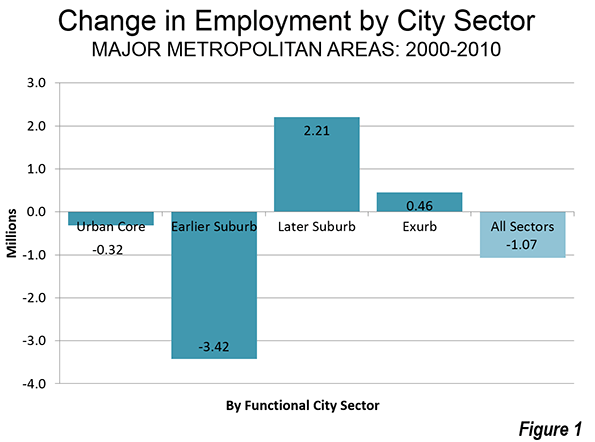
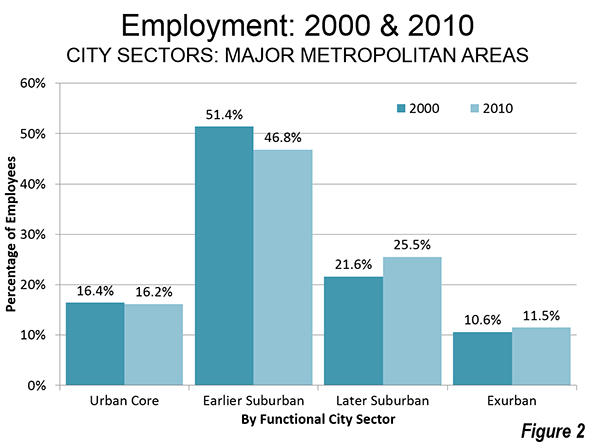
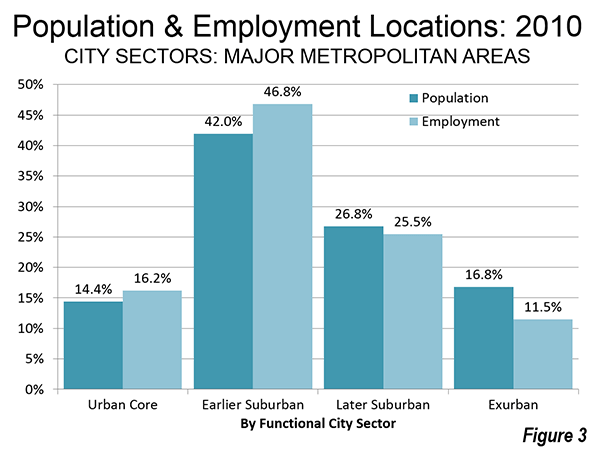
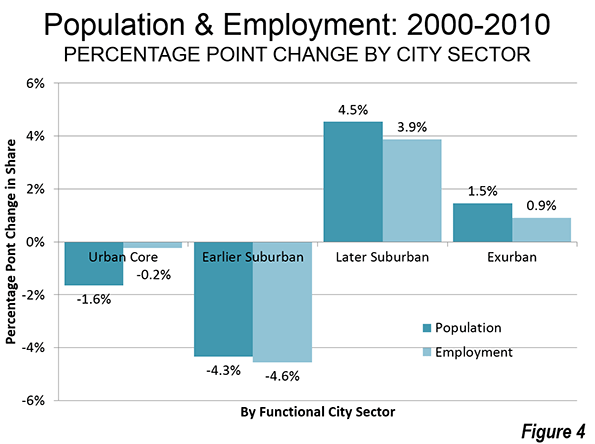
When our urban pundit class speaks of the future of cities, we are offered glittering images of London, New York, Singapore, or Shanghai. In reality, the future for most of the world’s megacities—places with more than 10 million people—may look more like Dhaka, Mumbai, or Kinshasa: dirty, poverty- and disease-ridden, and environmentally disastrous.
Harvard’s Ed Glaeser suggests that megacities grow because “globalization” and “technological change have increased the returns to being smart.” And to be sure, megacities such as Jakarta, Kolkata (in India), Mumbai, Manila, Karachi, and Lagos—all among the top 25 most populous cities in the world—present a great opportunity for large corporate development firms and thrilling treasure troves for both journalists and academic researchers. But surely there’s a better alternative to celebrating misery, as one prominent author did recently in aForeign Policy article bizarrely entitled “In Praise of Slums.”
