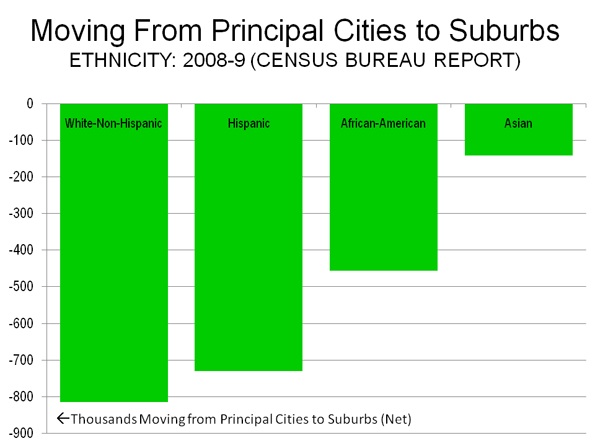
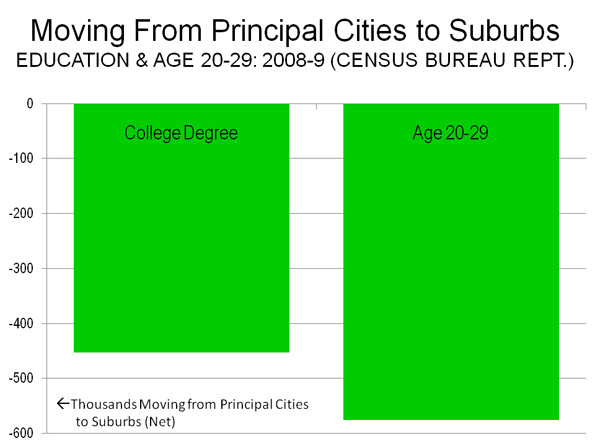
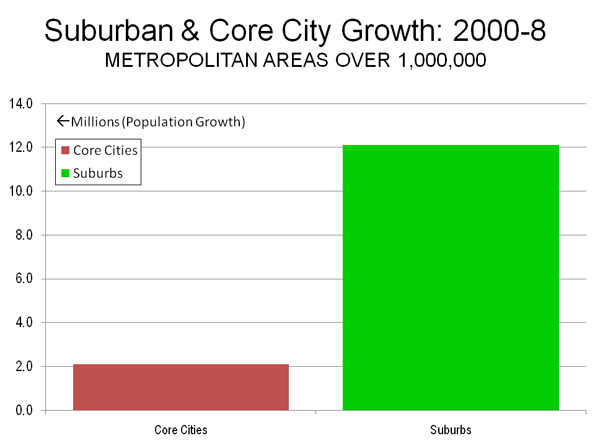
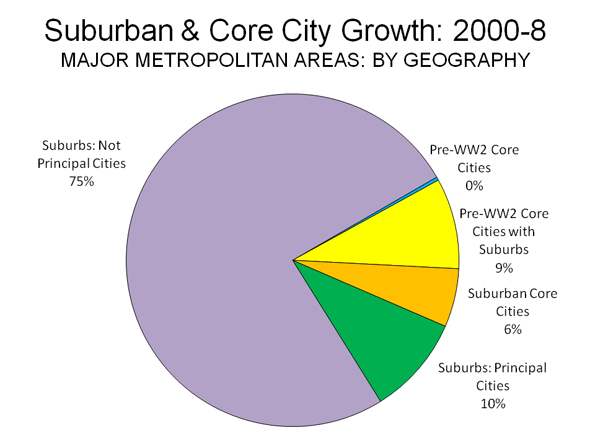
This is part one of a two-part piece. Read Part two.
Human settlements are always shaped by whatever is the state of the art transportation device of the time. Shoe-leather and donkeys enabled the Jerusalem known by Jesus. Sixteen centuries later, when critical transportation has become horse-drawn wagons and ocean-going sail, you get places like Boston. Railroads yield Chicago – both the area around the “L” (intraurban rail) and the area that processed wealth from the hinterlands (the stockyards). The automobile results in places with multiple urban cores like Los Angeles. The jet passenger plane allows more places with such “edge cities” to rise in such hitherto inconvenient locations as Dallas, Houston, Seattle and Atlanta and now Sydney, Lagos, Cairo, Bangkok, Djakarta, and Kuala Lumpur.
