For many years, critics of the suburban lifestyles that most Americans (not to mention Europeans, Japanese, Canadians and Australians) prefer have claimed that high-density housing is under-supplied by the market. This based on an implication that the people increasingly seek to abandon detached suburban housing for higher density multi-family housing.
The Suburbs: Slums of the Future?
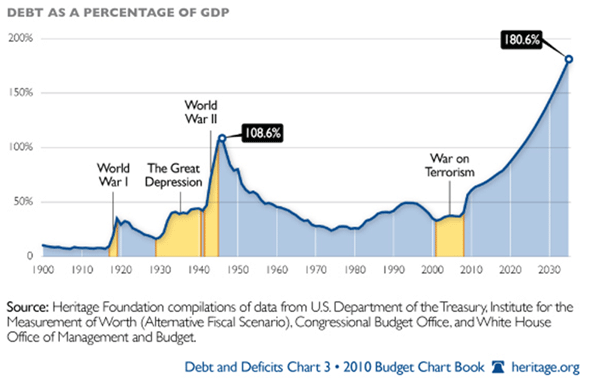
The University of Utah’s Arthur C. (Chris) Nelson, indicated in an article (entitled “Leadership in a New Era“) in the Journal of the American Planning Association. that in 2003, 75% of the housing stock was detached and 25% was attached, including townhouses, apartments, and condominiums. By 2025 he predicts that only 62% of consumer will favor detached homes, (Note 1). He also predicts a major shift in consumer preferences from housing on large lots (defined as greater than 1/6th of an acre) to smaller lots (Note 2). This, he suggests, would create a surplus of 22 million detached houses on large lots.
This predication is largely made on the basis of “stated preference” surveys which the author, Dr. Emil Malizia of the University of North Carolina (commenting on the article in the same issue), and others indicate may not accurately reflect the choices that consumers will actually make. Dr. Nelson’s article has been widely quoted, both in the popular press and in academic circles. It has led some well-respected figures such as urbanist and developer Christopher Leinberger to suggest in an Atlantic Monthly article that “many low-density suburbs and McMansion subdivisions, including some that are lovely and affluent today, may become what inner cities became in the 1960s and ’70s—slums characterized by poverty, crime, and decay.”
The Condo Market Goes Crazy
Misleading ideas sometimes have bad consequences. The notion that suburbanites were afflicted with urban envy led many developers to throw up high-rise condominiums in urban districts across the country. Sadly for these developers, the Suburban Exodus never materialized, never occurred. As a result, developers have lost hundreds of millions, if not billions of dollars and taxpayers or holders of publicly issued bonds could be left “holding the bag” (see discussion of Portland, below).
This weakness has been seen even in the nation’s strongest condominium market, New York City, where one developer offered to pay purchaser’s mortgages, condominium fees and real estate taxes for a year as well as closing costs.
But the damage is arguably worse in other major markets which lack the amenities and advantages of New York.
Take, for example, Raleigh (North Carolina), where low density living is the rule (the Raleigh urban area is less dense than Atlanta). The News and Observer reports that the largest downtown condominium building (the Hue) “considered a bold symbol of downtown Raleigh’s revitalization,” has closed its sales office and halted all marketing efforts. The development’s offer of a free washing machine, dryer, refrigerator, and parking space were not enough to entice suburbanites away from the neighborhoods they were said to be so eager to leave.
This is not an isolated instance. Around the nation, condominium prices have been reduced steeply to attract buyers. New buildings have gone rental, because no one wanted to buy them. Other buildings have been foreclosed upon by banks; and units have been auctioned. Planned developments have been put on indefinite hold or cancelled.
Miami: Of Little Dubai and Cadavers
Miami’s core neighborhood (downtown and Brickell, immediately to the south) has experienced one of the nation’s most robust condominium building booms. More than 22,000 condominium high rise units were built between 2003 and 2008. Miami could well have more 50-plus story condominium towers than any place outside Dubai.
