Victor’s Restaurant, a nondescript coffee shop on a Hollywood side street, seems an odd place to meet for a movement challenging many of Los Angeles’s most powerful, well-heeled forces. Yet amid the uniformed service workers, budding actors, and retirees enjoying coffee and French toast, unlikely revolutionaries plot the next major battle over the city’s future. Driving their rebellion is a proposal from the L.A. planning department that would allow greater density in the heart of Hollywood, a scruffy district that includes swaths of classic California bungalows and charming 1930s-era garden apartments. The proposal—which calls for residential towers of 50 stories or more along Hollywood Boulevard, where no building currently tops 20 stories—has been approved unanimously by the city council and will now probably be challenged in court.
That proposal isn’t the only densification plan making its way through city hall. Another is a “wholesale revision” of L.A.’s planning code that would strip single-family districts of their present status and approve the construction of rental units in backyards and of high-density housing close to what are now quiet residential neighborhoods. “We are going to remake what the city looks like,” Mayor Antonio Villaraigosa told the New York Times in March. Richard Abrams, a 40-year Hollywood resident and a leader of SaveHollywood.Org, puts it differently: “They want to turn this into something like East Germany. This is all part of an attempt to worsen the quality of life—to leave us without backyards and with monumental traffic.” The rebels gathered at Victor’s note that many of the density scheme’s most tenacious advocates, such as councilman and mayoral aspirant Eric Garcetti, live in leafy residential areas removed from the traffic nightmare that the new development would bring.
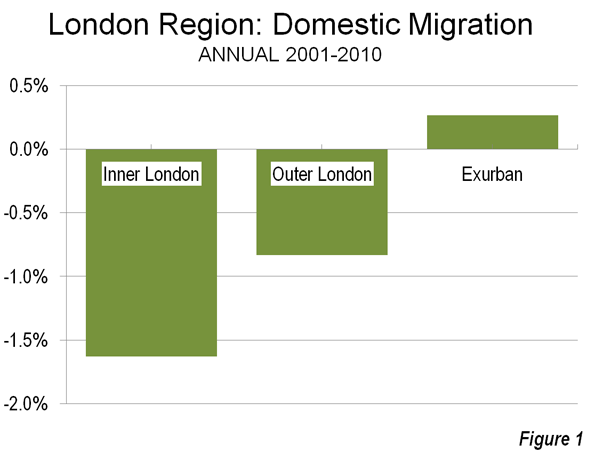
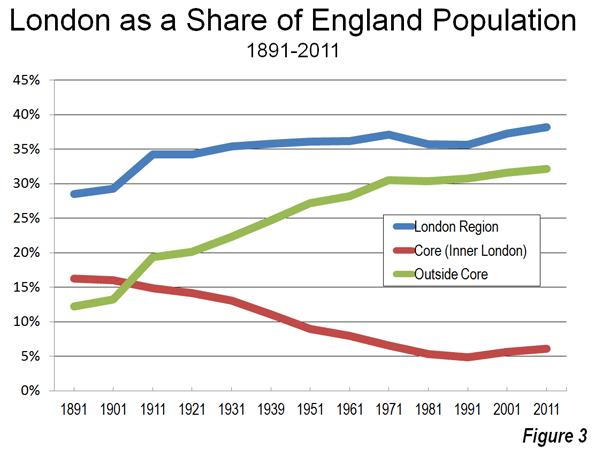
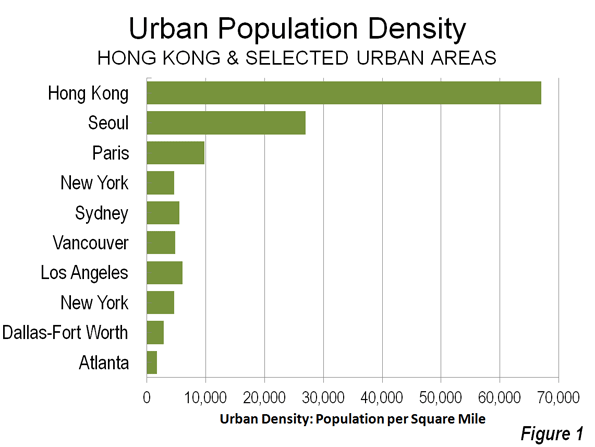
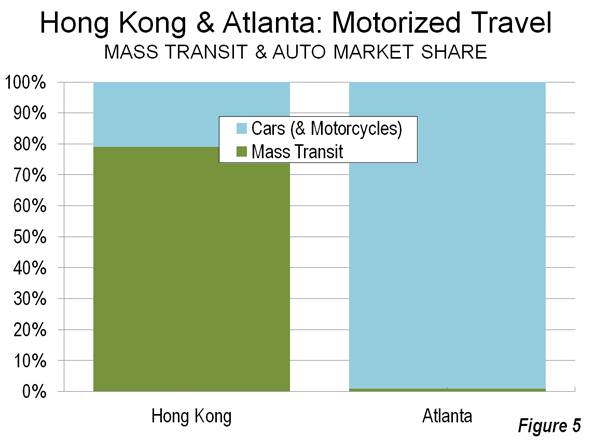
Despite public outcry, Los Angeles’s political, labor, and real-estate elites almost unanimously support what Villaraigosa calls “elegant density,” pushing for the transformation of the city’s low-rise, multipolar, and moderate urban form into something more like vertical, transit-oriented New York. Dissenters from this view are often called “antiurban.” But to activists like Susan Swan, who leads the Hollywood Neighborhood Council, it’s really about letting L.A. remain L.A. As she notes, New York and Los Angeles have evolved in radically different ways. New York, particularly its urban core, was built largely before the automobile age. Manhattan and the surrounding boroughs are transit-dependent: 56 percent of commuters take public transportation. By contrast, L.A. remains overwhelmingly car-oriented, with only 11 percent of commuters using public transit, despite the $8 billion invested in rail lines over the past two decades. Los Angeles’s downtown is nowhere near as important as New York’s; just over 2 percent of L.A. metropolitan-area employment is downtown, compared with about 20 percent in greater New York. Instead of revolving around one mega-center, L.A. boasts commercial centers in each of its major neighborhoods, many of which are close to single-family homes and low-rise apartments.
