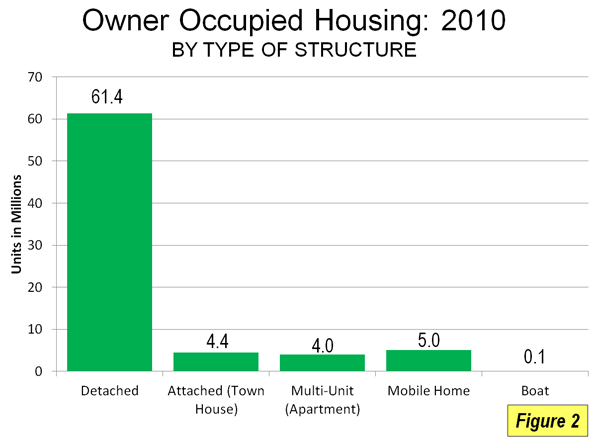
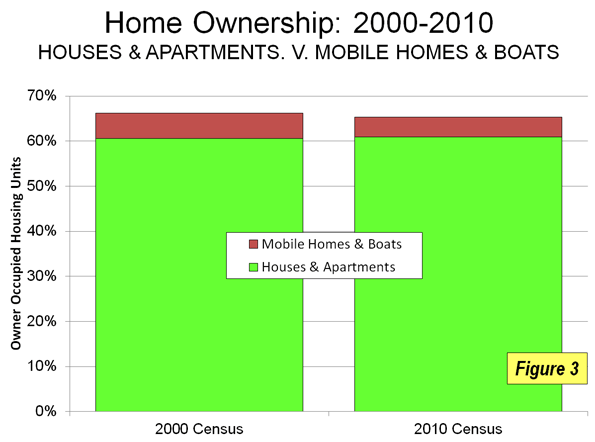
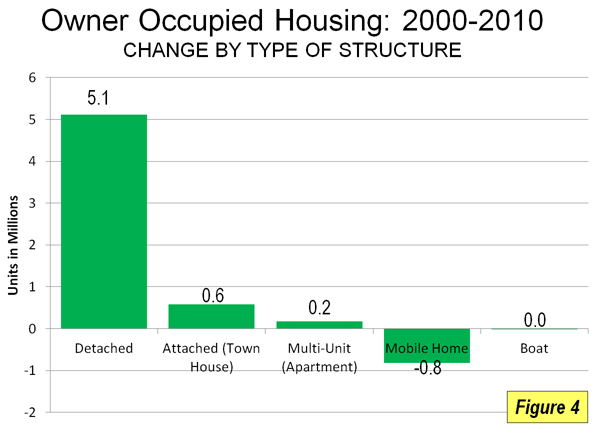
All science fiction agrees. History is leading to the unification of earth. The united world may be governed by benign world federalism or by a dystopian global tyranny. But the modern literature of prophecy is clear: the age of competing nation-states is coming to an end. There are no visions of the future in popular culture in which advanced technology is combined with the continued sovereignty and competition of nation-states like China, India, and the United States or blocs like the European Union. The only near-equivalent is George Orwell’s nightmare vision, in 1984, of endless rivalry among the three totalitarian blocs of Oceania, Eurasia, and Eastasia.
Most educated people today are similarly in accord, associating historical progress with the increasing scale of our moral and political loyalties. Individuals are liberated from the communities into which they happened to be born. The tribe gives way to the nation and the nation gives way to humanity. History will soon culminate in a secular millennium in which emancipated individuals will be citizens of a postnational, global community.
