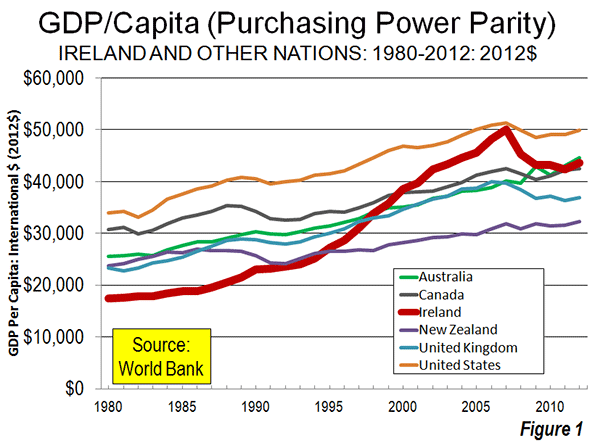
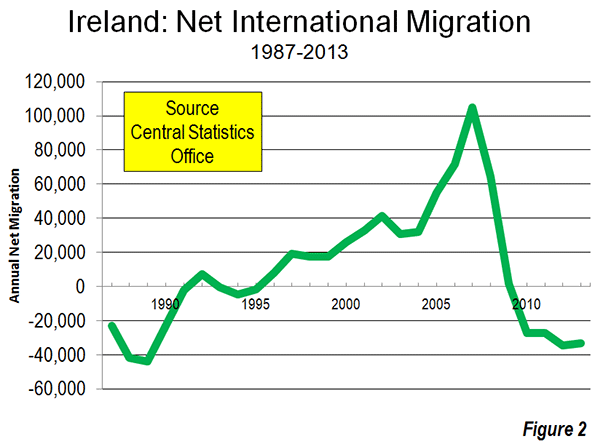
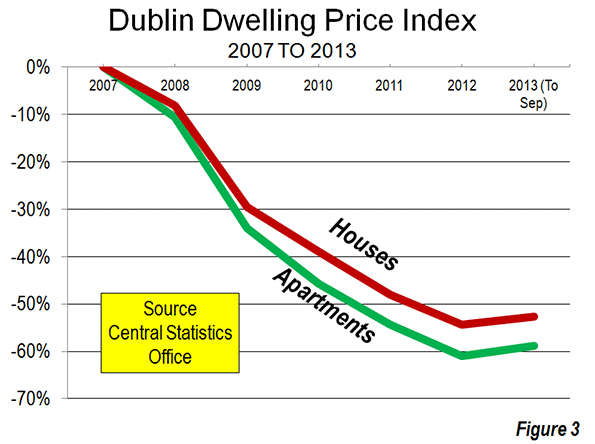
Its image further enhanced by the recent IPO of Twitter, Silicon Valley now stands in many minds as the cutting edge of the American future. Some, on both right and left, believe that the Valley’s geeks should reform the nation, and the government, in their image.
Increasingly, the basic meme out of the Valley, and its boosters, is that, as one venture capitalist put it: “We need to run the experiment, to show what a society run by Silicon Valley looks like.” The rest of the country, that venture capitalist, Chamath Palihapitiya, recently argued, needs to recognize that “it’s becoming excruciatingly, obviously clear to everyone else, that where value is created is no longer in New York, it’s no longer in Washington, it’s no longer in L.A. It’s in San Francisco and the Bay Area.”
But do we really want these people in control? Not if we care at all about privacy, social justice, upward mobility and the future of our democracy.
In control
Let’s start with the Valley’s political agenda, which is increasingly enmeshed with that of the Obama-led Democratic Party. The scary thing about the Valley’s political push is not its ideology, which is not particularly coherent, but its unparalleled potential to dominate the national political agenda.
Joe Green, a former roommate of Facebook founder Mark Zuckerberg and head of the Valley lobbying group FWD.us, made this clear in a memo leaked to the political site Politico. Green contended that “people in tech” can become “one of the most powerful political forces” since they increasingly “control” what he labeled “the avenues of distribution.”
Some liberals might be thrilled by the prospect of having such powerful allies, but not if they retain any concern, for example, for civil liberties. This is not merely a matter of informing people, as traditional media does, but using technology to penetrate the private lives of every individual consumer, largely for the economic gain of those “people in tech.”
There certainly seems no desire to curtail their ongoing invasion of people’s privacy. Facebook, for example, recently disabled a key feature in its website to guarantee privacy. The Huffington Post has already constructed a long list of Google’s more-egregious violations. No surprise, then, that Silicon Valley firms have been prominent in trying the quell bills addressing Internet privacy, in both Europe and closer to home.
Increasingly, the oligarchs see invasive technology as something of their divine right, as well as a source of unlimited profits. As Google boss Eric Schmidt put it: “We know where you are. We know where you’ve been. We can more or less know what you’re thinking about.”
