People are expecting British house building to pick up. Sadly they will be disappointed, even as the housing market inflates into another bubble.
There have been declines and recoveries in British house building before the 2007 collapse in construction activity. Data is in abundance. The total number of homes built annually has more than halved since the late 1960s, as successive governments withdrew from publicly funding the post-war welfare programme of council house building. There have been ups and downs in the volume of private housing built. After building 175,000 private homes in 2007 many expected that the market for new private housing would eventually recover from the financial crisis. The pent up demographic demand for new private housing would surely lead to a recovery of building if financing were made available. It seems irrational to suggest that the supply of housing will not recover to meet demand.
In July 2008 audacity argued that British house builders would be collectively reduced in the planning regulated market to building 100,000 homes in 2009. They would shift from aspiring to build in “volume” to making their money from planning approved “eco-homes” for a luxury market. This has already occurred and there will be no necessary recovery of volume in a few years. Production may even decline from that level of inactivity.
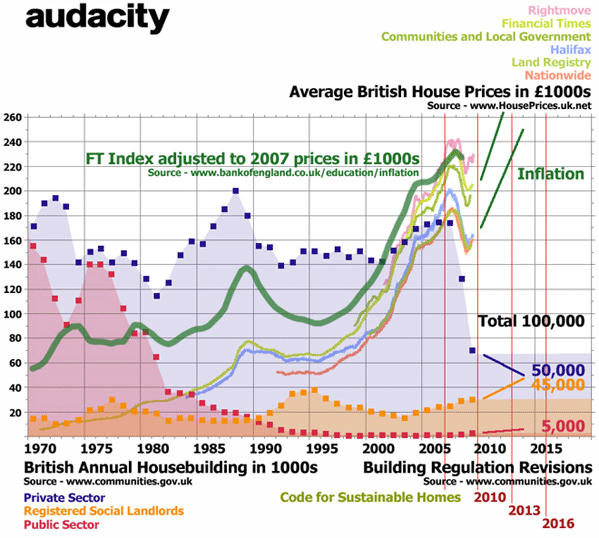
There seems little demand for new housing from the Public. Instead, we seem to be most concerned that housing continues to inflate in value as an asset. Most see obvious advantages in housing asset inflation, while complaining of the unaffordability of better housing. Britain is experiencing house price inflation again, but home owners know that the worsening gap between household income and the cost of buying a home, even on very low rates of interest, is frustrating new buyers, and the young in particular.
Gordon Brown knows that playing the housing market is a mainstream activity for the electoral majority. New Labour is doing what is necessary to revive housing asset inflation. Some had hoped that the bursting of the bubble in 2007 would reconnect house prices with household income. Young people were understandably most hopeful of that prospect. Now prices are drifting upwards again to unaffordable highs. This is happening nationally, but is particularly true in greater London, where average house prices have recovered to nearly £270,000, which is where they were before the collapse of Lehman Brothers in September 2008. This makes an average house “affordable” to those earning more than £90,000 a year. That is a very small percentage of the region’s home buying public.
Here’s what the restoration of higher prices means nationally, and in London in particular. There will be greater social immobility, expressed in more commuting, an extension of families, and several households living in the same home. Overcrowding will be more likely. Homelessness may slightly increase, but most housing difficulty will be accommodated within the existing stock.
The mainstream majority of the electorate – those already owning homes – is likely to be grateful that the burst bubble did not turn into a crash. New Labour will try to take the credit for averting any further financial disaster. What will be ignored is that house price inflation suits Britain’s politicians, and the lending institutions in The City. The British economy is too weak to pay higher wages, and the mainstream majority are too politically weak to challenge that predicament. What other future is there for Britain except another asset inflation bubble?
The problem then with restoring the Brown bubble is it solves none of our fundamental problems: notably a weak economy, low wages and lack of decent housing. David Cameron’s Conservative opposition will not make any difference to that predicament. They want to get rid of regional tiers of planners and to return control to local authorities, as was the intention of the 1947 Town and Country Planning Act. That is the legislation that stops the British public from building housing on cheap farmland.