As a result, Miami has suffered perhaps the most severe condominium bust in the nation. According to National Association of Realtors data, the median condominium price in the Miami metropolitan area has dropped 75% from peak levels (2007, 2nd Quarter). By comparison, the detached housing decline in the metropolitan area was 50%; the greatest detached housing price decreases among major metropolitan areas were from 52% to 58% (Riverside-San Bernardino, Sacramento, San Francisco and Phoenix).
The most recent report by the Miami Downtown Development Authority indicates that 7,000 units still remain unsold. The Brickell area is home to the greatest concentration and largest buildings and has the highest ratio of unsold units at 40%.
Icon Brickell (see photograph above) may be the largest development in the core. Icon Brickell consists of three towers, at 58, 58 and 50 floors and a total of nearly 1,800 units. Despite opening in 2008 and offering discounts of up to 50%, barely one-third (approximately 620) of the units have been sold, according to the Daily Business Review, which also reported on May 13 that the developer had transferred control of two of the towers to construction lenders.
One building, Paramount Bay, was referred to by The New York Times as a “47-story steel and glass cadaver” with a lobby “like a mortuary.” A real estate site indicates that only one of the buildings 350 units has been sold.
More recently sales have inched up in the core but due not to any suburban exodus. According to The Miami Herald, huge discounts that have lured Europeans, Canadians, and Latin Americans to the core. The real estate and consulting firm Condo Vultures notes that more than 1,000 of the sales are to a few bulk buyers, a market segment some might refer to as “speculators.”
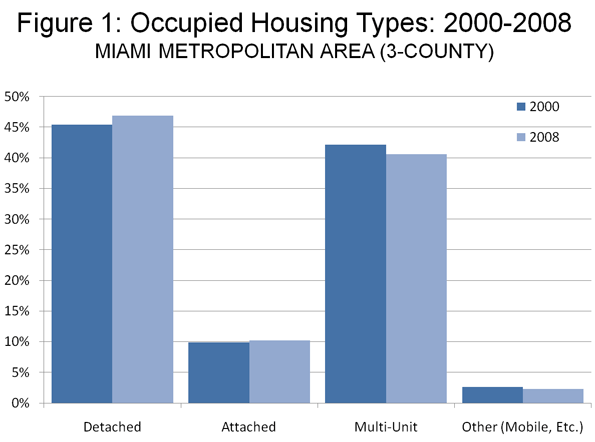
The latest data from the US Bureau of the Census confirms that there is no fundamental shift away from detached housing in the Miami area, as housing trends point toward more detached housing. In 2000, 48.1% of residents in the Miami metropolitan area lived in detached housing. By 2008, the figure had risen to 49.2% (Figure 1). Essentially, the Suburban Exodus remains a mirage.
Portland: Gift Certificates for Distressed Developers
If developer greed was the motive in Miami, government subsidies have been the driving force in Portland. The city of Portland will soon have issued nearly $450 million in urban renewal bonds, provides 10-year tax property tax forgiveness, and reduced development fees, which the Portland Development Commission (PDC) has called “gift certificates” for developers (Note 3).
Gift certificates have not been enough to cure Portland’s sickly downtown condominium market. The Oregonian reported that prices were down, on average, 30% over the year ended the first quarter of 2010. Remarkably prices in the much ballyhooed Pearl District are plummeting even more than those in the rest of the Portland area. According to DQ News, the median sale price of a house in the Pearl District dropped four times the average in Multnomah County and an even greater six times decline relative to suburban counties over the past year.
There is more. Just this year, the Pearl District has seen its Eddie Bauer, Adidas, and Puma stores close.
One condominium building the Encore, is reported to have sold only 17 of 177 units. A recent auction of units at the largest building in the city, the John Ross brought prices “far below the replacement cost” according to The Oregonian’s Ryan Frank, who noted that “it will likely be years before there’s a new high-rise condo built.” Late last year, the Pearl District’s Waterfront Pearl was reported to have sold only 31% of its units and had not sold a unit for a year.
