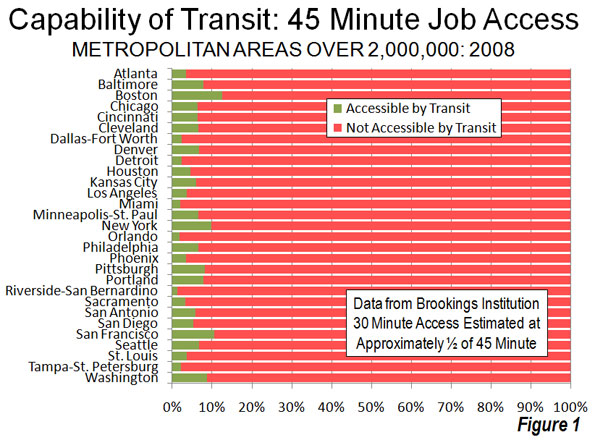
There is probably no large urban area in the world that better illustrates the continuing dispersion of urban population and declining urban population density than Jakarta. Recently released 2010 census data indicates over the past decade that 84 percent of the metropolitan area (Jabotabek) population growth occurred in the suburbs (Note 1). This continues a trend which saw more than 75 percent of growth in the suburbs between 1971 and 2000 (Figure 1).
Savannah State University (Georgia) Professor Deden Rukmana notes that this trend includes “many moderate and high-income families” who left the central city for better amenities while many poor people moved out to the fringe areas to escape what might be seen in the West as gentrification .
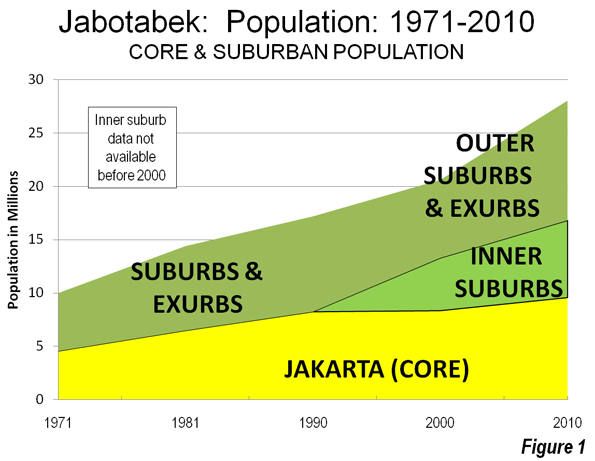
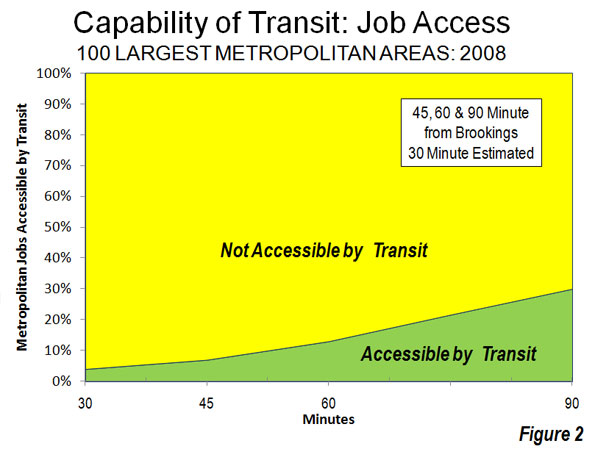
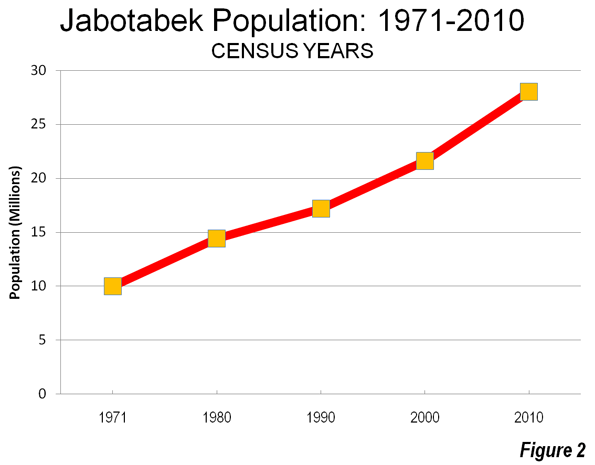
The Megacity: Jabotabek: Jakarta is one of only a few world megacities (over 10 million) that have changed their names in recognition of their regional rather than core city focus (this sentence corrected from original). The most recent megacity with a new name is Mexico City, now referred to as the Valley of Mexico (Zona Metropolitana del Valle de México). Other examples are Tokyo-Yokohama (Kanto) and Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto (Keihansh1n). Jakarta’s changed name, Jabotabek, represents an acronym made up of the beginning letters of the municipality of Jakarta and the three adjacent regencies (subdivisions of provinces), Bogor, Tangerang and Bekasi (Note 3). Jabotabek is one of the fastest growing megacities in the world and is experiencing accelerated growth. This is in contrast to the situation identified by the McKinsey Global Institute, which noted the declining growth rates of most megacities. In 2000, Jabotabek had a population of approximately 20.6 million, which by 2010 had risen to 28.0 million or 36 percent, nearly doubling its rate of population from the 1990s. Jabotabek’s additional 7.4 million people is nearly equal to that of London (Greater London Authority), nearly as large as the city of New York and more people than live in the entire Greater Toronto area. In 2000, Jabotabek had a population of approximately 20.6 million, which by 2010 had risen to 28.0 million (Figure 2).
