Throughout much of history, cities have served as incubators for upward mobility. A great city, wrote René Descartes in the 17th century, was “an inventory of the possible,” a place where people could lift their families out of poverty and create new futures. In his time, Amsterdam was that city, not just for ambitious Dutch peasants and artisans but for people from all over Europe. Today, many of the world’s largest cities, in both the developed and the developing world, are failing to serve this aspirational function.
Though leading urban theorists love to celebrate the most rarified parts of the city economy—Saskia Sassen refers to “urban glamour zones” that thrive in what New York Mayor Michael Bloomberg proudly calls the “luxury city”—they tend to forget about working- and middle-class residents. Unfortunately, these urban ideas appear to be contagious, as they’re being applied to the expanding cities of Asia and other developing regions. A recent World Bank report argued that large urban concentrations—the denser, the better—are the most prodigious creators of opportunity and wealth. “To spread out economic growth,” the report claimed, is to discourage it.
A closer look, however, suggests a more nuanced reality. Cities in the developing world are growing, but largely because they’re the only alternative to poverty and even starvation in the countryside. These cities are not only failing to provide opportunities for upward mobility; they’re producing the class inequalities found in “luxury cities” such as London and New York.
Once rigidly egalitarian, China now has some of the world’s highest rates of income inequality. The central cores of Beijing and Shanghai employ legions of well-paid European and American architects and planners, but few concern themselves with the camps inhabited by poor, often temporary workers, who constitute roughly one-fifth of the population and live in conditions more reminiscent of a Brazilian favela than an “urban glamour zone.”
This same stratification is also happening in India. Mumbai, one of the fastest-growing cities, is creating wealth at the top of the economic spectrum but leaving millions of others scrambling for mere subsistence. The New York–based author Suketu Mehta has described his hometown of Mumbai (formerly known as Bombay) as “an urban catastrophe,” an example of the mounting woes of rapidly expanding cities in the developing world. “Bombay is the future of urban civilization on the planet,” he wrote. “God help us.”
A majority of Mumbai’s population now lives in slums, up from one-sixth in 1971—a statistic that reflects a lack of decent affordable housing, even for those gainfully employed. Congested, overcrowded, and polluted, Mumbai has become a difficult place to live. The life expectancy of a Mumbaikar is now seven years shorter than an average Indian’s, a remarkable statistic in a country still populated by poor villagers with little or no access to health care.
In spite of World Bank proclamations, the most rapid urban growth in India is actually occurring in smaller, less dense cities, such as Bangalore and Ahmedabad, places with lower living costs and more business friendly governments. This mirrors a trend occurring in the United States. In the last decade, middle-income people have been moving out of our megacities. Between 2000 and 2008, according to the demographer Wendell Cox, regions of more than ten million people suffered a 10 percent rate of net domestic out-migration. (Often the only reason for population growth in these cities was immigration.) The big gainers were cities between 100,000 and 2.5 million residents: the business-friendly Texas cities Dallas, Houston, and San Antonio; Raleigh and Durham, North Carolina, which now form the fastest-growing metro area in the nation; and the heartland cities of Columbus, Indianapolis, Des Moines, Omaha, Sioux Falls, and Fargo.
One reason for this movement has been the shift of jobs away from the coasts to lower-cost, less dense cities. The fastest growth in middle-income jobs has been concentrated in many of the places listed above: Houston, Dallas, Austin, Raleigh-Durham, and Salt Lake City. This pattern also includes high-tech, science-oriented employment. In contrast, those jobs have been stagnant or shrinking in such cities as New York, Los Angeles, San Francisco, and Chicago.
As a result, America’s largest cities are increasingly divided into three classes: the affluent, the poor, and the nomadic class of young people who generally come to the city for a relatively brief period and then leave. New York, the aspirational city of my grandparents, now has the smallest share of middle-income families in the nation, according to a recent Brookings Institution study, with Los Angeles and San Francisco not far behind. In 1980 Manhattan, New York’s wealthiest borough, ranked 17th among U.S. counties for social inequality; by 2007 Bloomberg’s “luxury city” was first, with the top fifth earning 52 times the income of the lowest fifth, a disparity roughly comparable to that of Namibia.
