From a Rural to Urban Dispersion in the Middle Kingdom
China’s rise to economic prominence over the past 30 years has rested in large part to its rapid urbanization. Prior to ‘reform and opening up’ that started in earnest during the 1970s, cities in China were viewed as pariahs by the party leadership. Millions of young urban dwellers were forced into the countryside to labor on farming communes during the Cultural Revolution. In stark contrast, today millions of rural migrants make their way to the city.
The scale at which this is happening is unprecedented. Currently, there are 85 metropolitan areas in China with more than 1 million people, compared to 51 in the US. By 2015, urban regions will account for half of China’s population and by 2025, the urban population’s share should reach about 75%.
To date, international attention has remained fixated on China’s largest cities of Beijing and Shanghai (and to a lesser extent, Guangzhou and Shenzhen). This is not without good reason, as Beijing and Shanghai are not only the respective government and financial centers of mainland China, but both were host to two of the most visible world events of the past decade: the 2008 Summer Olympics and the recently concluded World Expo.
Second and Third-Tier Cities Enter Onto the World Stage
Increasingly, however, the real trajectory of urban growth is shifting to China’s so-called ‘second-tier’ and ‘third-tier’ cities. To the outside observer, China’s lesser-known cities might seem all too similar to one another given the monotonous aesthetic of their newly constructed cityscapes. Indeed, the newfound appearance of Chinese cities is a point of contention among local urban development scholars who are concerned about the converging ‘identical faces’ of these urban areas.
Yet to Chinese locals and foreigners who have spent some time living here, it Chinese cities are defined more by their local cuisine, dialect, history, geography, culture and climate rather than their architectural character. These often-overlooked nuances of local culture are much more essential to the identity of these cities than buildings. In the future, these distinctions may prove more effective in attracting investment and talent than flashy new construction projects.
Here’s a short guide to these rising urban areas by region and their current identities and prospects.
| TOP 20 URBAN AREAS IN CHINA: 2010 ESTIMATES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rank
|
Urban Area
|
2010
|
Area: SqMi
|
Density
|
Area: SqKM
|
Density
|
Base Year
|
Base Year Pop.
|
| 1 |
Shanghai, SHG |
18,400,000 |
1,125 |
16,400 |
2,914 |
6,300 |
2010 |
18,400,000 |
| 2 |
Shenzhen, GD |
14,470,000 |
550 |
25,900 |
1,425 |
10,000 |
2008 |
14,000,000 |
| 3 |
Beijing, BJ |
13,955,000 |
1,275 |
10,800 |
3,302 |
4,200 |
2008 |
13,545,000 |
| 4 |
Guangzhou-Foshan, GD |
13,245,000 |
760 |
17,000 |
1,968 |
6,600 |
2007 |
12,600,000 |
| 5 |
Dongguan, GD |
10,525,000 |
535 |
19,200 |
1,386 |
7,400 |
2007 |
10,000,000 |
| 6 |
Tianjin, TJ |
6,675,000 |
500 |
13,100 |
1,295 |
5,000 |
2007 |
6,400,000 |
| 7 |
Chongqing, CQ |
5,460,000 |
280 |
19,100 |
725 |
7,400 |
2007 |
5,240,000 |
| 8 |
Hangzhou, ZJ |
5,305,000 |
250 |
20,600 |
648 |
8,000 |
2007 |
5,015,000 |
| 9 |
Wuhan, HUB |
5,260,000 |
275 |
18,700 |
712 |
7,200 |
2007 |
5,040,000 |
| 10 |
Shenyang, LN |
5,160,000 |
280 |
18,100 |
725 |
7,000 |
2007 |
4,950,000 |
| 11 |
Chengdu, SC |
4,785,000 |
220 |
21,300 |
570 |
8,200 |
2007 |
4,585,000 |
| 12 |
Xi’an, SAA |
3,955,000 |
205 |
18,900 |
531 |
7,300 |
2007 |
3,785,000 |
| 13 |
Harbin, HL |
3,615,000 |
235 |
15,100 |
609 |
5,800 |
2007 |
3,460,000 |
| 14 |
Suzhou, JS |
3,605,000 |
245 |
14,300 |
635 |
5,500 |
2007 |
3,400,000 |
| 15 |
Nanjing, JS |
3,550,000 |
330 |
10,500 |
855 |
4,100 |
2007 |
3,400,000 |
| 16 |
Dalian, LN |
3,255,000 |
270 |
11,800 |
699 |
4,500 |
2007 |
3,105,000 |
| 17 |
Changchun, JL |
3,170,000 |
145 |
21,300 |
376 |
8,200 |
2007 |
3,010,000 |
| 18 |
Kunming, YN |
3,070,000 |
130 |
23,100 |
337 |
8,900 |
2007 |
2,925,000 |
| 19 |
Wuxi, JS |
2,925,000 |
150 |
19,000 |
389 |
7,300 |
2007 |
2,760,000 |
| 20 |
Taiyuan, SAX |
2,900,000 |
120 |
23,600 |
311 |
9,100 |
2007 |
2,755,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Source: Demographia World Urban Areas: Population & Projections: 6th Edition. http://demographia.com/db-worldua.pdf |
The Interior Rises
Chengdu (成都): It was the devastating 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake that first out Chengdu onto the international radar, but it’s the rapid expansion of its massive high tech sector that may define its long term prospects. The aerospace industry also plays an important role in the capital city of Sichuan Province as it is the site of the development of China’s first stealth fighter, the Chengdu J-20. Despite all the new development, Chengdu remains a pleasant city, known for pandas and spicy food as well as its generally relaxed and agreeable disposition. The local government has done a good job of promoting ‘quality of life’ and relatively low cost of living to attract both investment dollars and skilled labor away from the prohibitively expensive eastern metropolises.
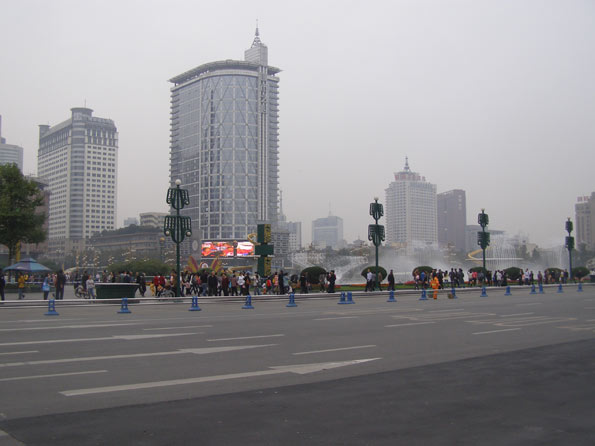

