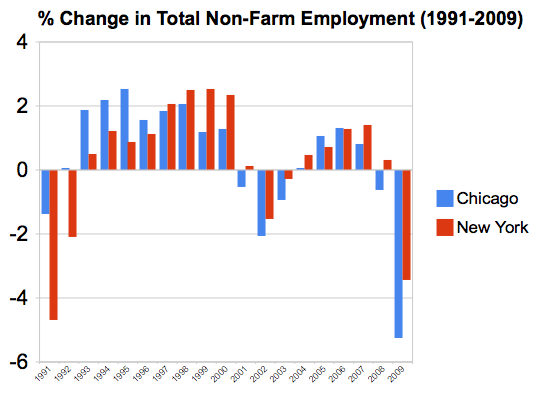
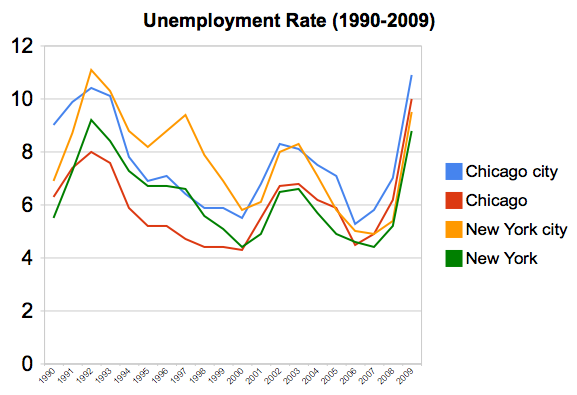
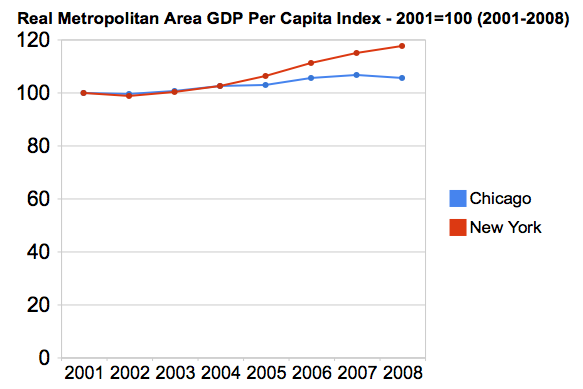
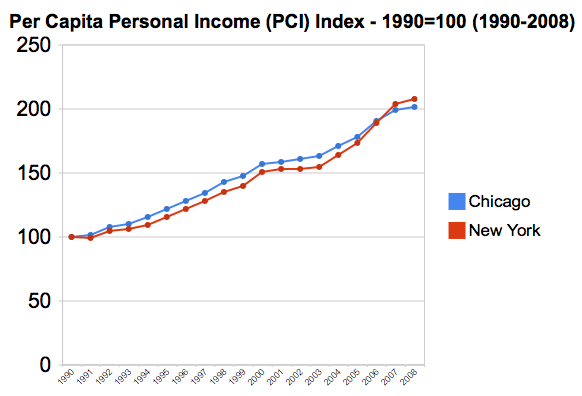
In recent decades, an unprecedented variation has developed in the price of new tract housing on the fringe of US metropolitan markets. Nearly all of this difference is in costs other than site preparation and construction, which indicates rising land and regulation costs.
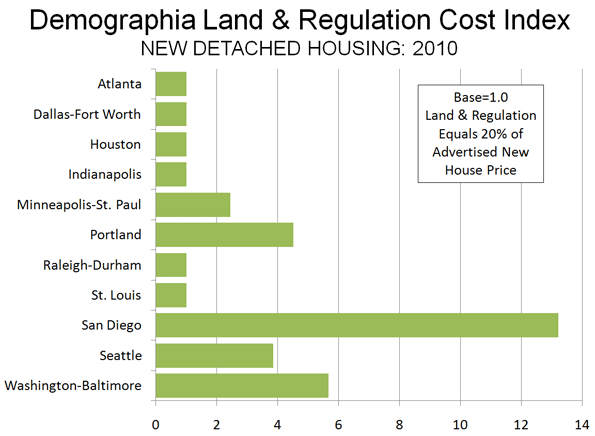
Our first annual Demographia Residential Land & Regulation Cost Index estimates the price of land and regulation for new entry level houses compared to the historic norm in 11 metropolitan regions (Note 1). Metropolitan regions in which land and regulation costs remain at or below normal have an Index of 1.0 while those with land and regulation costs above normal will have an Index above 1.0 (Figure 1).
More restrictive land use regulation is variously referred to as “smart growth,” “growth management” and other terms. More restrictive land use regulation is estimated to have added from nearly $30,000 (in Minneapolis-St. Paul) to more than $220,000 (In San Diego) to the price of a new home.
Economic research has associated rising residential land costs with more restrictive land use regulations. The table indicates some of the more important price increasing impacts of more restrictive land use regulation.
|
More Restrictive Land Use Regulation: Factors that Can Drive House Prices Higher |
|
1.. Increases underlying land costs |
|
2.. Increases planning and development costs |
|
3.. Raises financing costs |
|
4.. Encourages more expensive houses. |
|
5.. Increases construction costs |
|
6.. Encourages concentration of market power and land banking |
|
7.. Encourages land and housing speculation |
The Land and Regulation Ratio
For decades, construction costs of tract house on the urban fringe in the United States have represented 80% or more of the advertised house price. The balance of 20% or less has been for land and regulation costs and will be referred to as the “land and regulation cost ratio.” In metropolitan markets with less restrictive land use regulation, the historic 20% or less land price ratio remains in place. The Demographia Residential Land & Regulation Cost Index assumes a 20% expected land and regulation ratio.