Similar patterns can be found in Europe, despite its countries’ more developed welfare states. The U.K. has witnessed a relentless centralization of urban functions in London, as once proud cities such as Manchester, Liverpool, Glasgow, and Birmingham have continued their long slide into obscurity and irrelevance. The bulk of London’s growth, however, has not taken place in the central core but in what the historian James Heartfield calls “the greater southeast.” This vast “conurbation” stretches from west of Heathrow Airport to the booming coastal city of Brighton, roughly an hour’s train ride from the“ city center.
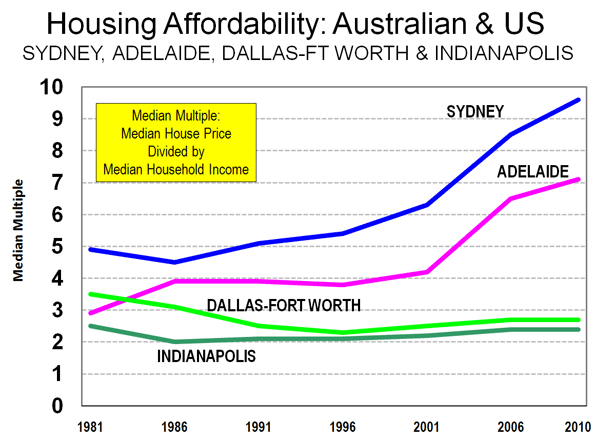
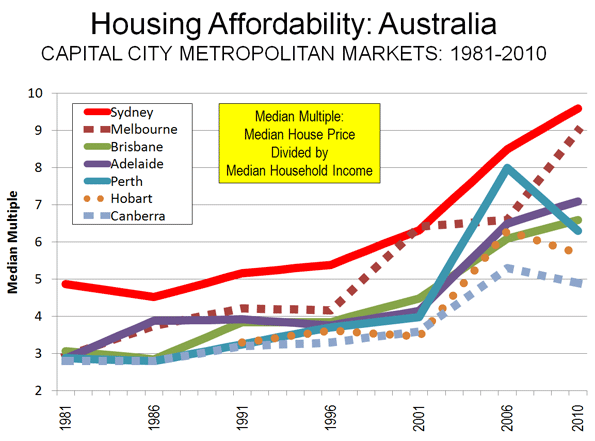
As the middle class has decamped, central London has become more stratified. Residents and workers there and in the West End account for some of the most concentrated wealth on the planet. At the same time, prospects for London’s middle class have weakened, with many fleeing to the suburbs or even leaving the country. (Britain remains a large exporter of educated workers to the rest of the world.) The major issue here is the high cost of housing. Even in its poorest neighborhoods, London now ranks as one of the most unaffordable places for middle-income people to buy a home.
Still, life is much tougher for the city’s poor, many of whom live less than an hour’s walk from the wealthiest neighborhoods. Take a stroll just a mile or two from the Thames and you enter a very different London. It is here where you’ll see why the financial capital of the European Union also has the highest incidence of child poverty in Great Britain (more even than in the beleaguered North East). Thirty-six percent of children in London live in poverty, a figure that rises to more than one-half when the city’s housing costs are factored in.
The same split has emerged in other countries considered far more open than class stratified Britain. A recent University of Toronto study found that between 1970 and 2001, the portion of middle-income neighborhoods in the city had dropped from two-thirds to one-third; poor districts had more than doubled to 40 percent. By 2020, middle-class neighborhoods could fall to less than 10 percent, with the balance made up of poor and affluent residents.
Much the same can be seen in continental Europe, a trend greatly exacerbated by the growth of immigration. Unlike Amsterdam in Descartes’s time, Europe’s great cities are failing in their historic mission of incorporating newcomers, as German Chancellor Angela Merkel recently conceded. In Berlin, one fourth of the workforce earns less than 900 euros a month, while 36 percent of children are poor. The city once known as “Red Berlin” has emerged as “the capital of poverty and the ‘working poor’ in Germany,” Emma Bode, a left-wing journalist, wrote in 2008.
Given these global realities, it might be time for our urban boosters to curb their enthusiasm for the “luxury city” and refocus on how to meet the aspirations of their middle- and working-class residents. If they don’t, lack of opportunity will drive more and more of this crucial aspirational class farther and farther away, mostly to smaller cities and suburbs that still offer “an inventory of the possible.”
This piece originally appeared in Metropolis Magazine.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University, and an adjunct fellow of the Legatum Institute in London. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050
, released in February, 2010.
Photo by Premshree Pillai