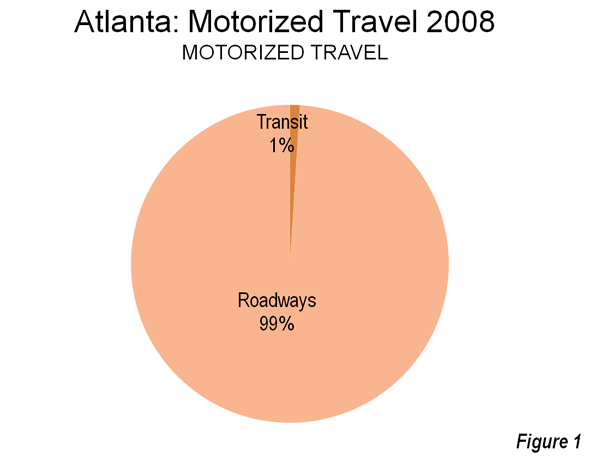
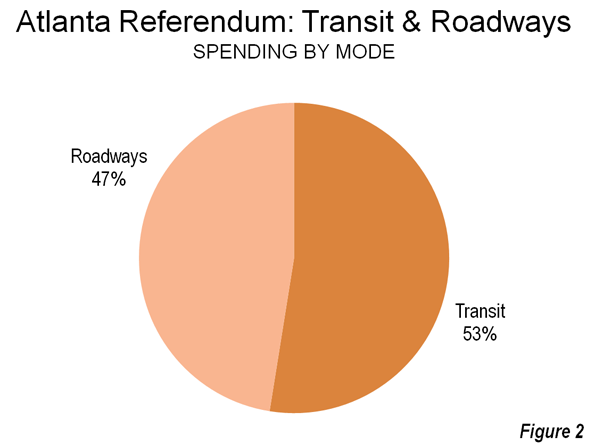
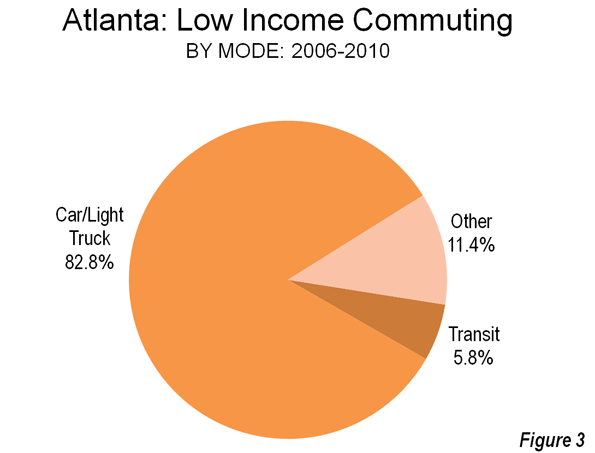
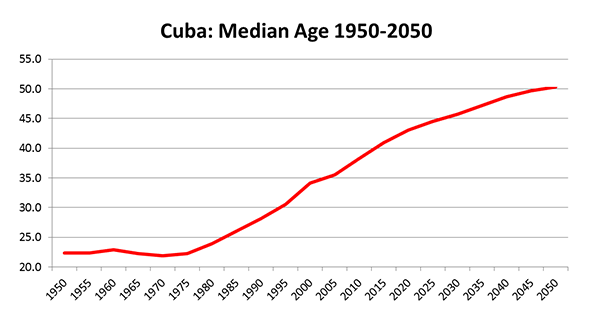
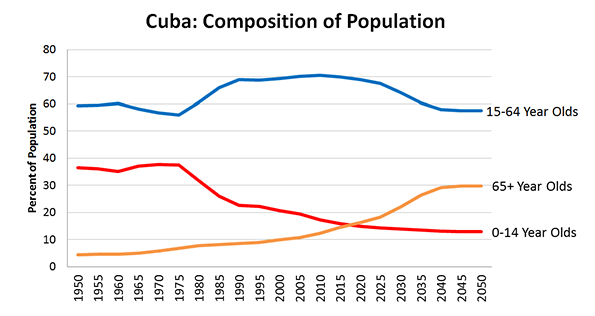
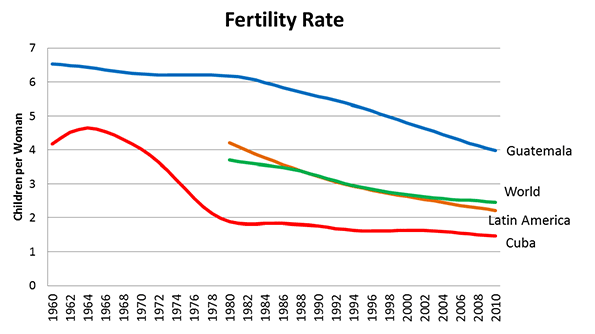
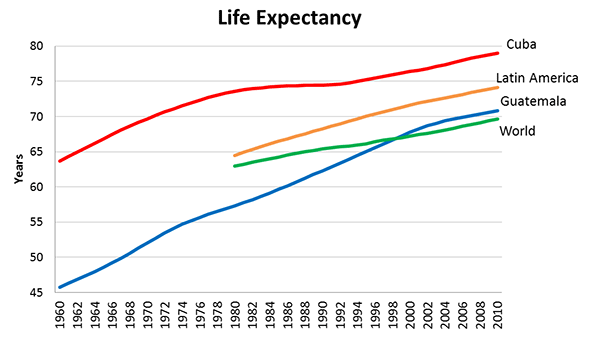
Surely you’ve seen it in your own neck of the woods: great contrasts between prosperity and wealth on the one hand, and hardship and despair on the other. I have certainly seen it in every place I have been over the last four years. FDR described the Great Depression as “one-third of a nation ill-housed, ill-clad, ill-nourished.” Yet do we not today have one-third of a nation either unemployed, underemployed, underwater on their one greatest asset (their homes), in crushing debt (which I define as unserviceable from current income), insolvent/bankrupt, on food stamps, unemployment or disability payments, or otherwise dependent on government? The diminishing of the middle class is daunting, but most disturbing is the diminishing of its prospects.
