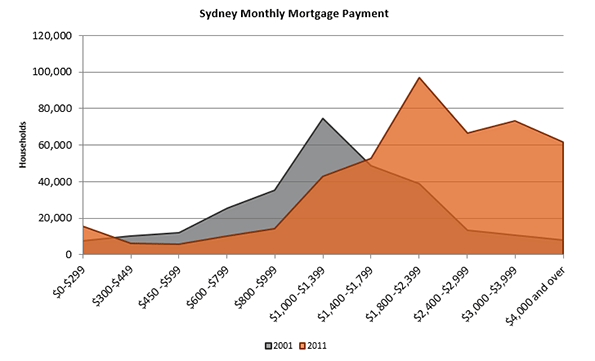
Figure 4: Weekly Rent Payments in Melbourne12
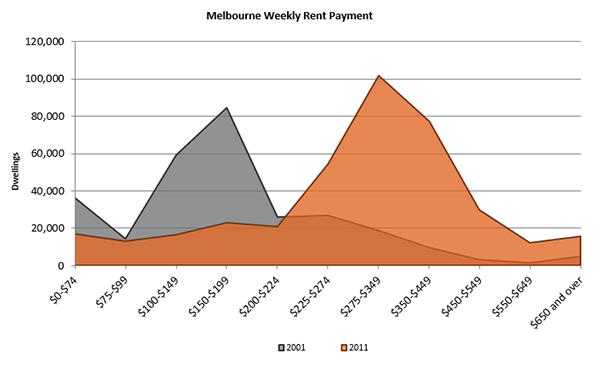
Figure 5: Monthly Mortgage Payments in Melbourne13
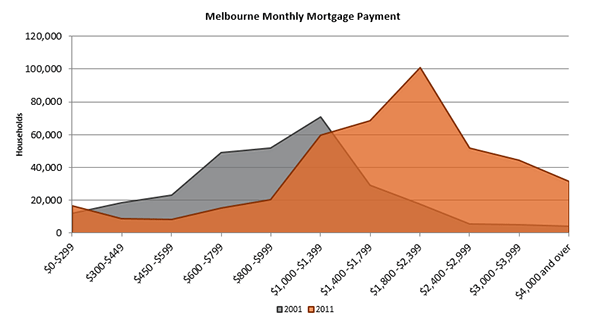
4 Randolph, Bill. "Delivering the Compact City in Australia: Current Trends and Future Implications." City Future Research Centre, University of New South Wales, 1 June 2006.
Sydney suburb photo by BigStockPhoto.com.