Bigger is no longer better.
Let’s start with the idea that, in an urbanizing world, bigger is no longer necessarily better. In a recent study I conducted with Ali Modarres, Aaron Renn, and Wendell Cox for Singapore’s Civil Service College and Chapman University, we ranked cities by importance as global centers. Of the world’s estimated 29 megacities, only a handful made into the top 20. Most leading megacities were either long-established Western cities—Tokyo, New York, London, Los Angeles—or located in booming East Asia, including Beijing, Shanghai, and Seoul.
Notably missing are fast-growing growing megacities such as Lagos, Karachi, and Dhaka, as well as the 16 additional megacities—mostly in developing countries in Africa and south Asia—that will pass the 10 million mark by 2030. Yet despite their girth, the majority of megacities are not particularly attractive for foreign investors or as locations for regional corporate offices. These firms tend to cluster instead in westernized cities such as Singapore, Hong Kong, or Dubai, and visit places like Jakarta, Manila, and Cairo only when necessary.
History drives some of this. The great global cities rose as centers of industry and trade, while developing from there an excellence in related services. They created pockets of a more advanced economy to serve the predominately rural hinterland, or in some cases colonial possessions. This imperial relationship spurred the rise of London, Paris, and New York in the early 20th century, and also that of Tokyo, still the world’s biggest city.
Some new megacities, some such as Guangzhou and Shenzhen (which in 1979 had roughly 30,000 people, compared to its 10.6 million today) have a real economic shot at becoming top global cities due to China’s emergence as the world’s workshop. But, as we explain in a recent paper from Chapman University, this is far less the case for most megacities in the developing world.
Unlike their Chinese counterparts, these megacities’ expansion has not been driven by economic growth but more by bringing people from their own impoverished countryside into the city. Critically, in contrast to the peasants who came to Tokyo in the ’50s or Shanghai in the ’90s, there is no huge demand for an industrial workforce in cities in South Asia, Africa, or Latin America, where manufacturing is far less prevalent—manufacturing’s share of India’s GDP, for example, is half that of China.
Here’s the difficult truth: Most emerging megacities, particularly outside of China, face bleak prospects. Emerging megacities like Kinshasa or Lima do not command important global niches. Their problems are often ignored or minimized by those who inhabit what commentator Rajiv Desai has described as “the VIP zone of cities,” where there is “reliable electric power, adequate water supply, and any sanitation at all.” Outside the zone, Desai notes, even much of the middle class have to “endure inhuman conditions” of congested, cratered roads, unreliable energy, and undrinkable water.
The slums of Bangladesh’s capital, Dhaka, swell by as many as 400,000 new migrants each year. Some argue that these migrants are better off than previous slum dwellers since they ride motorcycles and have cellphones. Yet access to the wonders of transportation and “information technology” don’t compensate for physical conditions demonstrably worse than those endured even by Depression-era poor New Yorkers. My mother’s generation at least could drink water out of a tap and expect consistent electricity, if the bill was paid, something not taken for granted by their modern-day counterparts (PDF) in the developing world.
More serious still, the slum dwellers face enormous risk from unsafely built environments. Traffic, as anyone who has spent time in these cities easily notices, poses particular threats to riders and pedestrian alike. According to researchers, developing countries now experience a “neglected epidemic” of road-related injuries accounting for 85 percent of the world’s traffic fatalities.
And don’t drink the water, please. Nearly two-thirds of the sewage in the megacity of Dhaka, with 15 million people, is untreated. As Dr. Marc Reidl, a specialist in respiratory disease at UCLA, puts it, “Megacity life is an unprecedented insult to the immune system.”
Cities of disappointment.
Over these environmental problems loom arguably greater social ones. Many of the megacities—including the fastest growing, Dhaka—are essentially conurbations dominated by very-low-income people; roughly 70 percent of Dhaka households earn less than $170 (U.S.) a month, and many of them far less. “The megacity of the poor,” is how the urban geographer Nazrul Islam describes his hometown.
