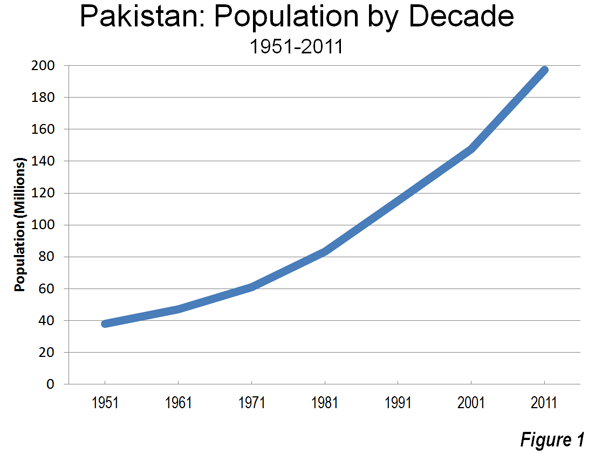
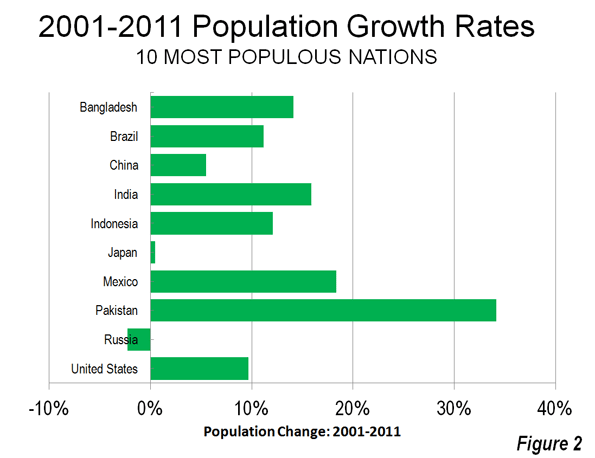
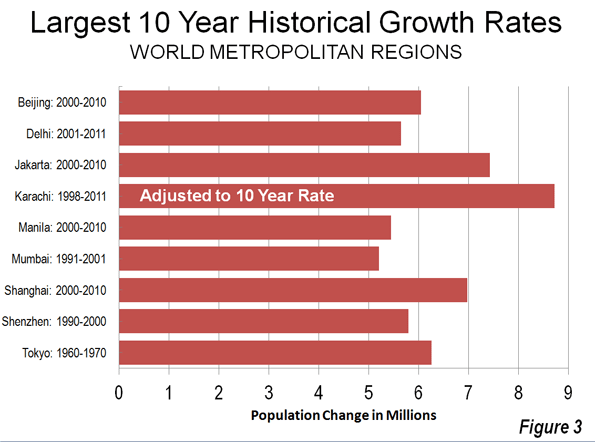
Last week Hong Kong’s new leader Leung Chun-ying was sworn into office by Chinese President Hu Jintao. The ceremony coincided with the 15th anniversary of the British handover of Hong Kong to China so there was plenty of rhetoric about ‘strengthening ties with the motherland’. Yet not far from the ceremony, tens of thousands of Hong Kong citizens marched in protest showing discontent with growing inequality and what they perceive as Beijing’s increasing assault on the territory.
The relationship between Hong Kong and mainland China is complex. Beijing for the most part has kept its promise to uphold the ‘one country, two systems’ mandate. Officially, Hong Kong is considered a ‘Special Administrative Region’ (SAR), which means that it is treated as a separate country from an immigration standpoint and continues to circulate its own currency, the Hong Kong dollar. Hong Kong also retains an independent legal and judicial system inherited from the previous British rulers.
Most importantly, Hong Kong has avoided the draconian media censorship common on the mainland. A free press is consistent with its reputation as a global center of banking and commerce. Hong Kong’s ease of trade and doing business frequently leads it to being named one of the world’s freest economies.
So if Beijing continues to hold up its end of the deal, why do so many Hong Kong residents march in protest? The relationship is more nuanced than it appears on the surface. Politically, Hong Kong residents do not have the freedom to elect their leader (CY Leung was appointed by a 1,200-person electoral college made up primarily of pro-China business leaders), although democratic elections are set to commence in the next five years. Underlying this frustration is what Hong Kong residents see as an infiltration of growing mainland influence on the city.