This dispersion creates an aesthetic rarely appreciated by density boosters, enabling residents to enjoy fully L.A.’s unique ambience—its superb Mediterranean climate, lush foliage, tall trees, and, most of all, magnificent light. Even when you walk down Hollywood Boulevard, what’s most striking is not the skyline but the steep hills, framed by palms, rising toward a clear blue sky. For a glimpse of the Hollywood imagined by Villaraigosa and his confederates, take a look at the much-reviled Hollywood and Highland Center, home of the Dolby Theatre, which hosts the Academy Awards. Instead of brilliant light and blue sky, visitors confront a boxy hulk that obscures the hillside views.
Swan and other activists deny that opposing mass densification is synonymous with opposing development. With many nearly abandoned blocks and downscale businesses around its core, Hollywood certainly could use a face-lift. But local community activists want development to be congruent with the area’s architectural traditions. “There is real dismay in our community that the opportunity to make Hollywood a world-class destination is slipping away to these ‘Manhattanization’ fantasies,” says Swan, a retired bookbinder. “We have always said that we love Manhattan—in New York.”
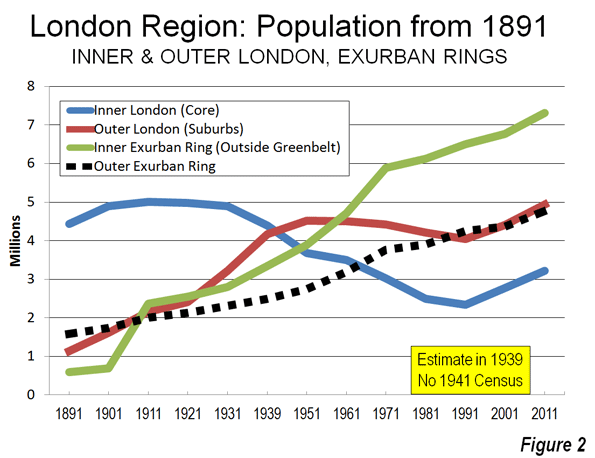
Demographics also make a mockery of the densification argument. With the exception of downtown, most of the central parts of Los Angeles have either stagnated or lost population over the last 20 years. Hollywood, for example, shrank from 213,000 residents in 1990 to 198,000 today. Within the last decade, Los Angeles County’s growth slowed to barely 3 percent—roughly one-fifth the rate that it enjoyed during the go-go 1980s, a period of extraordinary prosperity in the region. Yet Garcetti, Villaraigosa, and their allies continue to base their grands projets, as the French would call them, on outmoded assumptions of exploding economic and population growth. Particularly revealing is the experience of the Residences at W Hollywood, a luxury-condo project located a stone’s throw from the proposed new high-rise towers in Hollywood. According to recent reports, only 29 out of 143 units have sold since the project opened in May 2010, despite prices that have been slashed by more than half. The market, in short, is unwilling to embrace density here, “elegant” or otherwise.
Yet the city keeps planning big, as though hordes of the well-heeled were eager to move to L.A. It has offered massive subsidies, accounting for nearly $640 million in tax breaks, to three hotel projects. Public bonds are also underwriting expansion of L.A.’s convention center and a new football stadium, which received unheard-of exemptions from state and local environmental laws even though the city currently has no football team. “Everything we are doing, like the mass build-out of transit and density, provides an excuse for creating things people don’t want,” says Cary Brazeman, founder and president of L.A. Neighbors, a citywide alliance of neighborhoods, and a candidate for city controller in 2013. “To build this city back, you have to approach things in ways that enhance the gloriousness of L.A. Sunshine, it’s transcendental. You take away the sun, hell, I’m leaving my condo.”
Without backing from rent-seekers or unions, Brazeman’s campaign runs on a shoestring. His better-funded opponent, former police officer Dennis Zine, epitomizes L.A.’s dysfunctional political system, drawing both his generous police pension and a city council salary of $178,000, the highest in the nation. Though he represents a largely residential area in the San Fernando Valley, Zine has proved a reliable vote for the elaborate “incentives” that encourage large, often uneconomic, building and ever-greater spending on transit projects. A more serious challenge to the existing order could come from Zev Yaroslavsky, a member of the Los Angeles County Board of Supervisors. Yaroslavsky hasn’t declared his candidacy for mayor yet, but he is known to be skeptical of the proposed remake of L.A. The question is whether he’s too comfortable with the status quo to take on the “elegant density” agenda.
For now, the best hope for Los Angeles resides with the activists who meet at Victor’s. They may not scare the political incumbents or the real-estate developers, but they do represent a motivated opposition to the effort to recast the city. “Los Angeles started because people want to live here,” Abrams says. “We are not a cut-rate New York and don’t want to be. The developers and the politicians want to take away all that makes us unique and get rid of us tomorrow. It won’t be so easy.”
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University, and contributing editor to the City Journal in New York. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050, released in February, 2010.
This piece originally appeared in The City Journal.