Chongqing (重庆): Also known for spicy food, this municipality, which falls under direct control of the central government, is bisected by the Yangtze River. Its urban vista is unique, with deep gorges. It long has been known as a rough and tumble place, long plagued by organized crime. This has abated under the leadership of Communist Party Secretary Bo Xilai who has waged a war against organized crime in Chongqing since assuming office there in 2007. Though a controversial leader with a penchant for strong “red” leanings, the ambitious Bo has been applauded for cleaning up the city and implementing a large-scale public housing program.
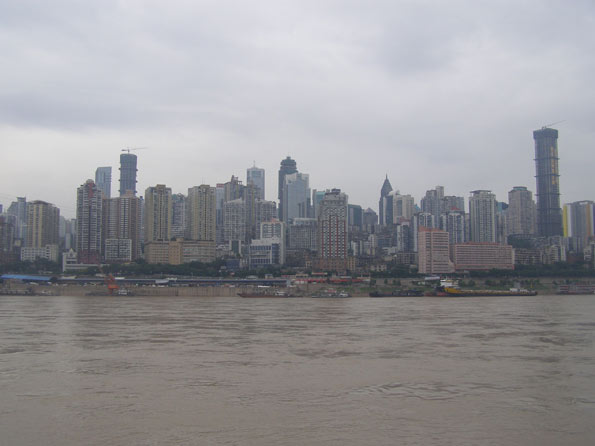