In some metropolitan markets, however, house prices have increased far more rapidly than in the rest of the nation. The greater increase in house prices and escalation of land costs above the historic 20% land and regulation cost ratio has occurred in metropolitan markets burdened by more restrictive land use regulations. Urban growth boundaries, limits on the number of houses that can be built, large lot zoning and excessive development impact fees and the like are regulation strategies that increase the cost of land for building houses. These land cost increases are not the result of more rapidly rising construction costs or underlying market forces such as consumer demand.
More restrictive land use land use regulation also creates obstacles to people buying houses, requiring them to devote more money to housing than necessary and increases their vulnerability to losses in the event of a financial downturn. This exposes mortgage lenders to increased risks of loan defaults. Finally, more restrictive land use regulation makes residential land development more dependent on politics, with the potential for greater influence through campaign contributions.
The first annual Demographia Residential Land & Regulation Cost Index estimates cost of land and regulation for new entry level houses compared to the historic norm in 11 metropolitan markets. Each of the metropolitan regions in which house prices have risen above normal have adopted more restrictive land use regulations. Conversely, in each of the metropolitan regions in which house prices have not risen above normal levels, there is less restrictive land use regulation. During much of the Post-World War II era, all metropolitan markets had less restrictive land use regulations.
Results
The overwhelming majority of new housing in the United States continues to be detached and is built near or on the urban fringe (Note 2). For new detached homes, the Index is 1.0 in six metropolitan markets (Atlanta, Dallas-Fort Worth, Houston, Indianapolis, Raleigh-Durham and St. Louis). This indicates that land use regulation is less restrictive and does not add more than normal to the price of new homes (Note 3).
In the other five metropolitan markets, the land and regulation cost ratio has risen above 20%, resulting in a higher Index. The Index is 2.4 in Minneapolis-St. Paul, 3.9 in Seattle, 4.5 in Portland, 5.7 in Washington-Baltimore and 13.2 in San Diego. It is estimated that more restrictive land use regulation raises the price of the least expensive detached houses from nearly $30,000 (in Minneapolis-St. Paul) to more than $220,000 (in San Diego) than would be expected if these metropolitan markets had retained less restrictive land use regulation (Figure 2).
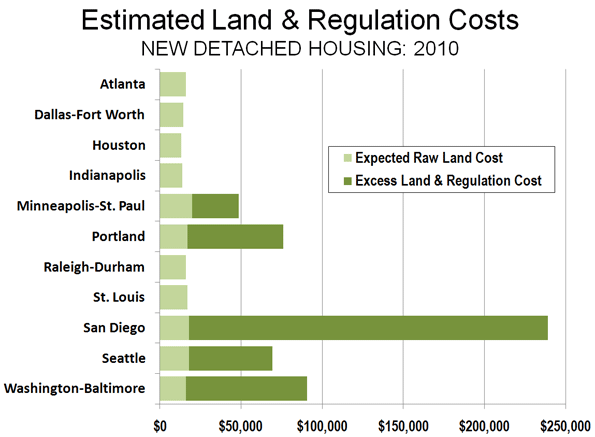
The metropolitan markets with more restrictive regulation have an average Demographia Residential Land & Regulation Cost Index of 5.9 for detached housing, while the metropolitan markets with less restrictive regulation average 1.0.
Housing Affordability: Through the Bubble and Bust
There is increasing concern about declining housing affordability across the nation. Even after the deflation of the housing bubble, house prices in some metropolitan markets remain well above pre-bubble prices and historic affordability standards. The housing affordability of the included metropolitan markets is illustrated by land use regulatory category in Figure 3. The Figure indicates the National Association of Home Builders-Wells Fargo Housing Opportunity Index for 1995, the peak of the bubble and early 2010, showing the percentage of households able to afford the median priced house. Similar affordability measures can be reviewed in the Annual Demographia International Housing Affordability Survey.
Future Editions
The 11 metropolitan regions included in the initial Demographia Residential Land & Regulation Cost Index were selected to provide a geographical and regulatory balance and because they had sufficient data from which to develop the Index. Additional areas will be added in future editions, with the intention of including all metropolitan regions with more than 1,000,000 population.

——-
Note 1: The Index was derived from a database developed of new house offerings by national, regional and local builders, using internet sites and published metropolitan home guides. The period covered is January through June 2010.
Note 2: In 2006, more than 85% of new single family houses sold in the United States were detached, according to Bureau of the Census data. Detached housing represents approximately 62% of all US housing units (including multi-unit dwellings).
Note 3: In each of the metropolitan markets with less restrictive regulation, the estimated construction costs were more than 80% of the house price. By using a 20% land and regulation ratio, the house construction cost was capped at 80% of the house price. In each of the metropolitan markets with more restrictive regulation, the estimated construction cost was less than 80% of the house price.
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris and the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life”
Photo: Will County, Chicago urban fringe (By author)