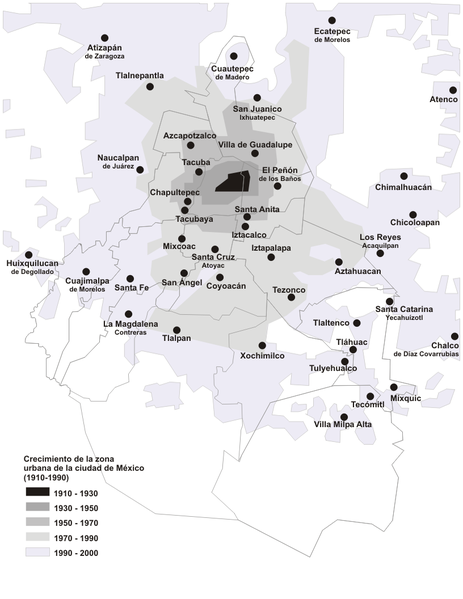
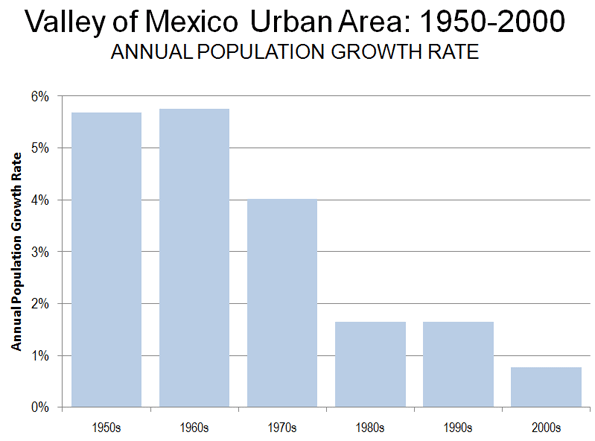
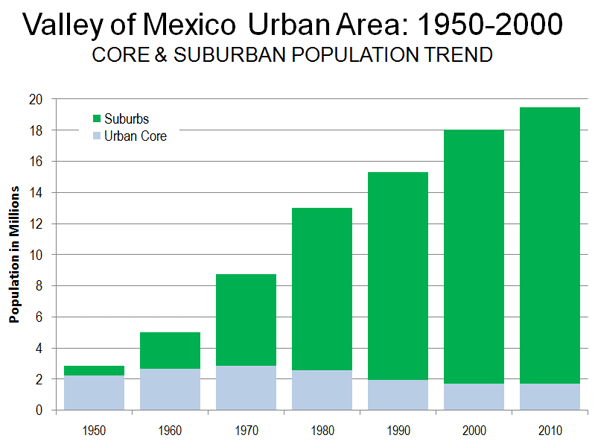
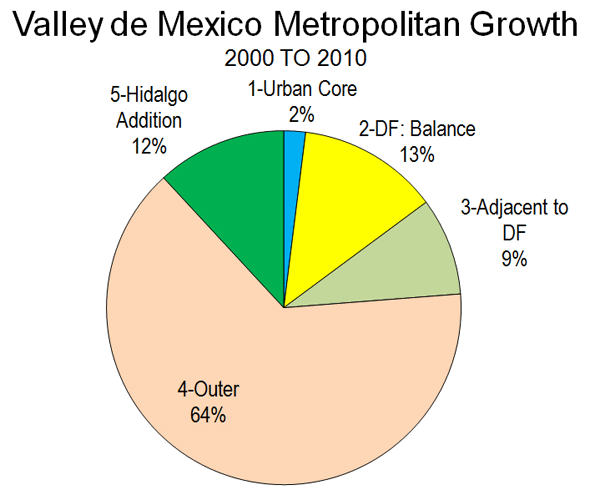
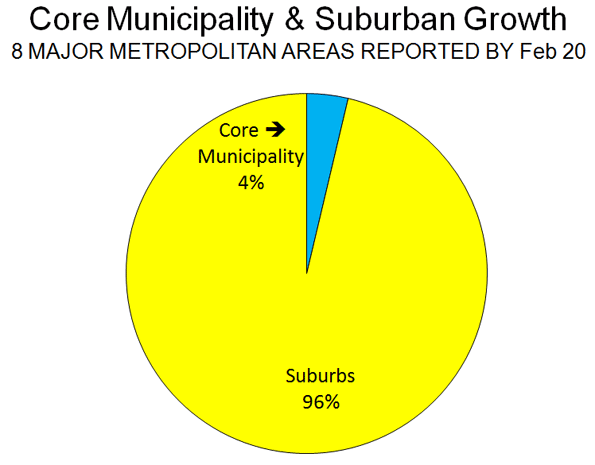
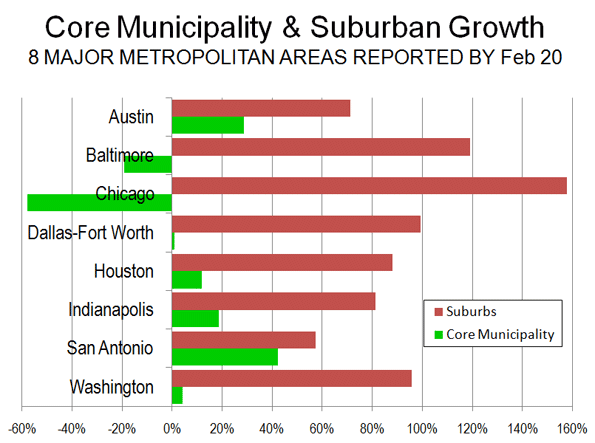
The ongoing Census reveals the continuing evolution of America’s cities from small urban cores to dispersed, multi-polar regions that includes the city’s surrounding areas and suburbs. This is not exactly what most urban pundits, and journalists covering cities, would like to see, but the reality is there for anyone who reads the numbers.