On the ground, Hong Kong experienced a huge increase in mainland tourists to the city since the handover. Hong Kong doesn’t have the same high tax rate on imported goods that mainland China does, so mainlanders flock to the city primarily for shopping, hunting for bargains on electronics and luxury fashion brands. It is not uncommon to see long queues of mainland tourists in front of shops of famous fashion brands like Gucci, D&G or Prada. The droves of mainland shoppers spending money in Hong Kong are great for the local economy, but many locals decry the constant flow of tourists as invading ‘locusts’.
Yet more significant than what is happening on the ground is what is taking place high above in the sky. The phenomenon of wealthy mainlanders purchasing real estate in the city has driven housing prices to astronomical levels, approaching the market just before the Asian Financial Crisis of 1997. For well-off Chinese mainlanders, Hong Kong real estate is seen as a safer long-term investment than China’s still somewhat risky real estate market and unpredictable stock market. A severely limited land supply coupled with the fact that a handful of powerful real estate oligarchs control the market for new development means that prices will probably stay high barring another economic crisis.
Land-use policy is perhaps the most critical factor in determining both the future of Hong Kong and the mainland. As anyone who has been to the city can attest to, Hong Kong has some of the best infrastructure in the world, including a first-class international airport, extensive rail system and a booming seaport. Much of that infrastructure comes from the city’s land-auctioning system, which is the government’s primary source of revenue. This is also what helps keeps taxes low.
Furthermore, unlike in the U.S., where infrastructure is traditionally financed publicly, Hong Kong’s infrastructure is increasingly built with private funds. For instance, the city’s Mass Transit Railway (MTR) Corporation, founded as a public entity, went fully private in 2000 and is traded on the Hong Kong’s stock exchange. In addition to operating and maintaining the city’s existing rail system, MTR Corporation is responsible for building new lines. What makes MTR Corporation different from most other transit authorities is that its primary earnings do not come from passenger ticket sales but from developing the land on top of and around its metro stations.
Cheung Kong Holdings, led by Hong Kong’s richest man Li Ka-shing, is not only one of the city’s largest property developers, its business interests also include Hutchinson Port Holdings (a port operator that handles 13% of the world’s container traffic) and Hutchinson Telecommunications Limited (which builds and operates mobile phone networks). Sun Hung Kai, another powerful Hong Kong property developer also owns stakes in logistics and telecommunications businesses (although its founders, the Kwok brothers, were recently arrested on corruption charges).
The mode of urban development in mainland Chinese cities is heavily influenced by Hong Kong. Yet instead of powerful corporations, State-Owned Enterprises (SOE), large entities owned by the government, dominate urban development related businesses. China’s land auctioning system is far from perfect, with well-documented instances of corrupt land seizures and the unfair advantages government backed SOEs have in the bidding process over private developers. But with virtually no property taxes in mainland cities, land sales remain the primary source of revenues for local governments to support infrastructure development.
There is growing evidence that suggests China plans to alter the direction of its development model in the coming years by consolidating and privatizing its SOEs. Already, Hong Kong property developers are active in the mainland real estate market with Chinese companies eager to learn from their expertise. The cozy relationship between Hong Kong developers and mainland SOEs is a cause for concern by Hong Kong citizens, as they see their local developers as more interested in appeasing Beijing authorities than providing affordable housing for its own citizens.
Yet this is inevitable. The city of 7 million cannot expect to forever be completely independent of a country of 1.3 billion to which it is now irrevocably attached. This is true even in spite of Hong Kong’s role as an international center of trade.
Throughout history, Chinese culture survived through its sheer mass and cultural osmosis. When CY Leung gave his inaugural speech last week, it was in Standard Mandarin, the official language of China. Although the citizens of Hong Kong are also Chinese, their official language is Cantonese, a completely different and not mutually intelligible dialect. Leung’s move was seen as a slight to the people he was chosen to serve, yet given who he has to report to in Beijing, it made perfect sense.
Adam Nathaniel Mayer is an architectural design professional from California. In addition to his job designing buildings he writes the China Urban Development Blog.
Follow him on Twitter: AdamNMayer
Hong Kong photo by BighStockphoto.com