Since the late 19th century, hopeful visions of the future have almost always been identified with the transcendence of nation-states. In the early 1900s, many in the West looked forward to the fulfillment of Alfred Tennyson’s vision in "Locksley Hall" (1842) of "the Parliament of man, the Federation of the world." Wendell Willkie predicted in 1943 that World War II would be followed by a new age of unity given its title by his book: One World. The fall of the Berlin Wall triggered yet another wave of claims that a postnational epoch was dawning. These forecasts took crude forms, like Thomas L. Friedman’s inaccurate depiction of a global market compelling the convergence of national policies, or sophisticated ones, like the British diplomat Robert Cooper’s claim that premodern and modern societies would give way gradually to postmodern societies.1
Although philosophical cosmopolitanism today is generally associated with secular elites, its roots are religious. The idea that all human beings belong to a single moral community was part of ancient Stoicism. But the Stoics did not believe in progress. Instead, they envisioned a cyclic universe, like that of Hinduism, in which the world was periodically incinerated and re-created. The combination of progress and cosmopolitanism comes from the apocalyptic tradition in Zoroastrianism, which influenced apocalyptic Second Temple Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. According to this school of thought, at some point probably in the near future, history would be brought to an end by God whose direct rule would replace the division of humanity among languages and nationalities that the Biblical tradition explained with the myth of Babel.
The combination of moral cosmopolitanism with unidirectional progress constitutes Christianity’s greatest legacy to the secular intelligentsia. The idea that a moral person must not be a selfish localist or nationalist, but must take a personal interest in the well-being of poor, suffering, far-away people was a Christian notion long before it informed the view of secular intellectuals of themselves as world citizens who have transcended petty local loyalties and interests. In its secularized version, Providence takes the form of social forces like the economy and culture, but the result is the same: the formation of a single planetary community free from ethnocentrism, wars, and trade conflicts. This kind of secular providentialism informs the philosophies of numerous thinkers including Immanuel Kant, G.W.F. Hegel, Karl Marx, and more recently Martha Nussbaum, Ulrich Beck, Peter Singer, and Kwame Anthony Appiah.
The underlying providential structure of cosmopolitanism explains the combination of certitude and moral fervor found among liberal and socialist one-worlders. In Christianity, to deny God’s providential plan for the world is a sin, as it is to obstruct the unfolding of that plan. The same is the case in secular providentialism. Globalist liberals and socialists predict that a single cosmopolitan society will inevitably be brought about by irresistible social forces and then condemn anyone — nationalist or capitalist — who resists those forces. Postnational liberals tell us that the nation-state is withering away and then condemn those who defend national sovereignty for delaying the allegedly inevitable postnational future. The sun will rise tomorrow precisely at 7:00 a.m., therefore we must help it rise and fight those who would prevent its rising.
1.
Contemporary cosmopolitanism, in defiance of Hume, combines an "ought" with an "is." The "ought" is the view that the nation-state is a parochial form of organization and should be replaced by broader, more inclusive loyalties. The "is" takes the form of the claim that the nation-state is destined to wither away because of irresistible technological or economic forces, whether we like it or not.
But the trends proffered as evidence of a historic shift toward postnational cosmopolitanism are in fact consistent with the persistence of the nation-state as the main actor in world politics. Changes in the global economy, most significantly, are not signs of cosmopolitanism. The popular conception of globalization is overly simple and misleading. As Alan M. Rugman has pointed out, instead of a single global market there is today a somewhat Balkanized world economy organized around the "triad" of Europe, North America, and East Asia.2
The emerging world economy is highly regionalized and remains connected to the nation-state. While some industries, like computer electronics manufacturing, are truly global, others, like the automobile industry, are dominated by corporations with most of their production and sales based in one of the three major blocs. New blocs might join the existing triad — India-centered South Asia, for example — but it is naïve to think that all barriers to the free flow of capital, goods, and labor among countries and regions will disappear.
Even multinational corporations turn out to be not quite so multinational. The 100 largest multinationals in 2008 held 57 percent of their total assets and 58 percent of their total employment abroad, with foreign sales making up 61 percent of their total.3 But this merely means that most multinationals are half-global, at best. The typical multinational still has a distinct national identity, with around half of its assets, employment, and sales within its home market. In fact, very few multinational corporations conduct an overwhelming majority of their business outside of their home countries.
