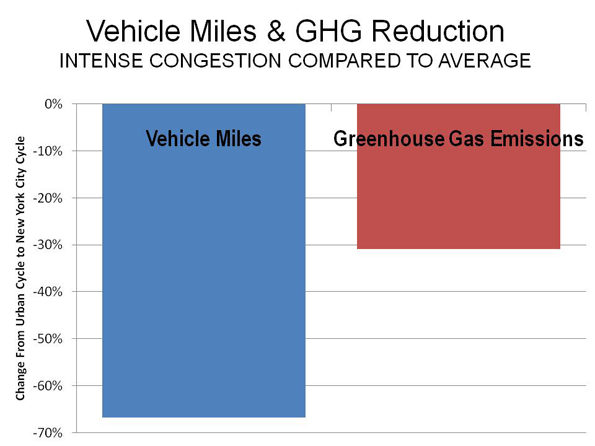
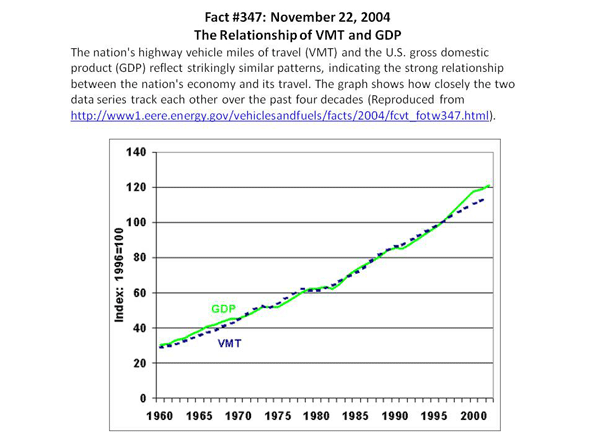
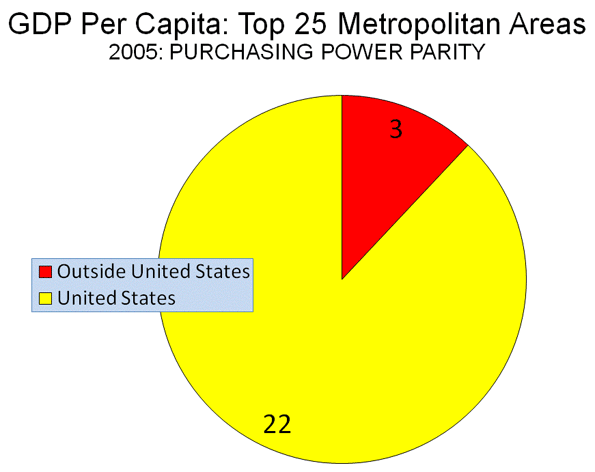
Barack Obama ran for President with his headquarters in downtown Chicago. Obama’s election night victory speech was just blocks away in Chicago’s Grant Park. To historians of organized crime both locations are located in a significant place: Chicago’s old First Ward. This valuable plot of land is where Chicago’s Democratic Machine and Al Capone’s criminal organization both began. The connection between the two is of great historical significance. Why? Because the Chicago Mob is nothing but an outgrowth of Chicago’s old First Ward Democratic Organization.
The First Ward contained not only the big office buildings of downtown Chicago but also the near south side which contained the Levee (which was America’s premier vice district for prostitution and gambling) in the early part of the twentieth century. Crime researcher Ovid Demaris explains the origins of the First Ward in the first decade of the Twentieth Century:
The chain of command on the levee started at the top with committeeman Michael “Hinky Dink” Kenna and Alderman Bathouse John Coughlin, bosses of the First Ward, the wealthiest plot of real estate (it contains the Loop) in the Midwest. Their bagman was Ike Bloom, a ward heeler and proprietor of a busy dance hall. The next in command was Big Jim Colosimo, an Italian pimp and restaurateur, who started out as a street cleaner. When he married a madam with a pair of dollar houses, Hinky Dink made him a precinct captain in charge of getting out the Italian vote.
By 1912, Jim Colosimo owned 200 brothels, many located in the First Ward. Colosimo is considered by the FBI to be the first head of the Chicago Mob. His base – organizing street sweepers – presaged the powerful role of public unions in Chicago nearly a century later.
Another important First Ward Democratic precinct captain with connections to Kenna and Coughlin was Harry Guzik. Guzik, like Colosimo, was a pimp who passed his political connections on to his son, Jake. Jake Guzik, also a pimp, became the Chicago Mob’s accountant until his death in 1956. Guzik (note 1) was considered the number two man in the Chicago Mob and the financial brains behind the operation until his death in 1956.