Inequality is expanding in most of these places. A recent Euromonitor International study found that larger “city size remains the key explanatory factor for income inequalities across the world’s urban agglomerations.” Even megacities that we might refer to as “middle income,” such as Tehran and Istanbul, are becoming what geographer Ali Modarres calls “cities of disappointment.” In many cases, high housing prices and a lack of space have already reduced the birthrate to well below the replacement level. Increasingly, many women are choosing to remain single—heretofore something rare in these countries.
One scholar, Jan Nijman, suggests that most gains in recent years have accrued to the upper echelons of the middle class in Indian cities while “the ranks of the lower middle income classes have shrunk, and the ranks of the poor have expanded rapidly.” Much of the growth in a perceived middle class, Nijman argues, is based not on income but on consumption driven by credit. The informal sector—drivers, stall-owners, repair-people, household industries—account for much of Mumbai’s employment growth.
Housing costs are the key here. Researcher Vatsala Pant estimates a monthly total household “middle class income” in Mumbai at 40,000-50,000 rupees; equivalent to less than $1,000 U.S. dollars. Yet monthly salaries for teachers, police officers, and other mid-level jobs are often half that amount. Not surprisingly, even these workers often find themselves living in slum neighborhoods, which are also known as jhopad-patti, jhuggi-jhopadi or busties. “It’s the dream of an immigrant for a place in Mumbai … and ends up with a slum,” she notes.
Is there a better alternative?
Future urbanization does not need to pose a choice between rural hopelessness and urban despair. This is a critical issue, even for high-income countries. The rise of a mass of poor slum dwellers—estimated as high as 1 billion—threatens the social stability not only of the countries they inhabit, but the world, as they tend to generate high levels of both random violence and more organized forms ofthuggery, including terrorism.
Fortunately, an alternative structure of urbanization is beginning to emerge that emphasizes a spreading diversity of cities as opposed to gigantic agglomerations. In the coming decade, McKinsey predicts megacities will underperform economically and demographically, as growth shifts to “fast growing middleweights,” many of them in China and India.
There needs to be a far greater emphasis on these smaller cities, as well as working to develop a viable economy for the villages. In India, migration to large cities already is beginning to slow, as more potential migrants weigh the costs and opportunities of making such a move as opposed to staying closer to home. This phenomenon has been called “rurbanization” and was an important provision of the campaign of India’s new prime minister, Narendra Modi, who implemented such programs as chief minister of the state of Gujarat. Modi speaks of human settlements with the “heart of a village” and developing “the facilities of the city.”
A growing array of critics understand the need to break with the megacity mantra. Ashok R. Datar, chairman of the Mumbai Environmental Social Network and a longtime adviser to the Ambani corporate group, says the emerging megacities of the developing world need to stop emulating the Western model of rapid, dense urbanization. “We are copying the Western experience in our own stupid and silly way,” Datar says.
He suggests a policy focusing on more human-scale growth. One does not have to be a Gandhian idealist to suggest that Ebenezer Howard’s “garden city” concept—conceived as a response to miserable conditions in early 20th century urban Britain—may be a better guide to future urban growth than the current trend of relentless concentration.
The “garden city” alternative could help ameliorate the downsides of mass urbanization in China as well, where the government is seeking to move 250 million more people from the countryside to urban areas over the next decade. “There’s this feeling that we have to modernize, we have to urbanize, and this is our national-development strategy,” said Gao Yu, China country director for the Landesa Rural Development Institute, based in Seattle. Referring to the disastrous Maoist campaign to industrialize overnight, he added, “it’s almost like another Great Leap Forward.”
As the world urbanizes, we need to start thinking about how to make cities better, not simply bigger. The primary goal of a city should not be to enrich already wealthy landlords and construction companies. It should not be to make politicians more powerful. And it certainly should not be mindless, pointless growth for its own sake. Urbanism should not be defined by the egos of planners, architects, politicians, or the über-rich but by what works best for the most people.
This piece originally appeared at The Daily Beast.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and Distinguished Presidential Fellow in Urban Futures at Chapman University, and a member of the editorial board of the Orange County Register. His newest book, The New Class Conflict is now available for pre-order atAmazon and Telos Press. He is author of The City: A Global History and The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050. His most recent study, The Rise of Postfamilialism, has been widely discussed and distributed internationally. He lives in Los Angeles, CA.
Dhaka photo by Wendell Cox.