Jabotabek’s unexpectedly high growth was greater than the 6.6 million added in both the Shanghai and Manila regions over the same period and above the 5.8 million increase in the Beijing region. The percentage growth in Shanghai and Beijing was slightly higher than in Jabotabek and slightly lower in Manila. The megacities of the United States, Western Europe and Japan have all fallen back to growth rates of less than five percent per decade (Tokyo-Yokohama, New York, Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto, Los Angeles and Paris).
Population Trends by Sector: Population growth and rates are indicated in the table for the sectors of Jabotabek and the constituent jurisdictions.
| Jakarta Region (Jabotabek) | ||||
| Population by Sector: 2000-2010 | ||||
|
2000
|
2010
|
Change
|
% Change
|
|
| Core: Jakarta | 8.36 | 9.59 | 1.23 | 15% |
| Inner Suburbs (Municipalities) | 4.94 | 7.23 | 2.30 | 47% |
| Tangerang | 1.33 | 1.80 | 0.47 | 36% |
| Tangerang Selatan | 0.80 | 1.30 | 0.50 | 63% |
| Depok | 1.14 | 1.75 | 0.61 | 53% |
| Bekasi | 1.66 | 2.38 | 0.71 | 43% |
| Outer Suburbs & Exurbs | 7.30 | 11.20 | 3.90 | 53% |
| Bogor (Municipality) | 0.75 | 0.95 | 0.20 | 27% |
| Bogor (Regency) | 2.92 | 4.78 | 1.86 | 64% |
| Tangerang (Regency) | 2.02 | 2.84 | 0.82 | 41% |
| Bekasi (Regency) | 1.62 | 2.63 | 1.01 | 63% |
| Jabotabek: Total | 20.60 | 28.02 | 7.42 | 36% |
| Population in millions | ||||
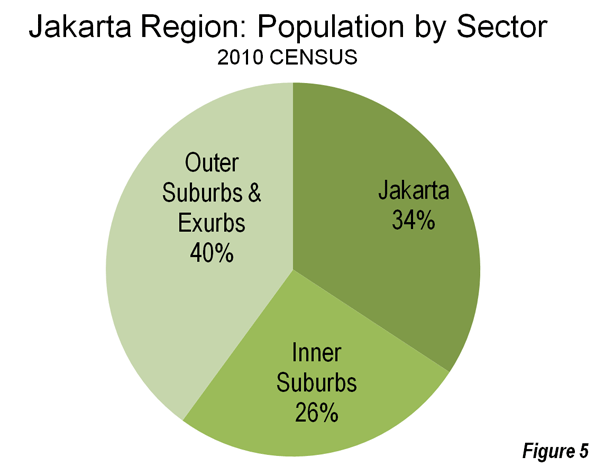
City of Jakarta: The core city of Jakarta is the "Special Capital Region" of Indonesia, similar to the District of Columbia in the United States, the Distrito Federal in Mexico or the Capital Federal in Argentina. This core of Jakarta grew 15 percent and added more than 1.2 million population, rising from 8.36 million in 2000 to 9.59 million in 2010, a turnaround from a loss of nearly 500,000 people between 1995 and 2000. The city of Jakarta captured 16 percent of metropolitan area growth and now accounts for 34 percent of the population of Jabotabek (Figures 3, 4 & 5).
