Just because China has 500 million bikes on the road or tucked away in sheds or courtyards does not mean the two-wheeler has a bright future there, especially in its largest cities.
Such is the growing indifference to the bike in China that no one seems to mind that the national model is manufactured in Taiwan (or under license on the mainland). With a single gear and heavy steel frame, the Giant is ideal for long rides on flat city streets. At a cost of US $180, it is the bike bargain of the world. Nevertheless, the dream for younger Chinese is a Honda scooter.
The problem now in Beijing, Xian, and Guangzhou, if not in the country at large, is that increased prosperity is making city bike riding that much more a thing of the past. Wonderful Asian bike cities like Hanoi have already been lost to the noisy scooter and small car. Is Beijing next?
Three years ago, Beijing was delightful by bike. Initially, I signed up with my friend George at Bicycle Kingdom to teach me the tricks of the narrow streets and the detours around Tiananmen Square. Ever since that first night of instruction, when we rolled out to the Olympic Park and down to the Temple of Heaven, I have been pedaling on my own power in Beijing and savoring every moment in the saddle.
One reason that biking in Beijing is such a pleasure is that riders are accorded privileges lost to those sitting in traffic jams or drifting around on tour buses. During the 60th anniversary of the Chinese Revolution, a bike got me a front row seat to the spectacle.
Beijing bikes have their own lanes, traffic lights, and rights-of-way, and a rider can easily thread his or her way anywhere. At railroad stations there are special bicycle parking lots, and even at the Forbidden City it is possible to leave your bike next to the front gate, as if you were a Mandarin.
A few of the parks are off-limits to riders, but to my mind the only way to explore the hutongs — the historic districts of old Beijing, laid out like rabbit warrens — is on a bike, with which it is possible to roll past tea houses, food stalls, and open shops, as if in a Venetian gondola.
Recently back in the capital, I spent a long day riding from Tiananmen Square out to Peking University, near the Summer Palace — about fifteen kilometers (a little more than nine miles) to the northwest.
I had mapped out my route using a mixture of back streets and boulevards, and rolled away to find the Beijing grave site of the American writer Edgar Snow, whose 1937 book, Red Star Over China, was the first English-language account of Mao Tse-tung and a reportorial classic. (They met near Yenan, to which I went by train, but where there are almost no bikes.)
To be sure, bike riding in Beijing is an acquired skill. I accept that it means weaving around buses, parked cars, delivery vans, and other obstacles. What surprised me on this long ride — about three hours in all — is how often the bikes lanes were flooded with motor scooters, cars, and a variety of motorized contraptions.
After a while, I had my eyes attuned to the demographics of bike riders. They tended to be school kids or the elderly. From this blacktop survey, I judged that middle-aged or prosperous Beijingers have little appetite for riding. Most were moving around on scooters, the kind that have clogged many Asian cities.
On earlier bike rides around Beijing, I found the experience sublime. This time it felt like I was riding for my life in New York City, outnumbered and outgunned by a variety of taxis, swerving motorists, and motorcyclists.
Not only is Beijing going the way of Bangkok and other Asian cities that have been lost to gridlock, but the effects of non-riding can been seen among the Chinese themselves, more of whom are obese; undoubtedly KFC and McDonalds don’t help, either.
Beijing is not the only Chinese city where I found biking on the wane. On my recent trip I also visited Xian, Chongqing, and Guangzhou, in search of Maoist redoubts and World War II battlefields. Chongqing (which has an excellent General Joseph Stilwell Museum and a Chou En-lai house) is built on hills, like San Francisco, so it has never been much of a bike city. Xian and Guangzhou are ideal for the bike, at least in their historic quarters. Yet each city is now overrun with cars.
In Xian, I spent a long time just trying to find a shop that would rent me a bike. I went to several where the owners just shrugged. Finally, I borrowed a neglected bike from a hostel, but first had to take it in for repairs. No one had ridden this Giant in weeks, and the seat was set for a Lilliputian.
You wouldn’t cycle to see the Terra Cotta warriors on a local clunker, as they are an hour by car from the city. But a bike is perfect to explore the Muslim quarter or to take in the Xian Incident Museum, which tells the story of Chiang Kai-shek’s kidnapping in 1936 and his subsequent agreement to recognize the Communist party. (Nothing focuses the mind like a kidnapping.) In Guangzhou I made it to the Sun Yat-sen Museum, but the snarling traffic scared me into a taxi.

In Beijing and other cities, you still see bicycles loaded with garbage bags, cords of wood, furniture, dumplings, racks of clothing, and things like hundreds of fresh eggs. Some riders can comfortably bike around several family members on one frame, and it’s not unusual to see children following a parent through a busy intersection. In one alley, I biked alongside a man using his bike to move a large desk.
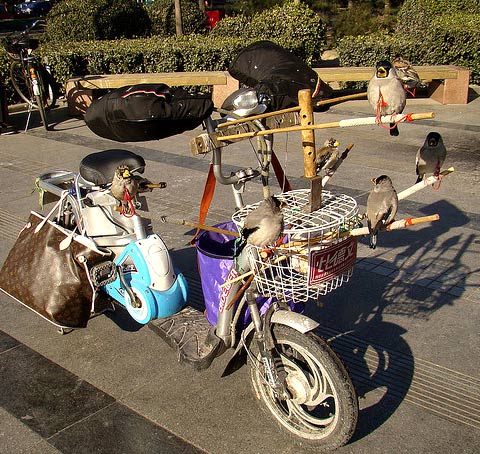
In Beijing and Xian, I especially love the cyclists who have rigged up devices so that they can ride around with their caged birds, although one cycling raven of my acquaintance just sat on a wooden perch across the handlebars. Where will he be in five or ten years? I hate to think that Edgar Allen Poe was a writing an elegy for, among other things, the Beijing bike:
Quoth the raven, “Nevermore.”
Matthew Stevenson, a contributing editor of Harper’s Magazine, is the author of Remembering the Twentieth Century Limited, a collection of historical travel essays. His next book is Whistle-Stopping America.
Photo: Raven on a Bicycle, Beijing, by the author.
Flickr Photo: Bird Scooter; birds and paraphernalia on a bike in Beijing by IstoletheTV.