In a year when modest – if not negligible – growth could nudge a city toward the top of the Best Cities for Jobs rankings you would suspect there to be little opportunity for big leaps up the scale. On the other hand, one could easily expect that there would be some places whose economic fortunes would resemble a vertigo-inducing fall.
A look at the 2009 rankings confirms that there are many cities whose job-creating engines have sputtered.
Among 336 cities in the rankings 46 cities fell more than 100 places compared to their position in 2008. Below are seven places that took the biggest fall and plummeted more than 200 places compared to 2008.
| Seven Falling Stars: Ranking Fell More than 200 Places 2008-2009 | |||
| City | 2008 | 2009 | Rank Change |
| Port St. Lucie, FL | 88 | 290 | -202 |
| Pensacola-Ferry Pass-Brent, FL | 98 | 302 | -204 |
| Reno-Sparks, NV | 104 | 314 | -210 |
| Myrtle Beach-North Myrtle Beach-Conway, SC | 10 | 230 | -220 |
| Prescott, AZ | 26 | 252 | -226 |
| Winchester, VA-WV | 73 | 299 | -226 |
| Yuma, AZ | 33 | 266 | -233 |
The Big Downstroke
Yuma, Arizona’s precipitous decline of 233 places is partly the result of its once envious position among the top ten percent of cities in 2008. It appears they came late to the economic wake that hit some towns with the collapse of the housing bubble in Arizona, Florida and Nevada as early as 2007 . In many communities in these states 2008 reflected things getting worse as commercial and industrial construction activity also dropped off.
The good news for Yuma, according to Paul Shedal of Yumastats.com is that the “biggest economic pillars,” agriculture and government, have remained relatively unscathed by the recession providing a fallback point that other markets don’t have. This means that our worst case scenario for recession “harm” would be returning to our pre-boom level of economic sustainability rather than some depression abyss.”
Another falling star, Winchester, Virginia, fell 226 places in the rankings, experiencing what some in northern Virginia have described as a dramatic turnaround. Manufacturing in this part of the Northern Shenandoah Valley is linked to housing and vehicles, two industries hard hit lately. American Woodmark, the third-largest kitchen and cabinetmaker in the U.S. scaled back production as sales to homebuilders continue to fall. The services sector, once a bright spot for the region, has been shedding jobs in the midst of the recession. And major retailers like Linens N’ Things and Circuit City recently closed.
One bright spot in the Winchester area’s economy is the increase of jobs in the federal government sector, an advantage of its 75 mile proximity to the nation’s capitol. In 2008, the federal government added 400 jobs to the local economy at the Federal Emergency Management Agency offices in Stephenson and the FBI training and recruitment center in Winchester.
Rising Stars
Even in a troubled economy one expects that some places will thrive simply through determination and bold leadership moves, the foresight to have done the right things, or the luck of the draw. Everyone shares a hopeful optimism that a meteoric rise can offer a glimpse of things to come and perhaps offer a roadmap to a more prosperous future.
| Rising Stars: Top Five Rankings Climbers 2008-2009 | |||
| City | 2008 | 2009 | Rank Change |
| Lafayette, IN | 287 | 85 | 202 |
| Champaign-Urbana, IL | 267 | 83 | 184 |
| Sioux City, IA-NE.-SD | 253 | 80 | 173 |
| Lubbock, TX | 242 | 74 | 168 |
| Wheeling, WV-OH | 305 | 138 | 167 |
This year’s rising star is without doubt Lafayette, Indiana with an astounding – and surprising given its Midwestern location – 202-place charge up the rankings from 2008. Like three of the other top five rising stars Lafayette came from a slightly above average position in 2008 to a respectable position in the top 100. These are by no means this year’s best places but their economies are defying the pervasive decline in the national economy.
A visit to the Lafayette Commerce website succinctly tells the tale. “Greater Lafayette wrapped up 2008 with a strong showing.” For Lafayette 2008 was a good year with new capital investments of $600 million, new employment in life sciences industries associated with the Purdue Research Park, and a second new hospital on the way as Greater Lafayette expands its regional healthcare base.
Equally important, Lafayette, like many university and college towns, benefits from the stabilizing presence of Purdue University, the area’s largest employer, which also serves as a force creating new economic opportunities through research, development and access to an educated workforce.
The annual report from Lafayette Commerce concludes by focusing on two key elements of their success. “In Greater Lafayette, we’re choosing not to participate in the national recession by using this opportunity for workforce development and innovation. That’s not to say we have been immune to the troubles of the national economy, but on the whole our community is growing, it’s thriving and improving every day.”
The Impending Future of Boom and Gloom
Science fiction author William Gibson’s famous quip that “the future is already here – it’s just not equally distributed” could have some credence in this year’s rankings –both up and down the scale.
The fastest rising cities boast stable employers in government and universities. They are leveraging this edge to create new opportunities in manufacturing, production agriculture and advanced producer services serving diverse sectors. Growth in health care services to the mixture, until recently one of the few remaining generators of new jobs, has also played a role.
Rising stars like Lafayette have made significant investments in infrastructure and advanced infrasystems, enabling them to create jobs in higher-value, innovation-generating economic activities.
This year’s cities that fell the furthest portend a return to pre-bubble growth patterns. As in the case of Yuma many places will refocus back on their historically strong core industries, like agriculture, and the economic activities that made them viable centers in the first place.
For all cities the ability to innovate locally and take advantage of demonstrated areas of competence represent two key ingredients of success – for building on existing momentum or hitting the reset button for a more prosperous future.
Delore Zimmerman is president and CEO of Praxis Strategy Group and publisher of Newgeography.com
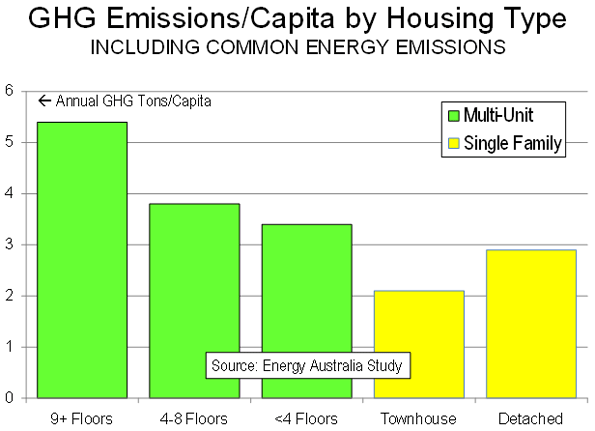
 Forcing Density: Urban consolidation is destroying not only housing affordability, but also the character of Sydney itself. Sydney is an urban area of low density suburbs. It is also an urban area of high rise living. These two housing forms have combined with one of the world’s most attractive geographical settings to create an attractive and livable urban area.
Forcing Density: Urban consolidation is destroying not only housing affordability, but also the character of Sydney itself. Sydney is an urban area of low density suburbs. It is also an urban area of high rise living. These two housing forms have combined with one of the world’s most attractive geographical settings to create an attractive and livable urban area.