First it was Portland, Oregon, touted as a poster child for urban planning in Australia. Now, Vancouver, Canada, is the comparison, and are we seeing another incarnation of Australia’s infamous cultural cringe?
Advocates of higher density and the “brawl against sprawl” in Australia frequently cite overseas cities as model case studies. Portland, Oregon, was for a long time cited as a good example of pro-density housing strategies which sought to limit ‘sprawl’, to promote public transport by investing in things like light rail, and to promote cycling and a range of other planning ‘solutions’ that would sound remarkably familiar in Australia.
The truth about Portland, however, didn’t match the hype of its city planners. Much of the boosterism focused on the mostly downtown area of Portland. Like Melbourne, or Sydney, this is its own municipality, with its own Mayor and its own planning officials. As they aggressively sold a story about the virtues of their planning strategy for the city core, they omitted the inconvenient broader metropolitan facts as they went.
The story of the real Portland, including the surrounding suburban areas, is different than what these policy promoters would have you believe. Portland today, despite hundreds of millions invested in a new light rail system and the promotion of inner city housing density, has fewer public transport trips as a percentage of total travel than in 1980. Urban Growth Boundaries introduced by Oregon State in the 1970s led to housing price pressures which eventually excluded the middle and working class. Leading US city demographer Joel Kotkin describes it as an ‘elite city’ which is ‘remarkably white, young and childless.’ And as international housing market expert Wendell Cox has pointed out, the suggestion that Portland has much to crow about in terms of urban consolidation doesn’t match the official statistics. Portland is as guilty of ‘sprawl’ as Los Angeles.
The same can be said of Vancouver. Touted by its city officials as a paragon of virtue in planning policy, the Vancouver story is almost entirely limited to its geographically confined downtown. Here, in the wake of overbuilding of office properties in the downtown core, city officials rezoned excess commercial capacity to permit high density residential housing in what we would call the CBD. This ‘living first’ strategy produced a wave of new residential development which saw the core population grow by 20,000 people to around 60,000, and to potentially 90,000 by 2015. Redundant waterside areas have been coverted into residential precincts, and commuting by public transport, cycling or walking are favoured over private vehicles.
Taken in isolation, the Vancouver story could start to sound convincing. But there are some glaring omissions. The City of Vancouver is home to around 600,000 people. The downtown area – the subject of much of the planning hype – is home to 60,000 people. The broader metro region, based on the same sorts of urban definitions we might use for Brisbane, or Sydney or Melbourne, is home to 2 million people. There is precious little said about the lives of the 1.4 million people who aren’t residents of the City of Vancouver, or the more than 1.9 million who don’t live in the revitalized urban core.
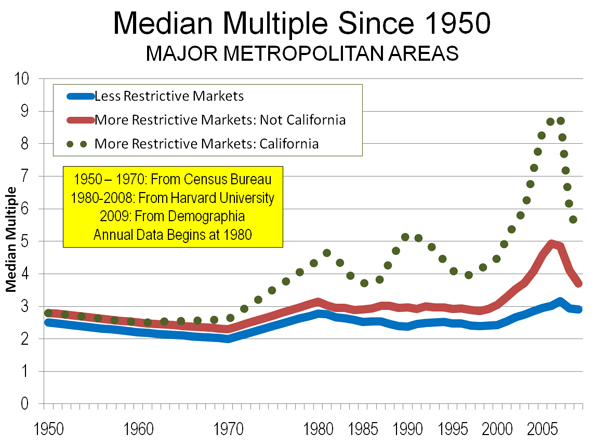
For these Vancouverites, life isn’t a rosy as the planning hype would have you believe. The most glaring omission about life in Vancouver is that it also happens to be one of the world’s least affordable cities in which to live. According to both the Reserve Bank of Canada and Demographia, Vancouver’s housing rates as severely unaffordable, eating up some three quarters of the region’s median pre-tax household incomes. The problem is so chronic that it has prompted an online game “Crack Shack or Mansion” where visitors are asked: “Can you tell the difference between a crack shack and a Vancouver, BC mansion, listed for one or two million dollars?” Play the game yourself, it’s an eye opener. [A Crack Shack, for the uninitiated, is a den of inequity where illegal drugs are produced].
That’s hardly the sort of model city you’d want to tout as a planning example we could learn from. The other glaring omission from the planning fairy tale of Vancouver is that life in the city core is vastly different from the overwhelmingly suburban conditions of the vast majority. To the south of Vancouver’s downtown lies an endless suburban grid of detached housing, with limited parklands or open space. Check it out for yourself on Google Maps or Google Earth. Jump into Google Street View and take a walk down a typical Vancouver street. Do that with a housing price list from “Crack Shack or Mansion” in hand and then convince me this is a model for any Australian city.
A final glaring omission is the climate. This from the official Living in Canada website: “Snow depths of greater than 1 cm are seen on about 10 days each year in Vancouver compared with about 65 days in Toronto. Vancouver has one of the wettest and foggiest climates of Canada’s cities. At times, in winter, it can seem that the rain will never stop.” Summers aren’t so bad though: for two months of the year, the average daily maximum even exceeds 20’c!
So Vancouver as the next poster child of planning for any Australian city is looking shaky. It’s hopelessly unaffordable (and we have enough problems of our own in that regard), the quality of its majority suburban environment is lower than the standards we already enjoy, and the climate could not be less similar.
The same can be said of other city-regions often described as examples of how Australian cities could develop. Copenhagen, Paris, or Venice have all in their time been selectively extolled as models for Australian urban planning.
Maybe this fascination with irrelevant urban models stems from a form of cultural cringe? Whatever the reason, the analogies can be dangerous, especially when they omit the more essential economic or lifestyle based criteria such as housing affordability, share of economic wealth amongst a city/region’s residents, or climate and lifestyle factors.
It might instead be more helpful if Australian planners referring to overseas examples also kept in mind some of these pragmatic metrics. For example, benchmarking cities with more affordable housing markets than ours and with strong local economies where wealth and standards of living are enjoyed across a wide spectrum of society would produce some very different case studies. Factor in similar climate patterns (which largely dictate recreational and lifestyle behavior) to our own and the choice of comparable cities reduces further.
We might even start to find that our own cities offer plenty of examples of ‘getting it right.’ Instead of this cultural groveling we could start to define the things we like most about our own existence and plan ways of replicating that, rather than imposing on our cities forms of existence that, appealing as elements might be, are incapable of replication in the Australian context.
Ross Elliott is a 20 year veteran of property and real estate in Australia, and has held leading roles with national advocacy organizations. He was written and spoken extensively on housing and urban growth issues in Australia and maintains a blog devoted to public policy discussion: The Pulse.
Photo by ecstaticist
 Now, a number of interior urban areas are now within a day’s truck drive of the East Coast ports and those that are not are within two days. According to
Now, a number of interior urban areas are now within a day’s truck drive of the East Coast ports and those that are not are within two days. According to