Kunming (昆明): The city of Eternal Spring and the capital of China’s ethnically diverse southern Yunnan Province, Kunming claims the best weather in the country. As such, Kunming’s residents would rather enjoy the sunshine then spend their days indoors working in factories. The lack of industrial production doesn’t mean this city isn’t important- as Kunming has China’s 6th busiest airport and is the country’s gateway to Southeast Asia. If China goes forward with its ambitious plans to link itself with Southeast Asia via high-speed rail, Kunming could enhance its status an international transportation node.
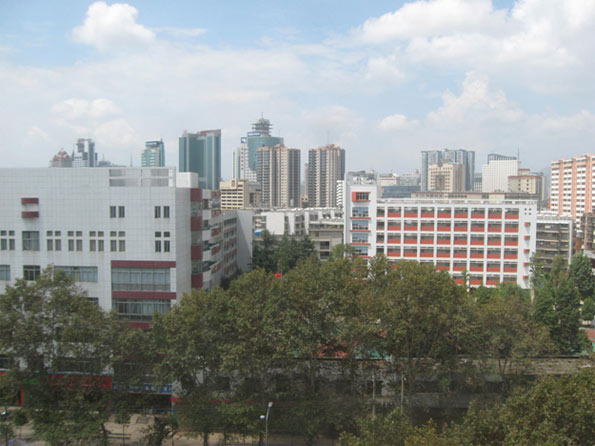

Wuhan (武汉): Wuhan, capital of Hubei Province, is an important rail and river transport hub at China’s central crossroads. Known for its unbearably hot summers, Wuhan sits on the Yangtze River a few hundred kilometers downstream from the infamous Three Gorges Dam. The city is China’s center for the optical-electronic industry, with a focus on the production of fiber-optics. It was also recently announced that Wuhan will get China’s third tallest building, the 606 meter Greenland Center.
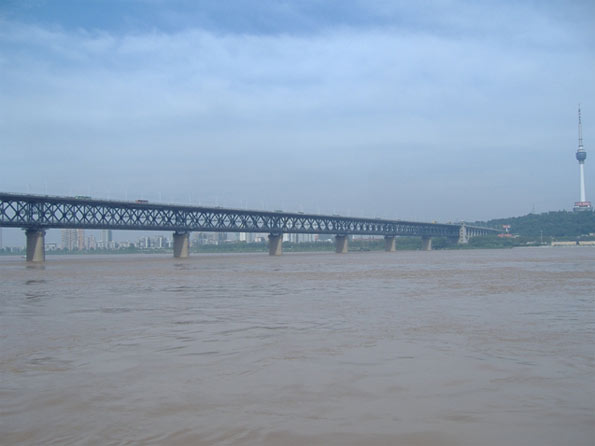

Xi’an (西安): Once known as Chang’an (‘eternal peace’), Xi’an was the capital of multiple Chinese dynasties throughout history. It remains as one of the most popular international tourist destinations in China thanks to its world-renowned Terracotta Warriors. But today this ancient city and present day capital of Shaanxi Province is also positioning itself as a hub for the development of the software and aerospace industries. The city is also host to several reputable universities, which could help supply a strong local talent pool.
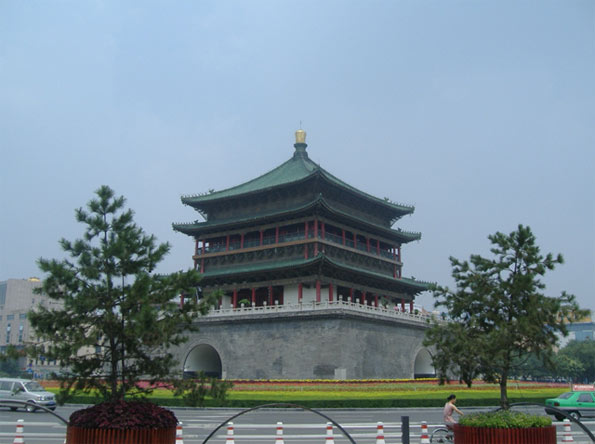

Yangtze River Delta (Greater Shanghai)
Hangzhou (杭州): Arguably China’s most naturally beautiful large city, Hangzhou is famous for its scenic Xihu or ‘West Lake’, which just became a UNESCO Heritage Site. The capital of Zhejiang Province not only attracts tourists, but investment as well, especially in the light manufacturing and textile industries. Already somewhat of a ‘bedroom community’ for Shanghai’s wealthy, The recently inaugurated Shanghai-Hangzhou high-speed rail line, which has cut travel time down to 45 minutes between the two cities, means that Hangzhou stands to further benefit from this connection.
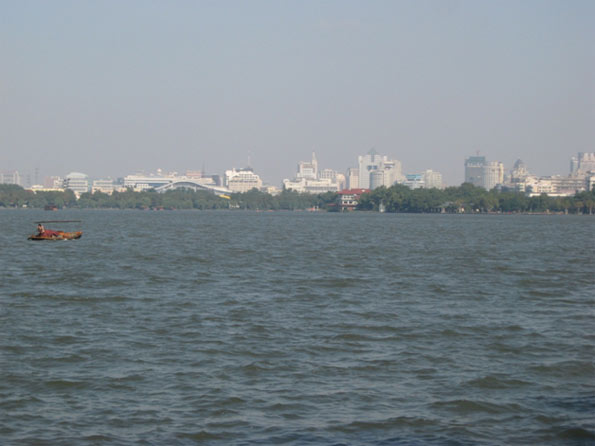