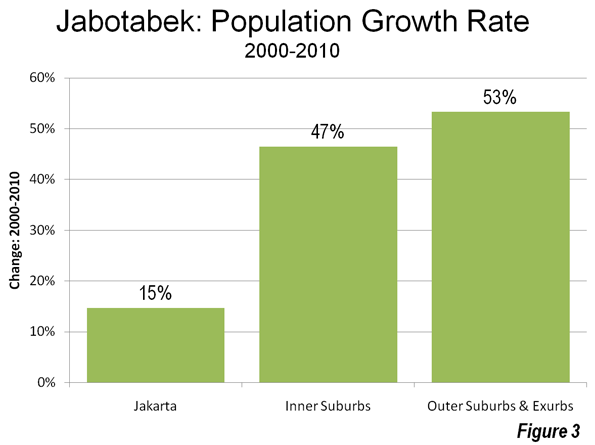
Inner Suburbs: The inner suburbs, which are made up for the purposes of this article by the municipalities of Bekasi, Tangerang, Depok and Tangerang Selatan (South Tangerang) grew 47 percent during the 2000, from 4.94 million to 7.23 million. These inner suburban municipalities captured 31 percent of the metropolitan area growth and now have 26 percent of the population of Jabotabek (Figures 3, 4 & 5).
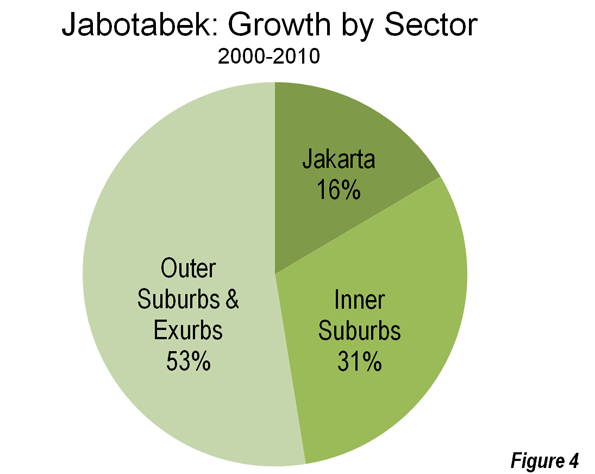
Outer Suburbs and Exurbs: The outer suburbs and exurbs (Note 2) experienced the greatest growth, at 53 percent, rising from 7.30 million to 11.20 million. For the first time, the outer suburbs surpassed the core with the largest population. The outer suburbs and exurbs accounted for 53 percent of the metropolitan area growth and now have 40 percent of the population of Jabotabek (Figures 3, 4 & 5).
Urban Area: The substantial growth of Jabotabek occurred principally in the urban area (the area of continuous development or the agglomeration). It appears likely that the urban area population will exceed 24 million (Note 4). It thus seems likely that the Jakarta urban area will again be ranked as the second largest in the world, following Tokyo-Yokohama. Jakarta had been displaced by Delhi (and Seoul-Incheon), for which United Nations 2010 estimates had indicated higher than anticipated population growth as Delhi passed Mumbai to become the largest in India.
Overall, the Jakarta urban area has a population density of approximately 22,000 per square mile or approximately 8500 per square kilometer. Yet the overall density of the Jakarta urban area has declined as population has moved to the outer suburbs which have a population density only one third that of the city of Jakarta. The inner suburbs have a population density that is only two thirds that of the city of Jakarta (Figures 6 and 7).