The dominant forms of transportation today are the automobile, the jet plane, and the networked computer. What does adding the networked computer get you? I think the answer is “the Santa-Fe-ing of the World.” This means the rise of places where the entire point of which is face-to-face contact. These places are concentrated and walkable, like villages. Some are embedded in the old downtowns – such as Adams Morgan in Washington, or The Left Bank of Paris, or the charming portions of what in London is referred to, somewhat narcissistically, as “The City.” Some are part of what have traditionally been regarded as suburbs or edge cities, such as Reston, Virginia, or Emeryville/Berkeley, California.
Santa Fe, New Mexico, is a remarkable example of this trend. Home to a world-renowned opera, charming architecture, distinguished restaurants, great places to buy used boots, quirky bookstores, sensational desert and mountain vistas and major diversity, it is also little more than a village of 62,000, far from the nearest major metropolis.
This “Santa-Fe-ing” means urbane well beyond the current definition of urban. It means aggregation and dispersal. As with all innovation, its impact is first seen among people with enough money to have choices.
The logic of this hypothesis starts with the question: “In the 21st century, is there any future for cities of any kind?”
After all, some would have us believe that with enough bandwidth, each of us can wind up on his or her own personal mountaintop in Montana, being lured down into the flatlands only to breed.
That’s a preposterous view of human nature, of course. There’s a reason solitary confinement is a punishment. We are social animals. But still, many of the historic reasons for human concentration are gone. It’s been a century since you’ve had to live within walking distance of your factory. Today, you often don’t even need be within driving distance of your office – as anyone with a cell phone knows. You certainly don’t need a metropolis to acquire anything a dot-com is willing to sell – which is a very big deal now and growing exponentially.
Absent a cataclysm of biblical proportions, I think this means the one and only reason for congregation in the near future is face-to-face contact. Period. Full stop. The places that are good at providing this will thrive – think Oxford, England. The ones that are not will die. Cities are not forever. You have not heard much lately from the Babylon chamber of commerce.
There are nearly 100 classes of real estate out of which you build cities, according to William J. Mitchell, the former head of the architecture and planning department at MIT. They are all being transfigured. The classic example is bookstores. If all you want to do is exchange money for a commodity, the path with least friction is often Amazon. In backwaters where, just ten years ago, buying or even borrowing a non-best-seller was a chore that took weeks, hundreds of thousands of titles are now within one click. Does this mean bookstores have disappeared? Of course not. The half of them that have survived and even grown since the ‘90s, however, have morphed. The critical elements are no longer the shelves. They are the couches, cappuccino machines, and cafes. Bookstores have become places to loiter, face-to-face, among like-minded people.
What about grocery stores? What happens when it becomes cheaper for the supermarket to deliver your toilet paper to you than it is to heat, light and pay rent and taxes on its store? Under what circumstances would you ever again get in your car to drive to market again? For me, the answer is that I want to have face-to-face contact with my tomatoes – or anything else you might find in a social setting like a farmers’ market. I’m not sure I’d trust the kid at the dot com to pick out my spare ribs. If the grocer wants to ship me my barbecue sauce, however, I won’t mind. Ninety-five percent of everything one finds in a supermarket is flash-frozen, shrink-wrapped, and nationally advertised. We are in the midst of a burgeoning freight revolution, in which the stuff is coming to us, rather than us going to the stuff – as anybody who has Christmas shopped lately may have noted. In fact, I can’t think of anything in an entire Wal-Mart that I would regret having delivered to me in a big brown van. Visiting a Wal-Mart doesn’t give me enough of a psychic boost to justify a drive now. Of course, if big-box retail migrates into the digital ether tomorrow, we’ll have an enormous challenge figuring out the adaptive re-use of their buildings. What will we make of them? Roller skating rinks? Greenhouses? Non-denominational evangelical churches? Artists lofts? Whatever the answer, I doubt their passing will be mourned.
What about college campuses? Is there any future for those? After all, the University of Phoenix, the online learning establishment, became one of the hottest growth stocks of the early 21st century. Internet MBAs abound from some of the world’s most distinguished schools. Why bother ever getting out of your pajamas to learn?
Again, the answer is face-to-face contact. After all, distance learning is nothing new. Benjamin Franklin engaged in correspondence classes. The United States military is awash in senior officers with advanced degrees from the University of Maryland, which has pioneered its outreach programs to people in remote locations.