Nanjing (南京): One of the ‘Four Great Ancient Capitals of China’, the capital of prosperous Jiangsu province is today a bustling modern metropolis. Located on the Yangtze River, Nanjing has greatly benefitted its location within the greater Yangtze River Delta Region. The city’s close proximity to Shanghai means that is has absorbed some spillover from investors looking for a lower-cost alternative. Nanjing is also home to one of China’s tallest towers, the newly opened Nanjing Greenland Tower and Asia’s largest railway station.
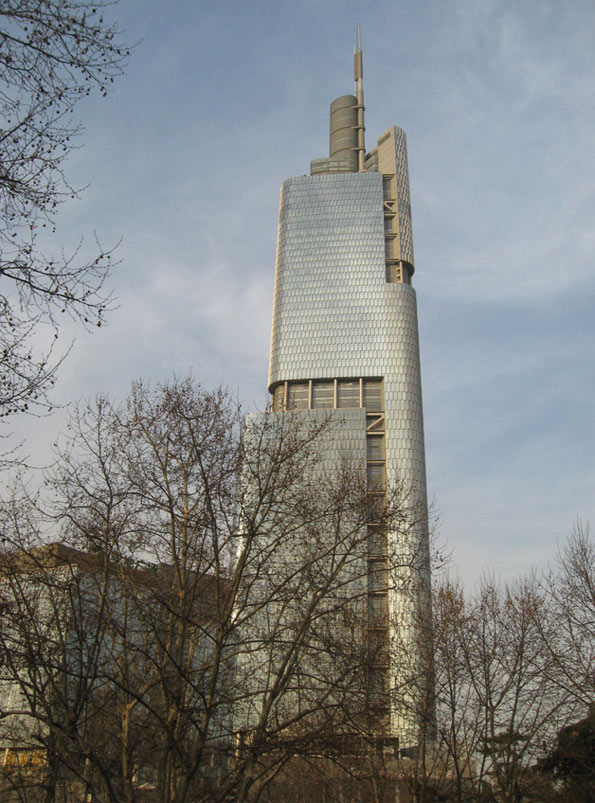

Suzhou (苏州): Situated in Jiangsu Province en route from Shanghai and Nanjing, Suzhou is strategically located in the center of a booming region. Often referred to as the ‘Venice of the East’, the city is famous for its historic canals and classic Chinese gardens. In addition to being a popular tourist destination Suzhou is an emerging hi-tech center. The China-Singapore Suzhou Industrial Park, the largest strategic partnership between the two governments, has been established in the city.
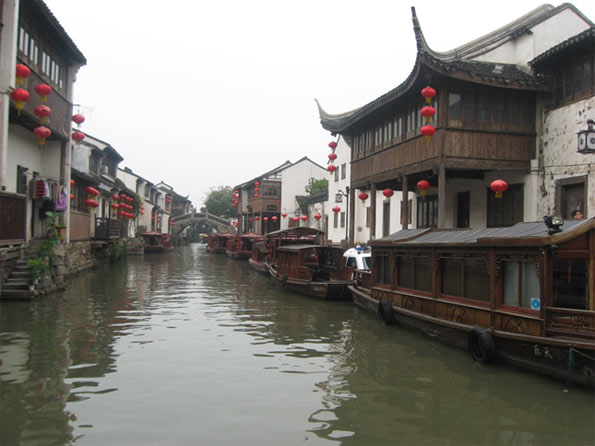