The domination of global commerce by corporations based in the United States, Japan, and Germany — the three most populous industrial democracies — shows the importance of a large domestic market as a base for multinational sales and operations. Despite the celebration of global corporations by libertarians and their denunciation by leftists and populists, global companies possess national identities after all. Even financial globalization proved more superficial than advertised: major global banks turned to their national governments for bailouts following the 2008 financial crisis.
The temporary influence of the Washington Consensus notwithstanding, the epoch of economic nationalism never ended. Outside of the Anglophone countries, this is the age of mercantilism. Instead of tariffs, post-1945 mercantilist nations have used subsidies (Europe and the United States); non-tariff barriers (Japan); and currency "tariffs," subsidies, and state-directed credit (China) to protect domestic markets and support export-oriented sectors of their economies. Mercantilism cannot work without a "patsy," and the United States agreed during the Cold War and post-Cold War period to play the role of consumer of first resort for mercantilist nations. This decision was based, partly on libertarian ideology, but mainly on national strategy, to encourage first Japan and West Germany and then China to become one-dimensional civilian manufacturing powers instead of rival military powers. In the long run, it is more likely that the United States — the world’s most protectionist nation before 1945 — will move back toward mercantilism than it is that China, Japan, and Germany will adopt the economics of the late Milton Friedman.
Current trends in immigration do not support the cosmopolitan claim that national borders are breaking down. Neither the fact that a country like the United States chooses to admit large numbers of legal immigrants nor the fact that it chooses to tolerate large numbers of illegalimmigrants demonstrates that it is powerless to do otherwise. With respect to transnational flows of labor, all advanced industrial countries, including the United States, have undertaken actions — ranging from issuing national identity cards to building border fences — to secure their borders and airports against illegal immigrants. The assertion of effective state control over immigration is driven, in part, by fear of international terrorism, but also by a backlash against poor immigrants among native-born citizens of developed countries — a backlash that is likely to deepen if the Great Recession is prolonged over many years.
At the same time that advanced countries are seeking to reduce unwanted immigration, many are competing for skilled immigrants. Britain, Australia, and Canada, for example, have adopted a "points system" in which educated immigrants are favored over the uneducated. When these trends are put together, the result is the opposite of the borderless world with free flows of labor predicted by prophets of globalization a decade ago. Most countries in the 21st century are likely to combine a tough attitude toward illegal immigration with selective legal immigration favoring skilled workers.
What about the political trends of the 21st century? The historical pattern is clear. The breakup of the Habsburg and Ottoman empires after World War I produced many new nation-states and some new multinational states, like Yugoslavia. Following World War II, the decolonization of the European empires in Asia and Africa produced dozens of new states, some of them multinational (like Nigeria and Pakistan, which may themselves break apart like Yugoslavia). With the dissolution of the Soviet Union and Yugoslavia, new states were again added to the United Nations General Assembly. It is a safe bet that the maps of the world in 2050 and 2100 will show still more independent countries than exist today.
The conventional wisdom of today’s cosmopolitans holds that ethnocultural nationalism is a barbaric relic of an earlier stage of civilization and that as enlightenment and prosperity spread, people become more cosmopolitan. But far from being moribund, nationalism — defined not as aggression or xenophobia, but as a preference for the nation-state as the unit of legitimate government — remains the most powerful force in global politics for the third century in a row.
Thus nationalism is not atavistic; indeed, it is modern — just as modern as industrialism and urbanism. The trend of reorganizing a world of premodern dynastic empires and city-states into a world of nation-states, in which most (though not all) states are identified with a majority ethnocultural group, has paralleled the conversion, in the economic realm, of an agrarian world into an industrial world.
As societies become urban and industrial, village societies give way to anonymous urban societies in which individuals identify with larger "imagined communities." These need not be national — Islamists, for example, identify with the imagined community of the Muslim ummah. But the community that has proven most effective in attracting the loyalty of individuals in modern, large-scale societies is the nation, which can be defined minimally in terms of shared language and customs, as in most liberal democracies, or maximally, in terms of shared "race" and/or religion, as in illiberal nationalism.