But it’s doubtful they will try to break the back of housing inflation and our country’s dependence on it. The British economy depends greatly on The City, which needs to expand the £1.2 trillion of mortgage lending in a secure way for lenders in the global financial system. This only happens when existing house prices are maintained well above the cost of constructing new ones, and best in a period of asset inflation. The trickle of new homes onto the market could reduce, and while any demographic demands of a growing population for the utility of housing would not be met, the political and economic demand for asset inflation and loan security will be satisfied.
The way in which existing homes are made more expensive than the cost of building new ones is to inflate the price of land and keep it inflated. It is the high price of land approved for development within the 1947 legislation that is unaffordable. That is why government and house builders recognise there is “planning gain” to be negotiated over, as the uplift in land value that follows an approval to develop.
Yet this stands in the way of a clear public interest. Government housing experts argue we need at least 240,000 new homes a year to meet demographic demand. Our inability, or even unwillingness, to tackle this issue would have shocked either the Conservatives or the Socialists of the last Century.
What matters is to make materialist sense of the future. Society can’t live off asset inflation and debt. We must build new housing.
We face a serious predicament today. Small quantities of highly subsidised and high density “eco-homes” are to be built by socially motivated architects, some working with the former “volume” house builders. How can building an insufficient number of homes be called “sustainable”? Instead of building new replacement homes Britain is also looking to finance a greener and endlessly refurbished housing stock, while producing too few “eco-homes” even to accommodate yearly household growth.
The finance obsessed Green Capitalists of today are worse than their counterparts from a century ago. At least the Capitalists of the past were materialists, who believed in building more, and developing a construction industry based on materials manufacture and the skills of the workers they exploited. Those Capitalists were progressive materialists.
The new capitalists in housing are not even interested in meeting the needs of the working and middle classes, but in pleasing environmentalists. Unsurprisingly, they also will not have to hire too many workers to build their meagre product. Today Capitalists are abandoning industrial production in favour of finance, and this is nowhere more evident than in housing. Hiding behind the moral claims of environmentalism the Capitalists of twenty-first century Britain have clearly abandoned any idea of social progress, when once they could claim to be materialists. What is noticeable is that they have so many moralistic Greens cheering them on.
Sadly, there is no political association today to oppose Green Capitalists operating a nationalised planning system, in their effort to realise asset inflation in the form of a housing market. New Labour under Gordon Brown will not change this – indeed he clearly favours housing inflation and the City over the needs of aspiring families. So do the Conservatives under David Cameron. At the same time, they can play to a green constituency, which now dominates the media.
Given the current planning regime and the moral imperative for building “eco-homes”, British house builders will be reduced to building around 100,000 homes for a very long time. They will aspire not to build in “volume” but instead take pride that their homes are “sustainable”.
Only a political challenge will improve the situation. Gordon Brown faces no political challenge from David Cameron. He never will. Under New Labour or the Conservatives the only future for house builders will be to offer highly differentiated luxury “eco-homes” for the equity rich, or the top quintile of earners, supported with high subsidies in some form to build affordable “eco-homes”. Architects will particularly benefit from this shift in the market.
New Labour will build a few council homes more as a publicity stunt to keep their middle class Old Labour supporters amused. Conservatives will not bother about such nonsense. They will both insist on “zero carbon” new housing by 2016. Both will focus on refurbishment of the existing stock, not replacement. Both will exclude more land from the planning system.
The only people who will challenge this predicament, this retreat of Capitalism from population growth and industrial productivity, will be the working mainstream middle. Brown thinks he has bought off the majority of home owners with asset inflation, and temporarily he might have relieved many. Cameron thinks he can further mobilise established local residents attempting to extract more “gain” from the planning system. He imagines local opposition to development aggregating to a general protection of house price inflation nationally.
These Red/Green and Blue/Green political leaders might be proved wrong. The construction industry matters, and with argumentative organisation materialists might push for house building against the greens of Britain. Most of all there is the new generation of British people – those entering their 20s and 30s – who will demand something other than over-priced, undersized and often miserably maintained housing for themselves and their families.
A longer version of this article originally appeared at www.audacity.org/IA-07-11-09.htm
Ian Abley, Project Manager for audacity, an experienced site Architect, and a Research Engineer at the Centre for Innovative and Collaborative Engineering, Loughborough University. He is co-author of Why is construction so backward? (2004) and co-editor of Manmade Modular Megastructures
. (2006) He is planning 250 new British towns.