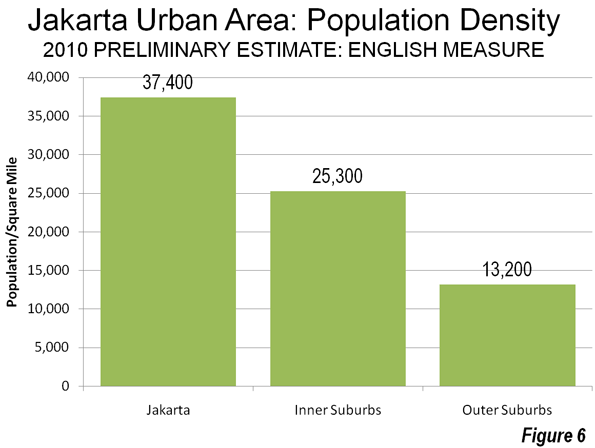
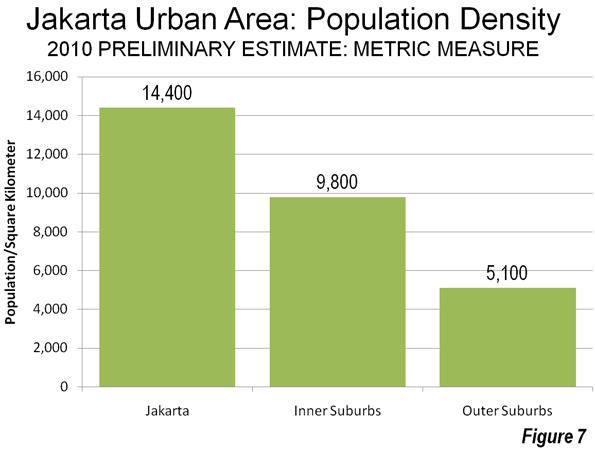
Despite this, the Jakarta urban area is much denser than most large urban areas in the high income world. Overall, the Jakarta urban area is approximately 2.5 times as dense as the Paris urban area, more than three times as dense as the Los Angeles urban area, and approximately seven times as dense as the Portland urban area. Other urban areas in the developing world are even denser: Delhi is more than 1.5 times as dense as Jakarta, Mumbai more than three times as dense and Dhaka is more than four times.

Informal housing, city of Jakarta (photo by author)
A Larger Metropolitan Area? This continuing population growth could cause Jabotabek to expand even further. Indonesia’s President Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono (SBY) has proposed expanding the metropolitan area to include the regencies of Karawang, Serang, Purwakarta and Sukabumi as well as the municipalities of Serang, Sukabumi and Cilegon. Already, Jakarta’s continuous urbanization nearly reaches the Karawang urban area to the east (population over 600,000) and is nearing Serang regency to the west. SBY’s "Greater Jakarta" has a population approaching 36 million according to the 2010 census. Further pressure on suburban growth could be generated by plans in Jakarta to limit the core city’s population to 12 million.
Yet even so it may take some decades, before Jakarta, or perhaps Delhi, could pass Tokyo-Yokohama’s nearly 37 million people to become the world’s largest urban area, assuming that they do not experience the reduced population growth so widespread in other megacities.
———
Notes:
1. Caution should be used in making comparisons of metropolitan areas, especially between nations. There is virtually no consistency in the delineation of metropolitan areas between nations. In some cases, such as Japan, the United States, France and Canada, Metropolitan areas are based upon commuting patterns, but even between these nations there is no consistency.
2. For the purposes of this article, suburbs are inside the urban area, but outside the central city (Jakarta). Exurbs are the portions of the metropolitan area (Jabotabek) outside the urban area.
3. The provinces of Indonesia and the state of Virginia are subdivided similarly. In Virginia, all of the land area is divided into municipalities or counties. In the provinces of Indonesia, all of the land area is divided into municipalities (kota) and regencies (kapupaten). The regencies are further divided into sub-districts (kecamatan). Jabotabek is located in three provincial level jurisdictions, the Special Capital District of Jakarta, and the provinces of West Java (Java Barat) and Bantan. West Java has a population of 43 million, approximately 6,000,000 more than the largest state in the United States, California. Banten is bordered on the west by the Sunda Strait, location of Krakatoa, the volcano.
Further, the name Jabotabek may not survive. As municipalities (Note 3) were carved out of the regencies in the 1990s and 2000s, the megacity was called Jabodetabek by some and proposed additions to the metropolitan area could bring even more variations. Inconsistent and alternative names probably make likely that sources will continue to call the megacity "Jakarta."
4. This urban area population is much larger than reported by the United Nations, which for Indonesian urban areas limits its estimates to the jurisdiction of the core city, and thus excludes suburbs. As is generally the case throughout the world, the continuous urbanization of Indonesian urban generally areas extends far beyond core cities.
—–
Photograph: Luxury housing in Cileungsi sub-district, Bogor regency (outer suburbs), by author
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris and the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life”