It follows that as people become more educated and more prosperous they are more likely to prefer to be members of the majority in a nation-state rather than minorities in someone else’s nation-state or one of several squabbling nationalities in a multinational state. As the world grows richer, movements by stateless nations, from the Scots to the Kurds, to obtain nation-states of their own, whether by peaceful or violent means, are likely to increase, not decrease.
Arguably, we are still in the early stages of the technological era in economics and the era of the nation-state in politics. In the most likely scenario, the 21st century will witness the completion of two trends that have been underway since the 18th — the conversion of all humanity from an agrarian lifestyle to an urban-industrial one, and the replacement of premodern forms of political organization almost everywhere by nation-states.
2.
In recognizing the continuing, and likely expanding, hegemony of the nation-state as the primary unit of global political, economic, and social organization, we need not deny the simultaneous expansion of cosmopolitan sympathies. Liberalization of government controls on trade and finance, greater cross-border immigration and global travel, and the constitution of something approaching a global public through mass media communication of serial cosmopolitan "moments" all contribute to the spread of cosmopolitan sentiments. But those sympathies are likely to continue to exist alongside national identities and allegiances.
To be sure, global initiatives such as the Millennium Development Goals and other antipoverty programs, as well as post-Cold War military interventions in the former Yugoslavia, Iraq, Afghanistan, and Libya have been justified, to some extent, on cosmopolitan grounds. The US intervention in Libya, to take one recent example, appears to have involved a protracted debate within the Obama Administration between advocates of the cosmopolitan notion of "Responsibility to Protect" (R2P) and pragmatists opposed to the application of US military power in conflicts where there is no clear national interest. In this debate, the cosmopolitans appear to have prevailed.
But we should be careful not to read too much into these examples. In virtually every case, the nation-state remains the institution through which economic and military resources are deployed in service of cosmopolitan objectives. In many cases, it is often difficult to disentangle where national interest ends and cosmopolitan interest begins. The wars in the Balkans and the Middle East can just as easily be explained in terms of the national interests of the United States and its allies in defeating sponsors of terrorist attacks (Afghanistan), securing US regional military hegemony (Iraq and Libya), and averting destabilizing flows of refugees to Europe (a motivation behind European participation in the Balkan and Libyan wars), as through cosmopolitan ones. As such, even where cosmopolitan sentiments succeed in galvanizing national or international action in response to global and regional challenges, those responses are likely to only further establish the nation-state as the focal point for making those decisions and the primary institution through which such interventions are likely to be carried out.
The resulting organization of global affairs is better explained by liberal internationalism than by cosmopolitanism. In this view, nation-states, rather than individuals, corporations, or non-governmental organizations (NGOs), will continue to be the main actors in world politics (though certainly not the only ones) for generations to come. Liberal internationalists maintain that all human beings have inalienable rights, which should be secured by governments resting on their consent. While those rights-securing governments may take various forms, the nation-state is the largest unit that has been able to combine effective government with a sense of solidarity among its citizens. The nation to which the state corresponds can be defined broadly, in terms of a shared culture and language, and it can be generous to minority nationalities that may share its territories. But there is a point at which linguistic and cultural diversity undermine the minimum of community needed to maintain a sense of shared citizenship. A global government would be a Tower of Babel which few would be willing to obey, to provide with taxes, or to support with military service.
Liberal internationalism answers the question of how the world can be organized, if each people, however defined, has a right to its own sovereign, accountable nation-state. The alternative to both Hobbesian anarchy and global cosmopolitanism is cooperation by nation-states. This cooperation can take the form of international law, international arbitration, and international agencies, as well as military alliances and concerts of power. But international is not supranational. Countries may delegate powers to international agencies for some purposes, but as long as the delegations are revocable, they are not surrendering sovereignty.
3.
The most important distinctions in 21st century world politics will be based on scale. By the middle of this century, the greatest powers may eventually be those, such as China, India, and the United States, which combine (or will combine) at least moderately developed industrial economies with populations of half a billion people or more.