To date the Census shows that growth in America’s large core cities has slowed, and in some cases even reversed. This has happened both in great urban centers such as Chicago and in the long-distressed inner cities of St. Louis, Baltimore, Wilmington, Del., and Birmingham, Ala.
This would surely come as a surprise to many reporters infatuated with growth in downtown districts, notably in Chicago, Los Angeles, Denver and elsewhere. For them, good restaurants, bars and clubs trump everything. A recent Newsweek article, for example, recently acknowledged Chicago’s demographic and fiscal decline but then lavishly praised the city, and its inner city for becoming “finally hip.”
Sure, being cool is nice, but the obsession with hipness often means missing a bigger story: the gradual diminution of the urban core as engines for job creation. For example, while Chicago’s Loop has doubled its population to 20,000, it has also experienced a large drop in private-sector employment, which now constitutes a considerably smaller share of regional employment than a decade ago. The same goes for the new urbanist mecca of Portland as well as the heavily hyped Los Angeles downtown area.
None of this suggests, however, that the American urban core is in a state of permanent decline. The urban option will continue to appeal to small but growing segment of the population, and certain highly paid professionals, notably in finance, will continue to cluster there.
But the bigger story — all but ignored by the mainstream media — is the continued evolution of urban regions toward a more dispersed, multi-centered form. Brookings’ Robert Lang has gone even further, using the term “edgeless cities” to describe what he calls an increasingly “elusive metropolis” with highly dispersed employment.
Rather than a cause for alarm, this form of development simply reflects the protean vitality of American urban forms. Two regions, whose results were released last week, reveal these changing patterns. One is the Raleigh region, which has experienced a growth rate of 42%, likely the highest of the nation’s regions with a population over 1 million. This metropolitan area, anchored by universities and technology-oriented industries, is among the lowest-density regions in the country, with under 1,700 persons per square mile, slightly less than Charlotte, Nashville and Atlanta.
Unlike the geographically constrained older urban areas, Raleigh’s historical core municipality experienced strong growth, from 288,000 to 404,000, a gain of 40%. This gain was aided by annexations that added nearly 30% to the area of the municipality (from 113 to 143 square miles). The annexations of recent decades have left the city of Raleigh with an overwhelmingly suburban urban form. In 1950, at the beginning of the post-World War II suburban boom, the city of Raleigh had a population of 66,000, living in a land area of only 11 square miles.
Even here, however, the suburbs (the area outside the city of Raleigh) gained nearly two-thirds of the metropolitan area growth (65%) and now have 64% of the region’s population. Over the last ten years, the suburbs have grown 43%. It is here that much of the economic growth of the Research Triangle has taken place, as companies concentrate in predominately suburban communities such as Cary.
Yet in most demographically healthy urban regions, the growth continues to be primarily in the suburban centers. One particularly relevant example is the Kansas City area, a dynamic region anchoring what we have identified as “the zone of sanity.” Like most American regions, the Kansas City area is growing, but in ways that often do not resemble the fantasies of urban density boosters.
KC’s growth pattern is important and could be a harbinger of what’s to come in this decade. Along with Indianapolis, this resurgent Heartland region is expanding faster than the national average. It is also attracting many talented people, ranking in our top ten list of the country’s “brain magnets,” a performance better than such long-standing talent attractors as Seattle, Portland, San Francisco, and Boston. Between 2007 and 2009, the Kansas City region’s growth in college-educated residents was more than twice the rate of our putative intellectual meccas of New York, Chicago or Los Angeles.
But despite the wishes of some in Kansas City’s traditional establishment, this cannot be interpreted as meaning that the “hip and cool” are being lured en masse to the city’s inner core. Over the past decade, as in most American regions, Kansas City has expanded far more outward than inward. Despite a modest increase in the city’s population of some 18,000 — much of it in the city’s furthest urban boundaries — the city’s population remains below its 1950 high. On the other hand, some 91% of its 200,000 population increase occurred in the suburban periphery.
Critically, it is important to note that this expansion reflects not so much the growth of “bedroom” communities, but a dramatic shift of employment to the periphery. By far the most important center for this new suburban growth in jobs and people lies across the river in Johnson County, Kan.. Over the past decade, Johnson County has accounted for roughly half of the region’s total growth.
Johnson County – which boasts among the highest levels of educated people in the country — also has become the primary locale for many technology and business service firms, with more people commuting into the area than out. This reflects an increasingly suburbanized economic base. Over the past decade the urban core of Jackson County has lost 42,000 jobs, while the surrounding suburbs have grown by 20,000, with the biggest growth in largely exurban Platte County.
So what does this tell us about the future of the American urban region? Certainly the expansion of relatively low-density peripheral areas negates the notion of a ”triumphant” urban core. Dispersion is continuing virtually everywhere, and with it, a movement of the economic center of gravity away from the city centers in most regions.
But in another way these patterns augur a bright future for an expansive American metropolis that, while not hostile to the urban center, recognizes that most businesses and families continue to prefer lower-density, decentralized settings. The sooner urbanists and planners can accommodate themselves to this fact, the sooner we can work on making these new dynamic patterns of residence and employment more sustainable and livable for the people and companies who will continue to gravitate there.
This piece originally appeared at Forbes.com
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University, and an adjunct fellow of the Legatum Institute in London. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050
, released in February, 2010.
Kansas City skyline photo by Tim Samoff