However, distance learning will always be everyone’s second choice. It works best for people who do not have the time or money for the conventional academic experience. First choice remains the traditional universities. Getting into them has become insanely competitive and expensive. Why are they so desirable? Because sitting in class absorbing information from a lecturer is only a tiny part of the college experience. College is where many people meet their first spouse. It’s where they develop a network of friends that they’ll likely maintain for life. It’s an entertainment center and an athletic center. Oh, and as for learning – most of the stuff that has stuck with me came out of dorm sessions at one in the morning, engaging in face-to-face contact with smart people.
As we shall see, the impact of face-to-face on urban calculations includes office space, and even home locations. But why is this transformation occurring now?
It all starts with Moore’s Law, first stated by Intel co-founder Gordon Moore As the core faith of the entire global computer industry, it has come to be stated this way: The power of a dollar’s worth of information technology will double every 18 months, for as far as the eye can see. Sure enough, in 2002, with a billion-transistor chip, the 27th doubling occurred right on schedule. The 30 consecutive doublings of anything man-made that we have achieved at this writing – an increase of well over 500 million times in so short a time — is unprecedented in human history. This is exponential change. It’s a curve that goes straight up.
For sure, railroads also changed everything they touched. They transformed Europe. North America was converted from being a struggling, backward, rural civilization mostly hugging the East Coast into a continent-spanning, world-challenging, urban behemoth. New York went from a collection of villages to a world capital. Chicago went from a frontier outpost to a brawny goliath. The trip to San Francisco went from four months to six days. Distance was marked in minutes. Suddenly, every farm boy needed a pocket watch. For many of them, catching the train meant riding the crest of a new era that was mobile and national. A voyage to a new life cost 25 cents.
Of course, as railroad expansion ran out of critical fuel – including money and demand for the services – things leveled off, and society tried to adjust to the astounding changes seen during the rise of this curve. The last transcontinental railroad completed in the United States was the Milwaukee Road in 1909. In part, that was because of the rise of a new transformative technology: The one millionth Model T rolled off the assembly line in 1915.
In contrast, the curve predicted by Moore’s Law did not stop. The computer industry still regularly beats its clockwork-like 18-month schedule for price-performance doubling.
The effect of Moore’s Law on the built environment is and will become ever more profound.
For example, will we ever need offices outside our homes? After all, haven’t we all heard plenty about telecommuting?
Sure, but how many of us have discovered with some chagrin that the most productive five minutes of our work day has occurred around the shared printer? Somebody asks what we’re working on. Conversations ensue. “Oh really? Did you know that Jane was working on something like that?” “There’s this guy you’ve got to talk to; I’ll send you his phone number as soon as I get back to my desk.” “I was just reading about that very subject; I’ll ship you the name of the book.”
This kind of casual face-to-face contact is irreplaceable no matter how cheap or immersive video technology gets. Humans always default to the highest available bandwidth that does the job, and face-to-face is the gold standard. Some tasks require maximum connection to all senses. When you’re trying to build trust, or engage in high-stress, high-value negotiation, or determine intent, or fall in love, or even have fun, face-to-face is hard to beat.
This would seem to argue that some old patterns endure, and that’s true. But think of the twists suggested by this new premium on human basics. Suppose you decided that you could get all the face-to-face you needed two days a week. Would that influence where you lived? Would the mountains or the shore start looking good to you? Suppose you decided that you could get all the face-to-face you needed three days a month. Would the Caribbean start looking good to you?
Residential real estate is being transformed for these reasons. In the U.S., the explosive growth is in places far beyond any metropolitan area, like the Big Sky Country of Montana, the Gold Country of the California Sierras, the Piedmont of Virginia and the mountains and coasts of New England. For eons, when we’ve visited a nice place on vacation, we’ve asked ourselves, “Why am I going back?” Now, however, we have a new question: “Why am I going back?” Santa Fe is more than 800 miles from Los Angeles, yet it is only semi-jokingly referred to as L.A.’s easternmost suburb. To find out why, check out the nearest airport – in this case Albuquerque – any Monday morning.
Joel Garreau is Lincoln Professor of Law, Culture and Values at the Sandra Day O’Connor College of Law and the Lincoln Center for Applied Ethics at Arizona State University. He is a fellow at The New America Foundation in Washington, D.C., and author of several best-selling books including Radical Evolution, Edge City
and The Nine Nations of North America
.