In 1909, Colosimo reached out for help in running his expanding empire. New York street gang leader John Torrio came to Chicago to help manage Colosimo’s empire from Colosimo’s Cafe at 2126 South Wabash Avenue at the south end of the First Ward.
In 1919, on the eve of Prohibition, Torrio wanted the operation to expand into bootlegging. Colosimo was content with the money he was making from the existing rackets. So, Torrio had Colosimo executed. Before Colosimo was executed, Torrio had brought to Chicago a street thug he mentored in New York: Al Capone. With Colosimo, out of the way, Torrio moved the operation headquarters a few blocks away to the 2222 S. Wabash. Capone acted as the underboss of the operation.
Torrio and Capone no longer needed to take orders from Kenna and Coughlin of the First Ward. Over time, as the Chicago Mob became wealthy, they began to tell Kenna and Coughlin how to operate. Jake Guzik became the de facto political boss of the First Ward issuing orders to Kenna and Coughlin.
By 1925, Torrio stepped down as boss after an assassination attempt and left Chicago. Al Capone took over. The mob extended its political influence into other Chicago wards, to the surrounding suburbs of Chicago and even downstate.
Capone’s reign only lasted until 1932, but his legacy and organization were just beginning. Robert Cooley and Hillel Levin in their monumental book When Corruption Was King explain:
Oddly enough, far less is known about his successors and their grip on the city during the last half of the twentieth century. But that is when Chicago’s Mafia became the single most powerful organized crime family in American history. While Mob bosses knocked each other off on the East Coast, in Chicago they united into a monolithic force called the Outfit…By the Seventies, the FBI reported that Chicago’s Mob controlled all organized criminal activity west of the Mississippi – including and especially Las Vegas. Millions were skimmed from casinos like the Tropicana and the Stardust, and bundles of cash, stuffed in green army duffel bags, found their way back to the Outfit’s bosses.
By the 1950s, the Chicago Mob realized it would be more efficient to send one of their own “made members” to City Council (Note 2). John D’Arco was a high ranking made member elected to City Council in 1951. D’Arco also became the First Ward Democratic Committeman, the boss of the precinct captains. He got caught by the FBI meeting with Sam Gianciana near Chicago’s O’Hare Airport, in 1962, and stepped down from City Council but kept his ward committeemanship until the 1990s. He was a regular visitor to Mayor Jane Byrne’s office in the late 1970s and early 1980s.
In 1968, the Chicago Mob sent Fred Roti, one of their most effective high ranking made members, to the City Council. Roti grew up in the First Ward just blocks away from Capone headquarters. He was a precinct captain for John D’ Arco. Roti’s success on City Council surpassed John D’Arco. By 1982, the Chicago Tribune reported that Roti was Chicago’s most powerful City Council member:
Roti’s name is always called first during council roll calls, and he revels in that privilege. His initial response gives other administration aldermen their cue as to what Roti – and, therefore, the mayor – wants. It’s often said that roll calls could stop after Roti votes – the outcome is already known. Roti, an affable fellow, controls the Chicago City Council with an iron fist.
According to the Justice Department, Roti was an important co-conspirator in turning a large segment of Chicago’s organized labor movement into a racketeering enterprise.
In the 1980s, criminal defense lawyer Robert Cooley wore a wire on Alderman Roti and his boss Pat Marcy. Cooley became the star witness in a series of sensational trials from an investigation titled Operation Gambat. Roti was indicted in 1990 and “was convicted of RICO conspiracy, bribery and extortion regarding the fixing of criminal cases in the Circuit Court of Cook County, including murder cases involving organized crime members or associates, and was sentenced to 48 months’ imprisonment.” John D’Arco’s son was also indicted and convicted of taking bribes. John D’Arco Jr. was the Chicago Mob’s man in Springfield, rising to the position of Assistant Majority Leader of the Illinois Senate.
The Chicago Mob was never the same. Without Roti and Marcy, the judges could no longer be bribed into allowing the mob hitmen back on the street. The regular killings, to get people in line, stopped. The First Ward got mapped out of existence in the early 1990s. Senior FBI agent William Roemer explained the devastation to the Chicago Mob by Robert Cooley’s “Operation Gambat”:
As a result of Gambat, Tony Accardo’s people were deeply wounded. For decades Pat Marcy and John D’Arco, Sr., has been to Accardo what Hinky Dink and Bathhouse John were to Colosimo, Capone, and Nitti. Since 1950 – some forty years – John D’ Arco had been there. They were themselves a great one-two punch for Accardo and for Greasy Thumb…
So, the Chicago Mob has been in retreat. But, it still exists and has great access to power.