The Portland Development Commission itself has become part of the condominium bust story. PDC had indicated it was considering relocating its offices to a new 32-story mixed use tower (Park Avenue West), which was to have included condominiums, offices, and retail stores. For more than a year, the proposed 32-story tower has been an unsightly hole in the ground, with construction suspended. PDC decided to stay put in its older, less expensive offices. Even before PDC decided not to locate in Park Avenue West, the developers eliminated the plans for 10 floors of condominiums, doubtless because it made no economic sense to add to an already flooded market.
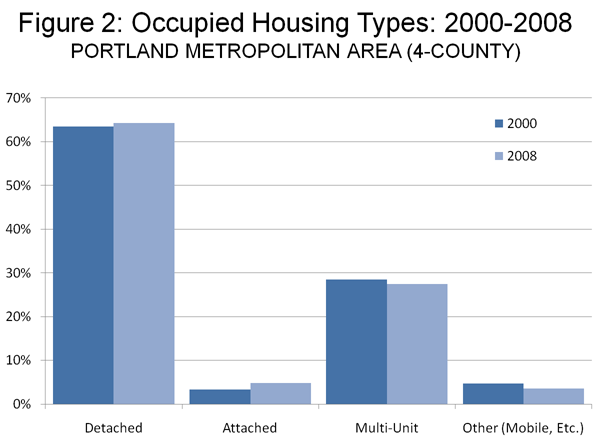
In Portland, like in Miami, the fact remains that suburbia has not been abandoned. Despite the high density over-building in the Pearl District and elsewhere in the core, detached housing has become even more popular in the region. According to data from the Bureau of the Census, the share of households living in detached housing in the Portland metropolitan area rose from 63.7% in 2000 to 64.5% in 2008 (Figure 2).
High-Rise Condos: Slums of the Future?
To say that the high-rise condominium market has fallen on hard times would be an understatement. The condo bust in New York has become so acute that Right to the City, a coalition of community organizations has called upon “the City to acquire the tax delinquent buildings through tax foreclosure and convert vacant units into permanently affordable housing for low-income New Yorkers.” In a report entitled People without Homes and Homes without People: A Count of Vacant Condos in Select NYC Neighborhoods, Right to the City points out that there are more than 4,000 empty condo units in 138 buildings, with owners delinquent on nearly $4 million in taxes to the city.
Owners of new condominiums around the nation who paid pre-bust prices for their units may not be inclined to stay around if they are surrounded by less affluent renters who have been attracted by desperate building owners and lenders.
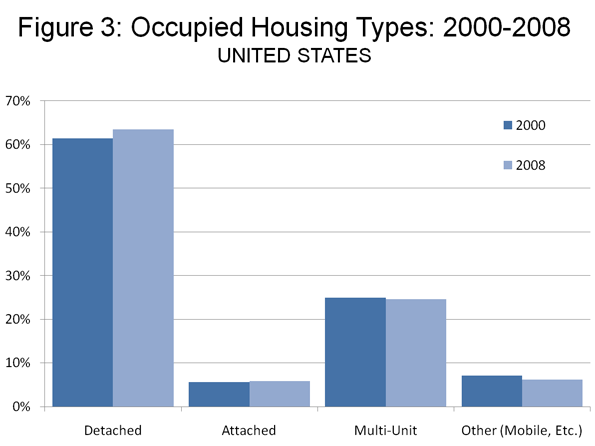
Are these dark towers of discounting the slums of tomorrow? Only the data and time will tell and it’s too early to know, but preliminary findings show little of the predicted shift toward higher density living (Figure 3). Certainly national data indicates, if anything, a slightly strengthening market for detached, rather than attached housing (Figure 4).
• Between 2000 and 2008, the share of households living in detached housing rose from 61.4% to 63.5%.
• A similar trend is shown by the national building permits data. Between 2000 and 2009, 75.2% of residential building permits in the United States were for detached housing. This is up strongly from 69.6% in the 1990s and nearly equals the highest on record (the 1960s), when 77.7% of residential building permits (housing units) were detached houses.