Tax avoiders
Perhaps more shocking for many liberal friends of the Valley folks is their attitude toward paying taxes. Here, the tech firms appear to have developed at least as much skill at manipulating the political system as the financial system. The New York Times recently described Apple as “a pioneer in tactics to avoid taxes,” while Facebook paid no taxes last year, despite making a profit of over $1 billion. For its part, Google avoided paying $2 billion by putting its revenue in a shell company in Bermuda.
OK, you can argue that the Valley tech types are a bit arrogant, dismissive of privacy rights and greedy. But is all that offset by their benefit to the economy? Tech industry boosters, such as UC Berkeley’s Enrico Moretti, extol the virtues of the “technigentsia,” claiming they constitute the key to a growing economy. This is also the conventional wisdom in both parties, among both Left and Right and throughout the media.
Yet, over the past decade, the Valley’s record on job creation is far from superlative. From 2000-12, Valley tech companies lost well over 80,000 jobs in high-tech manufacturing. Even with the current surge in hiring, Silicon Valley’s employment in fields related to science, technology, engineering and mathematics has still not recovered all the earlier losses, according to estimates by Economic Modeling Specialists Inc.
You hope your kid may get a good job at Facebook or Google. Well, increasingly those being sought by Valley employers are not the sons and daughters of the American middle – much less, working – class. A recent study by the left-leaning Economic Policy Institute points out that many Valley tech firms would rather hire “guest workers” – now accounting for one-third to one half of all new IT job holders. These workers are valued partly because they will work for less, and do not mind living in crowded, overpriced apartments as much as do native-born Americans.
The Valley defends its expanding the ranks of what Indians often refer to as “technocoolies,” based on an alleged critical shortage of skilled workers in the STEM fields. But, as EPI demonstrates, this country is producing 50 percent more information-technology graduates each year than are being employed, so the preference for foreign guest workers seems more tied to finding cheaper, more-pliable workers.
Even worse, those kinds of tech jobs being created in the Valley produce opportunities only for a narrow subset of highly skilled, or well-connected, employees. As industrial jobs – the mainstay of the Valley’s heavily minority working and middle classes – have cratered, most new jobs in the Valley, according to an analysis by the liberal Center for American Progress, earn less than $50,000 annually, far below what is needed to live a decent life in this ultrahigh-cost area.
New Feudalism
Rather than a beacon for upward mobility, the Valley increasingly represents a high-tech version of a feudal society, where the vast majority of the economic gains go to a very select few. The mostly white and Asian tech types in Palo Alto or San Francisco may celebrate their IPO windfalls, but wages for the region’s African American and large Latino populations, roughly on third of the total, have actually dropped, notes a recent Joint Venture Silicon Valley report, down 18 percent for blacks and 5 percent for Latinos, from 2009-11.
Meanwhile, the poverty rate in Santa Clara County since 2001 has soared from 8 percent to 14 percent; today one of four people in the San Jose area is underemployed, up from a mere 5 percent just a decade ago. The food-stamp population in Santa Clara County, meanwhile, has mushroomed from 25,000 a decade ago to almost 125,000 last year. San Jose, the Santa Clara County seat, is also home to North America’s largest homeless encampment, known as “the Jungle.”
What the Valley increasingly offers America is an economic model dominated by the ultrarich, and generally well-educated, with few opportunities for working-class people, women and minorities. As Russell Hancock, president of Joint Venture Silicon Valley, recently acknowledged, “Silicon Valley is two valleys. There is a valley of haves, and a valley of have-nots.”
This is a far cry from the kind of aspirational place for middle- and working-class people that the Valley represented just a decade or so ago. Instead, the Valley, and its urban annex San Francisco, increasingly resemble a “gated” community, where those without the proper academic credentials, and without access to venture funding, live a kind of marginal existence in crowded housing, or are forced to commute to distant jobs as servants to the Valley’s upper crust.
This exclusive future is being further enhanced by gentry liberal policies – as opposed to traditional social democratic policies – widely embraced by the Valley leadership. Instead of looking to spark growth in construction, logistics, manufacturing and other traditional sources of middle-class employment, the Valley’s leadership generally embrace “green” policies that limit suburban homebuilding, drive up energy prices and otherwise make it impossible for businesses capable of offering better paying blue-collar, or even middle-management work.
None of this suggests that the Valley does not have a critical role to play in the recovery of the American economy. Just like Wall Street, Beverly Hills or, for that matter, Newport Beach, clusters of well-connected and well-educated people play a critical role in taking risks in investment and innovation, whether it involves technology, finance, fashion or media. Yet given their dangerous hubris, disdain for privacy rights, lower rates of tax compliance and minimal ability to create middle-class jobs, the Valley’s elite should not be held up as supreme role models, much less the hegemons, of the Republic. That is, unless we have decided that we wish to live in a high-tech, 21st century version of a highly ossified, feudal society.
This story originally appeared at The Orange County Register.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and Distinguished Presidential Fellow in Urban Futures at Chapman University, and a member of the editorial board of the Orange County Register. He is author of The City: A Global History and The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050. His most recent study, The Rise of Postfamilialism, has been widely discussed and distributed internationally. He lives in Los Angeles, CA.