In 1999, at Fred Roti’s funeral, his best friend on City Council Alderman Bernard Stone spoke. Alderman Stone, set the record straight in case there was any illusion of how important Fred Roti was in the history of Chicago:
“Our skyline should say ‘Roti’ on it,” Stone said at the funeral. “If not for Fred Roti, half the buildings in the Loop would never have been built.”
At the time of his indictment in 1990, Roti was Chairman of the City Council Buildings Committee. This is the key committee in Chicago that determines the height of buildings.
After Fred Roti’s funeral, his body was laid to rest at the Mount Carmel Cemetery in the Chicago suburb of Hillside. Roti was buried in Section 34 of the Cemetery. Just a short walk from Roti’s casket in Section 35 of the Cemetery is Al Capone’s grave.
The man who brought down the First Ward, FBI informant Robert Cooley, is back in the news. Days after Governor Rod Blagojevich was arrested, WLS TV reported that according to Cooley, Blagojevich was bookmaker for the Chicago Mob. WLS TV did a follow up report in which a former senior FBI agent confirmed that Cooley made bookmaking allegations about Blagovich in the 1980s. This isn’t the only mob tie concerning Blagojevich. His wife is related to the recently deceased Chicago Mob Consiglerie Alphonse Tornabene.
Lurking in the background of the Blagojevich criminal case is a casino license that was to be auctioned off. The license was by far the most valuable asset Blagojevich had control over. Blagojevich wanted the casino built in the Chicago Mob dominated suburb of Rosemont. The Chicago Mob also wanted the casino built there. In November of 2005, Blagojevich brought in Eric Holder to give Rosemont a clean bill of health. Holder and Blagojevich had a news conference outside the Thompson Building, which is in the old First Ward.
The mob connection extends beyond the Blagojevich case. In their drive to retain President Obama’s U.S. Senate seat, the frontrunner is Obama’s friend, Alexi Giannoulis. He is so tainted by Chicago Mob allegations that Illinois Democratic Party Chairman Mike Madigan refused to endorse him in a past race for State Treasurer.
As the Senate race heats up, these connections between the Chicago machine and the mob could prove embarrassing at least for the man the machine has helped elevate to the White House.
Note 1: Jake “Greasy Thumb” Guzik earned his nickname from counting stacks of money and bribing public officials.
Note 2: In preparation for this article, a former FBI agent identified John D’ Arco Sr. as a high ranking made member of the Chicago Mob. His status was at the level of a capo in which he was allowed to run a political crew.
Steve Bartin is a resident of Cook County and native who blogs regularly about urban affairs at http://nalert.blogspot.com. He works in Internet sales.
 Yet physical public space continues to serve as medium of the new Street Art form. Stickers, tags, skateboards, and tattoos are all viewed on the street, offering a means to carry this new art form into the next century. The so-called “cutting edge” artists have retreated into their private studios to conceive their next moves in video or computers, but the street artists have taken over the city.
Yet physical public space continues to serve as medium of the new Street Art form. Stickers, tags, skateboards, and tattoos are all viewed on the street, offering a means to carry this new art form into the next century. The so-called “cutting edge” artists have retreated into their private studios to conceive their next moves in video or computers, but the street artists have taken over the city.
 Graffiti’s barrage of skulls, vacant-eyed cartoon children, and other signs of death and destruction are easy to ignore, but they are telling us something important about the urban environment. The sooner we stop and examine this evidence, the sooner we can begin a process to find common ground, and to seek out a shared vision that does not divide the urban world into an us-and-them mentality. Street art simply puts visual form to the voices we have so long shut out of the urban conversation.
Graffiti’s barrage of skulls, vacant-eyed cartoon children, and other signs of death and destruction are easy to ignore, but they are telling us something important about the urban environment. The sooner we stop and examine this evidence, the sooner we can begin a process to find common ground, and to seek out a shared vision that does not divide the urban world into an us-and-them mentality. Street art simply puts visual form to the voices we have so long shut out of the urban conversation.
 The graffiti artists have offered a philosophical change-up that should not be overlooked. The conversation about postmodern art seemed to have reached a dead end some time ago; artists
The graffiti artists have offered a philosophical change-up that should not be overlooked. The conversation about postmodern art seemed to have reached a dead end some time ago; artists