Wuxi (无锡): Only 50 km from Suzhou, Wuxi straddles the north shores of Lake Taihu. With 3,000 years of history, Wuxi is today one of China’s most business friendly cities. Wuxi is particularly attractive to Japanese businesses, with companies like Sony, Nikon, and Konica Minolta owning manufacturing and assembling facilities in the city’s New District. The city’s relatively new airport, which opened in 2004, serves the city as well as neighboring Suzhou.
The Industrial North: China’s Rustbelt
Changchun (长春): Changchun was the last capital of Manchuria and the seat of Japan’s ‘Puppet Government’ during their occupation of the region during WWII. Today the capital of China’s northern Jilin Province stands as “China’s Detroit” as the country’s largest automobile producer.The Changchun Automotive Economic Trade and Development Zone is home to the country’s biggest wholesaler of used cars, automotive spare parts and tires.
Dalian (大连): Consistently ranked as one of the ‘most livable’ of China’s big cities, Dalian sits strategically on the Liaodong Peninsula making it the principle seaport for the country’s northeast (‘DongBei’) region. Banking and IT is big here, with semiconductor giant Intel just having recently opened a $2.5 billion manufacturing facility in the city. The Dalian Commodity Exchange, highlighted by the trading of soybean contracts, is China’s largest futures exchange. Bo Xilai also left his mark on the city when he was Mayor before heading to Chongqing by initiating a campaign to add significant green space to the city.
Harbin (哈尔滨): The capital of Heilongjiang province, Harbin is the country’s northernmost big city. Famous for its local beer and annual winter ice sculpture festival, Harbin is China’s gateway to neighboring and resource-rich Russia. Russian culture has also left its mark on the city, influencing everything from the local cuisine to the architecture. Today Harbin’s economy is focused on textiles and power equipment manufacturing.
Shenyang (沈阳): Shenyang, the capital of Liaoning province, is the largest city in China’s northeast. Once the capital of the Manchurian Empire during the 17th Century, Shenyang is today an industrial powerhouse producing industrial equipment, construction vehicles, power tools, and biomedical equipment. Shenyang is also a hub for agriculture and the production of foodstuffs.
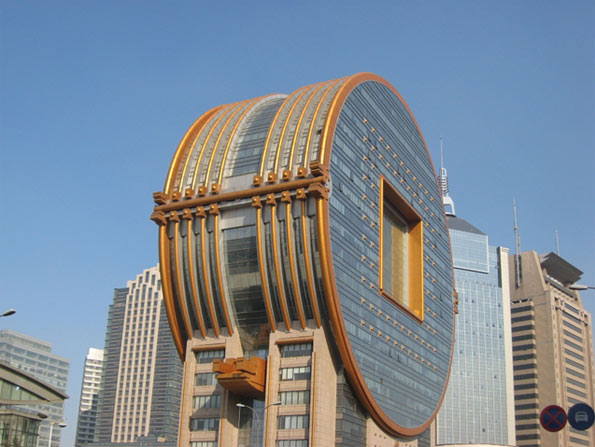

Taiyuan (太原): The capital of coal producing Shanxi province, Taiyuan is moving up on China’s urban radar. The city serves as the administrative center for both Chinese state-owned and foreign enterprises involved in the coal mining business. The city is also home to the Taiyuan Steel and Iron Company, China’s largest producer of stainless steel. Unfortunately, due to the heavy industrial activity in the region, Taiyuan is also one of the country’s most polluted cities.

Tianjin (天津): Long ridiculed by Beijingers, Tianjin is ambitiously positioning itself as a financial and sea logistics center for northern China. One of China’s four direct-controlled municipalities, Tianjin is less than 30 minutes from nation’s capital by high-speed train yet still has a distinct dialect and culture. The city is divided into two distinct parts: the charming historic city center, which retains colonial buildings from 19th Century foreign concessions, and the Binhai New Area, an up-and-coming Special Economic Zone next to the Bohai Sea. Tianjin is also aiming to become the center of China’s burgeoning biotech industry.
The Outlier
Dongguan (东莞): As the fifth largest city in China by population, Dongguan should register more prominently on the international radar. Unfortunately the most defining characteristic about this urban amalgam is its lack of character. A sprawling unplanned mass of factories in the Pearl River Delta situated between Shenzhen and Guangzhou, Dongguan is the largest city in the world without an airport. As the Pearl River Delta de-industrializes as more factories move into the lower-cost inland regions of China, Dongguan will need to reinvent itself.

Adam Nathaniel Mayer is an American architectural design professional currently living in China. In addition to his job designing buildings he writes the China Urban Development Blog.
Photos: Chengdu and Chongqing photos by author. All other photos by Wendell Cox.