The US investment bank Goldman Sachs predicts that by 2050 China will have the largest economy in the world, followed by the United States and India. The next tier might be occupied by Russia, Brazil, and Japan, and a third tier would include Germany, Britain, and other once-mighty European economic powers.4 Just as the Italian city-states of the Renaissance were dwarfed and marginalized by the national monarchies north of the Alps in the 16th and 17th centuries, so the large nation-states of the past — Britain, France, Germany, Russia, and Japan — will be overshadowed by the titans of the 21st and 22nd centuries.
The United States will owe its position in the club of titans to its immigration-fed population growth, which could produce an American population of 400-600 million by 2050. The 2010 medium fertility estimations of the United Nations suggested that in 2050 the most populous nations would be India (1.7 billion) and China (1.3 billion), followed by the United States (400 million), Nigeria (400 million), and Indonesia (300 million).5 It is Europe, not the United States, which faces a significant decline in relative population, wealth, and power. Europe, which accounted for 22 percent of the world’s population in 1945 and 12 percent in 2000, may have only 6 percent in 2050. Because GDP is based on working-age population and productivity, even though Europeans will grow richer, the European share of the global economy may decline from 22 percent today — roughly comparable to that of the United States — to only 12 percent in 2050.6
In modern industrial societies, technology and politics combine in what Edward Luttwak has called "geoeconomics." Technological economies of scale reward big enterprises in large, unified markets. As champions of the global market ceaselessly point out, technological and commercial economies of scale are best realized at the global level. But psychological and political economies of scale are best realized by nation-states.
In theory, both economic and political economies of scale could be realized by multinational blocs, but in practice this outcome is unlikely. As early as the 1840s, British and French observers speculated that the future would be dominated by two giant states, the United States and Russia. The imperialism of the industrial era, from the 1870s to World War II, was (among other things) an attempt by medium-sized nation-states like Britain, France, Germany, Italy, and Japan to create economic areas comparable in scale to those that existed inside the borders of the United States and Tsarist Russia (later the Soviet Union).
After World War II, largely at the insistence of the United States, the international system outlawed old-fashioned empire building. But even if 20th century history had taken a different course, it is doubtful that multinational empires, held together by repression and, in the case of maritime empires like the British and Japanese, separated by oceans, could have competed in the long run with giant nation-states.
The former Western European imperial powers have sought to achieve the same result by partially pooling their sovereignty in the European Union. But European countries retain their sovereignty in foreign policy, rendering a unified voice impossible in conflicts including the Balkan wars, the Iraq War, and the Libyan War. Meanwhile, the Greek financial crisis has proven that the European Union lacks the overarching central economic institutions, like a central bank with emergency lending capabilities, necessary to function as an efficient monetary and commercial union. Because of popular resistance to further political integration, the European Union is no more likely to be the successful equivalent of a giant nation-state than the former European empires proved to be.
Psychological economies of scale favor nation-states with a strong sense of solidarity among their citizens that makes them willing to fight in wars, pay taxes, and tolerate redistribution for the common good. China, with its overwhelming Han majority, has a far greater sense of national identity and solidarity than much smaller multinational states like Canada and Belgium, which are in danger of breaking up along ethno-national lines as Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia have done.
It follows, then, that in the future, as in the past, the economic gains from scale will be reaped chiefly by entities with immense, free, internal markets congruent with political boundaries. Concerns about national security and domestic distribution will always constrain market integration among nation-states. In a post-imperial, post-dynastic world, the most successful great powers will be very big nation-states.
4.
Contrary to the claims of the prophets of cosmopolitanism, the world is likely to remain divided among great sovereign powers for ages to come. Sometimes they will compete, at other times they will collaborate, but they are unlikely to sacrifice their sovereignty by merging into a single global government; if one were established, by force or intimidation, it would probably break apart quickly.
