I was a guest on the show “Where We Live” on WNPR radio in Connecticut this week. The theme was “Suburban Corporate Wasteland” – the increasing numbers of white elephant office campuses in suburbs. Apparently Connecticut has several of these and some buildings are actually being demolished because there’s no demand for them.
The entire program is worth a listen, particularly if you are someone trying to figure out how to redevelop one of these things. Several local officials join to talk about efforts to do that in their towns. If you want to just hear Yours Truly, I’m on for about 10 minutes starting at 38:30. Follow this link to listen to the show.
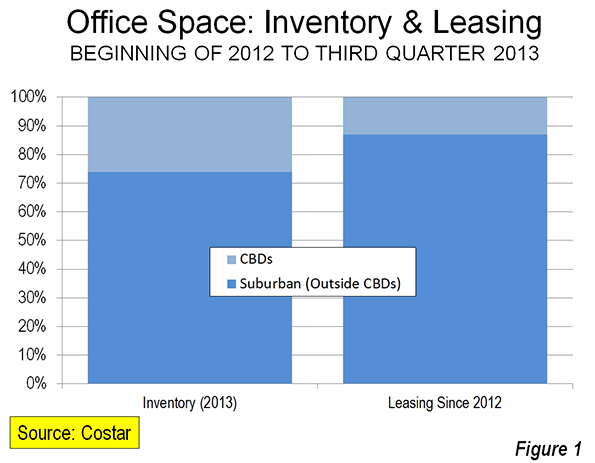
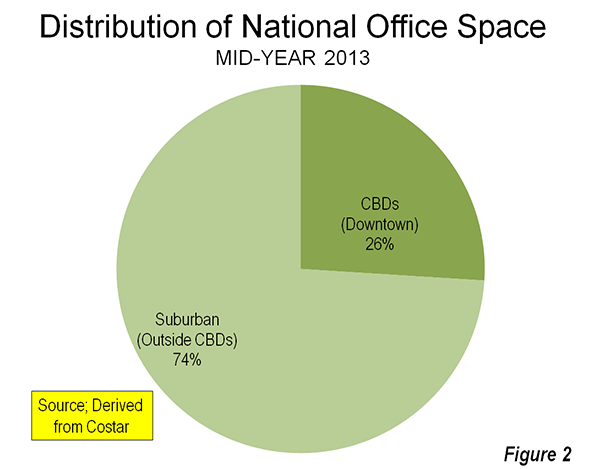
There are a number of challenges converging to put pressure on suburban office campuses in some places:
1. Decentralization has run its course. There was a massive wave of suburbanization in the post-War era that has finished. That’s not to say things are going to be re-centralizing. Rather, the massive move from the core to the periphery is largely complete. The development pattern of the United States will continue to be decentralized, but it will largely be driven by organic growth rather than relocations. I think something similar happened with driving. The factors driving VMT growth above the rate of inflation – more cars per household, women entering the workforce, and such – are pretty much played out in terms of driving huge additional travel miles.
2. Corporate M&A and industry restructurings have dampened demand in some areas. In Connecticut specifically, a number of the complexes in question were from pharmaceutical and insurance companies. There has been a lot of consolidation in the pharma industry, for example. And with a challenging environment for new drug development, pharma companies are now really focusing on cost cutting and reducing overhead, not building massive new office parks.
3. The nature of work is changing. There was a popular trend for a while towards massive suburban office HQ campuses. For example, Sears moved from its namesake tower in downtown Chicago to a big campus in Hoffman Estates. These campuses had tons of free parking and lots of onsite amenities like gyms, dry cleaners, cafeterias, day care, etc. They also offered an idyllic, almost pastoral setting in some respects. Workers could spend their days cocooned inside the campus. Today’s firms are less vertical integrated and more networked. They are heavily globalized and collaborative. They’ve also figured out that people who don’t get out and engage with the world around them end up cut off from information flows, leaving them a step behind. Workers are also demanding more flexible working conditions. And of course there’s cost cutting pressures. This leads to things like hoteling, co-working, and telecommuting – no massive suburban office park needed.
4. In select industries and cities, there has been a resurgence in the fortunes of downtown offices. This has particularly been the case in high tech. Google’s second largest office is in Manhattan. Salesforce.com’s Exact Target unit employs a thousand people in downtown Indianapolis. Amazon is building a large urban campus is Seattle. Many companies in Chicago have relocated downtown from the suburbs. I’ve probably seen more announcement of these types of moves in Chicago than anywhere else. I’d caution that in most downtowns the trends in private sector employment have remained negative. But in select locales and industries, things have been looking up. In industries where there’s a need for proximity to high end business services or where there are unique clustering or labor force issues, downtowns will retain an appeal.
Put it all together and it’s clear office space demand is weaker than it used to be. Joel Kotkin recently surveyed the same trends and suggests that the US may have hit “peak office”. The idea is not that office space will actually decline, rather that it won’t be growing at the same rates as in the past. This will affect both urban and suburban markets.
It’s easy to see how these trends combined to pound a place like Connecticut. It’s next to NYC, the premier central business district zone in America. But it is also far enough to make commuting to most of it a pain (even the express train to Stamford takes about an hour). And it’s an expensive and business hostile environment to boot. Large scale employers who want a suburban footprint can find many better places.
We are in fact seeing this happen in finance. Goldman Sachs is booming in Manhattan, but has what I believe is their second largest US office in Salt Lake City, presumably housing back office functions. Deutsche Bank is building a big facility in Jacksonville. JP Morgan Chase has a huge presence in Columbus, Ohio, where its former Bank One unit was based. A place like Connecticut is the odd man out. Suburban Chicago is probably set to be another loser. But in smaller cities the suburbs will do much better.
Also, don’t be too quick to write the eulogy for the suburban office campus, even in the tech industry. A recent article in Der Spiegel featured Silicon Valley’s new “monuments to digital domination” – including Apple’s $5 billion Norman Foster designed campus, Frank Gehry’s campus for Facebook, and others for Google, NVidia, and Samsung. In Houston, Exxon Mobil is putting the finishing touches on a three million square foot campus that will employ 10,000 people. But unlike Google moving 2,500 people to downtown Chicago, projects like that don’t make national headlines.
I don’t think there will be a massive back to downtown wave, and the suburban office park is not dead. But there are headwinds facing suburban office space, particularly in expensive, mature markets.
Aaron M. Renn is an independent writer on urban affairs and the founder of Telestrian, a data analysis and mapping tool. He writes at The Urbanophile, where this piece originally appeared.