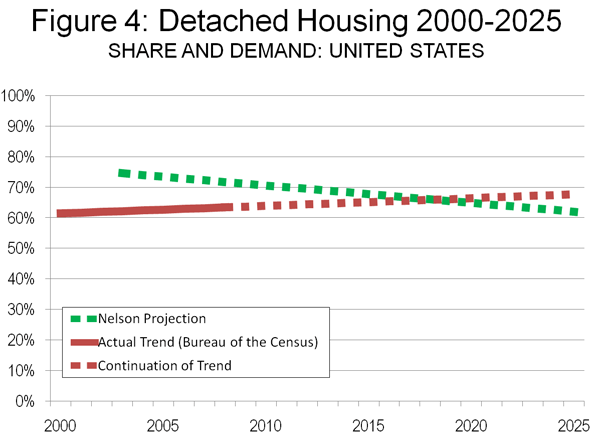
Looking at the data, there remains little evidence that the stated preferences on which the predictions relied have been translated into the reality of a shift in preferences toward smaller lots in cores or inner ring suburbs. Domestic migration continues to be strongly away from core counties to more suburban counties. Core cities are growing less quickly than suburban areas. Exurban areas are growing faster than central areas, including inner suburbs.
Clearly, the Suburban Exodus has not begun and there is little reason to believe that it will anytime soon.
Note 1: In estimating the 2003 share of detached housing (75%), Dr. Nelson uses “one-unit structures” data from the 2003 American Housing Survey Table 2-3. US Bureau of the Census American Housing Survey personnel responded to my request for clarification, indicating that “one-unit structures” includes … single detached housing units, mobile homes, and single attached housing units (such as a townhouse).” Thus the 75% detached estimate is high because it includes mobile homes and single attached housing. As is indicated above, data from the US Bureau of the Census data indicates that the share of detached housing of detached plus attached housing in 2000 was 61.4%. This figure, coincidentally, is virtually the same as the 62% Dr. Nelson predicts for 2025.
Note 2: The assumption that consumers prefer small lot detached housing may not be sufficiently robust and may even be exaggerated. Dr. Nelson appears to principally rely on research by Myers and Gearin (2001) (in the journal Housing Policy Debate) for concluding that consumers prefer small lot rather than larger lot detached housing, defining small lot development as 1/6th of an acre or less or less than 7,000 square feet. Yet neither figure appears in Myers and Gearin. Moreover, a National Association of Home Builders commenter (also in Housing Policy Debate) questions how its data was characterized by Myers and Gearin in justifying a finding of preference for smaller lots (the survey is unpublished). Without access to the original surveys referenced in Myers and Gearin, it is impossible to judge what respondents may have had in mind as the dividing line between large lots and small lots.
Note 3: This characterization was on the Portland Development Commission website (accessed January 2, 2007). It was cited in our report, Zero Sum Game: The Austin Streetcar and Development and subsequently removed from the website. A large share of Portland’s urban renewal bonds are insured by Ambac Financial Corporation, which has reported losses exceeding $1 billion in the last two quarters. Ambac indicated that it has “insufficient capital to finance its debt service and operating expense requirements beyond the second quarter of 2011 and may need to seek bankruptcy protection.” Ambac was the insurer of State of Nevada bonds to build the Las Vegas Monorail, which has already entered bankruptcy and is unable to pay its bonds.
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris. He was born in Los Angeles and was appointed to three terms on the Los Angeles County Transportation Commission by Mayor Tom Bradley. He is the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life. ”
”
Photo: Icon Brickell, Miami
 Dhaka is built on one of the most challenging sites for an urban area. It sits on one of the world’s largest river deltas (the Ganges-Brahmaputra). The combined river course (called the Padma) is only miles to the west.
Dhaka is built on one of the most challenging sites for an urban area. It sits on one of the world’s largest river deltas (the Ganges-Brahmaputra). The combined river course (called the Padma) is only miles to the west. 