The ideas of postmodernity and second modernity appeal primarily to thinkers in European nations where it is necessary to transcend and pool sovereignty in order to compete with huge nation-states like the United States and China. Large nation-states, in contrast, are powerful on the basis of their internal populations, resources, and economies, so it is unsurprising that they see no benefit in surrendering their sovereign powers to supranational organizations dominated by smaller countries. In a world of sovereign nation-states, the biggest nation-states are more sovereign than the others. Unilateralism is natural for the great powers. Whales do not consult the barnacles on their sides or the schools of small fish who swim in their wake.
The rise of the giants is likely to lead to less, not more, emphasis on international organizations like the United Nations and the World Trade Organization. If the United States, China, and India account for much of the world economy in fifty to a hundred years, then they may prefer setting the rules of world trade and investment by bilateral or trilateral negotiations. Why should giants consult with dozens or hundreds of pygmies before acting? International law has traditionally been championed by small- or moderate-sized, neutral countries (including the United States in the 19th century). Its influence may decline in an age in which a few titanic continental states have hundreds of millions or billions of inhabitants.
Unfortunately, cosmopolitanism is not simply a quaint, harmless religious faith held by global elites. Confusing the cosmopolitan "ought" with the cosmopolitan "is" results in all sorts of disastrously wrongheaded policies. If, for example, the world really is on the verge of full economic and political integration, then outsourcing all US manufacturing capacity to China might make sense in the same way that it might be reasonable for a state like California to outsource all of its manufacturing capacity to other US states. They share the same tax, regulatory, and social welfare systems; they make shared national investments in infrastructure and education; and they share the same military and national security interests. But in a world in which nation-states are likely to continue to retain their sovereignty and in which economic nationalism continues to reign, trade and investment policies that presuppose a borderless world make no sense at all.
The cosmopolitan error has similarly distorted international efforts to address global challenges. International climate policy has persistently foundered upon the basic realities of an international political economy that continues to be defined by the interests of national economies. International development and antipoverty efforts in recent decades have similarly failed to align themselves with the basic economic interests of donor economies. As such, the cosmopolitan error has had real consequences for both national efforts to build healthy, equitable economies and international efforts to address serious global problems and risks.
The frequently-made argument that extensive supranational cooperation is necessary to solve global problems is incorrect. Without question, destructive, zero-sum national rivalries are a threat to a peaceful and prosperous world — on this point, liberal internationalists and liberal cosmopolitans can agree.
Fortunately, most of the world-order goals of cosmopolitanism can be achieved by enlightened liberal internationalism without the need to sacrifice or weaken the democratic nation-state, the organization in which most of the progress toward equality and economic security over the last three centuries has taken place. Contrary to the commonly held views of pundits and science-fiction writers, a world government or a true global market is unlikely to emerge in the foreseeable future. But a successful and enlightened liberal internationalism would permit us to enjoy the benefits of both without the costs of either.
This piece was first published by the Breakthrough Journal.
Michael Lind is Policy Director of the Economic Growth Program at the New America Foundation and author of The Next American Nation.
Photo by BigStockPhoto.com.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1. Friedman, Thomas. 2005. The World is Flat: A Brief History of the Twenty-first Century. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux; Cooper, Robert. 2000. The Postmodern State and the World Order. London: Demos. (back)
2. Rugman, Alan. 2001. The Myth of Globalization: Why Global Strategy is a Myth and How to Profit from the Realities of Regional Markets. AMACOM. (back)
3. Nolan, Peter and Jin Zhang. 2010. "Global Capitalism After the Financial Crisis." New Left Review 64. July/Aug (102). (back)
4. Wilson, Dominic and Roopa Purushothaman. 2003. "Dreaming with BRICS: The Path to 2050." Global Economics Paper Number 99. Goldman Sachs. October 1.(back)
5. United Nations. 2010. Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat. World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision. (back)
6. Institut Francais des Relations Internationales (IFRI) 2002. "Le Commerce Mondiale au XXIe siecle [World Trade in the 21st Century] Scenarios for the European Union."; Walker, Martin. 2003. "French Study Says Europe Fading," UPI, May 14. (back)