Perhaps you attribute this state of affairs to the “rich get richer, poor get poorer” meme. But there’s something else, something more going on. I have written about this before (unraveling, stagnation, middle America, middle class is the future), but here bring a fuller picture.
In the years since the Great Recession started (and ended?) in 2008-2009, the US has been characterized by two economies. One of these American economies is thriving, as are the economic actors part of it. The other economy is miserable, as are its inhabitants. The divergence between these two economies is growing more pronounced. Why is this so, how did it happen, and what does it portend?
I have been debunking the “rich get richer, poor get poorer” theme for 30 years, maintaining that the relative income gap did not matter as long as absolute income growth was widespread, and economic growth was providing opportunities to all (which was the case). But now those caveats have come into play: middle-income, middle-class earnings, wealth and opportunities are under immense pressure. This is not because the rich get richer, or that redistribution is the answer (I find the debate over austerity vs. growth pretty stupid, when growth too often just means growth of government). It is because of fundamental, structural economic trends which may be with us for a long time to come.
Divergent Sectors, Divergent Fortunes
Perhaps you have heard of the manufacturing “renaissance” in America and the exporting “boom.” Both are true. American exports are booming, measuring in at about $180 billion each month (up from $140 per month two years ago). Exports account for about 14% of GDP, and are growing about 16% a year. American manufacturing employment has been hurt by globalization, but manufacturing output continues to grow and exporters are thriving.
American manufacturing and export prowess are likely to continue into the foreseeable future, as large American companies use innovation and technology to become more productive, and as the growing global middle class demands more American goods (including energy in the form of oil and natural gas).
The bad news is that exports and manufacturing do not translate into more jobs or even higher wages. Our new job growth has been in health care, education, services and government, areas that do not produce great income and wealth. This holds down the potential income gains of all wage-earning Americans.
But the income and potential of those in management, finance, high technology and the professions are not adversely affected. The benefits of productivity, manufacturing, exports and economic dynamism generally, therefore, accrue to the already well-situated capitalists, managers and properly skilled. Sure, the internet will continue to make it easier for many small businesses to survive (and some even to thrive), but they cannot be great founts of sustainable jobs.
Two-tiered economies are well-known and expected in developing countries – an export/manufacturing or raw material sector and a weak domestic service sector – but we’re not used to seeing it in an advanced, technologically sophisticated country like the United States. It actually could mean that the rich will get richer, but the economy will be missing its traditional ladder for those in the middle and below to climb.
Where will enough employment growth come from to maintain the middle class? Many analysts tell us it will come from the innovation sector, or the innovation economy. But again, the benefits of innovation seem now to accrue to the companies and individuals already in a position to exploit it, increasing productivity and profitability without a concomitant increase in employees.
Dystopian Economics
This is getting perverse, isn’t it? We have high unemployment and underemployment, huge debts and deficits, but companies are profitable and share prices continue to rise. There seems to have been a breakdown in the correlation between employment and GDP, between the housing market and overall economic strength, and between GDP growth and stock market valuations.
Statistics say we are in a low-inflation environment, but living expenses seem to be rising for food, energy, healthcare and education (the things on which the middle class must spend). Those with jobs and income in sectors that are doing well don’t seem to be as affected. That would certainly help explain the contrasts of wealth and hardship that one sees around the country.
In other words, what we seem to have created is a winners-take-all economy. Large companies with global exposure, highly skilled workers, and high net worth individuals are the main beneficiaries of current economic policy. Job creation, most small businesses, and low- and medium-end housing are not.
What if a rising tide no longer lifts all boats?
We now have the lowest percentage of Americans working or looking for work in 30 years. That really is devastating because the only way out of our fiscal and entitlement nightmare is to have more people working more hours and more years. Is the opposite our future?
The trends that are creating and sustaining two economies in the US have been building for years and seem to me to be so strong as perhaps impervious to amelioration. The “two economies model” meets my test of sustainability: being supported and reinforced by other fundamental social, demographic, political and technological trends (or at least not being incompatible with them). It is hard to foresee how the “two economies model” can be reversed or even tempered, though it is a path that will leave tens of millions of Americans behind even as the “working” economy improves.
I have been analyzing, writing and speaking on trends for 30 years. My audiences are often businesses or organizations looking for a picture of the future environment. I usually get a laugh from the observation that the future will be bright for some, dismal for others, and therefore recommend being in the first group. I don’t think I’ll make that joke anymore; somehow it’s no longer funny.
Dr. Roger Selbert is a trend analyst, researcher, writer and speaker. Growth Strategies is his newsletter on economic, social and demographic trends. Roger is economic analyst, North American representative and Principal for the US Consumer Demand Index, a monthly survey of American households’ buying intentions.
Finding a job photo by Bigstockphoto.com.