Michael Lind is quite right to suggest that American progressives need to reflect on their ideological differences, exposed by the defeat of Bush, and I think we need to, as well. In so doing, we also need to recover a sense of the possibilities of progressive politics, and not to rest content with a vaguely progressive desire to steer social and economic forces and actors this way or that.
Blog
-
Contributing Editor AARON RENN on Streetsblog regarding EIS
So big thanks to Aaron Renn of Streetsblog Network member blog The Urbanophile, who today takes a look at the creature known as an Environmental Impact Statement, or EIS. The EIS is a precondition for road projects receiving federal funding, and one of its components — the “Purpose and Need Statement” — determines the type of project that will be built.
-
Executive Editor JOEL KOTKIN on San Francisco Weekly regarding SF
The city’s ineptitude is no secret. “I have never heard anyone, even among liberals, say, ‘If only [our city] could be run like San Francisco,’” says urbanologist Joel Kotkin. “Even other liberal places wouldn’t put up with the degree of dysfunction they have in San Francisco. In Houston, the exact opposite of San Francisco, I assume you’d get shot.”
-
Executive Editor JOEL KOTKIN on POLITICO regarding Houston
“Houston is your post-racial, post-ethnic future of America,” said demographer Joel Kotkin. “It’s a leading-edge place.”
-
The Suburbs are Sexy
The Administration’s Anti-Suburban Agenda: Nearly since inauguration, the Administration has embarked upon a campaign against suburban development, seeking to force most future urban development into far more dense areas. The President set the stage early, telling a Florida town hall meeting that the days of building “sprawl” (pejorative for “suburbanization”) forever were over. Further, a number of bills have been introduced in the Congress that would attempt to discourage suburban development, some under the moniker of “livability,” which promises to improve people’s lives by enforcing planner-preferred density. The war against the suburbs is by no means new, but the Administration and some members of Congress have proposed their own “surge” in hopes of suppressing them permanently.
The Mythical “Demise” of the Suburbs: Nearly since the pace of suburbanization increased, following World War II, critics have been foretelling the demise of the suburbs. During the 1950s and 1960s, some planning “visionaries” such as Peter Blake were predicting widespread municipal bankruptcies in the suburbs and for residents. This was occurring even as other urban planners were tearing up cities with urban renewal projects and freeways
, setting the stage for “block-busting” and an ever-widening racial divide. The early criticisms have been repeated through the years, justifying a paraphrase of the old saw about Brazil (“Brazil is the country of the future and always will be”): “The suburbs are the wasteland of tomorrow and always will be.”
The Real Decline of the Cities: In fact, it has more generally been the central cities that nearly went bankrupt, not the suburbs. Examples include New York, Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, Cleveland and that jewel of municipal consolidation, Indianapolis, rescued last year by $1 billion in state taxpayer funds. There are hopeful signs of a renaissance in most central cities, however their financial difficulties remain intractable and large swaths of their land area remain desolate. Meanwhile, the lawns were mowed in the suburbs, the houses painted and a strong sense of community developed among residents that was far too subtle for the prophets of suburban doom to perceive.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: More recently, the effort to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions has given suburban critics new ammunition. A simple mantra was dictated by “planning common sense.” Cars produce greenhouse gases, therefore people must get out of cars and live in more dense conditions, where they will not need to drive as much. Further, they will live in smaller, multi-family dwellings, which planning common sense teaches are more GHG friendly than the despised – except by those who choose to live in them – detached housing in the suburbs.
But a funny thing happened on the way toward GHG inspired desurburbanization. Some academics actually began looking at data. The reality of the suburbs turned out to be rather different from that portrayed by the conventional wisdom of the planners. The most comprehensive research comes from Australia, some of which has been previously covered here.
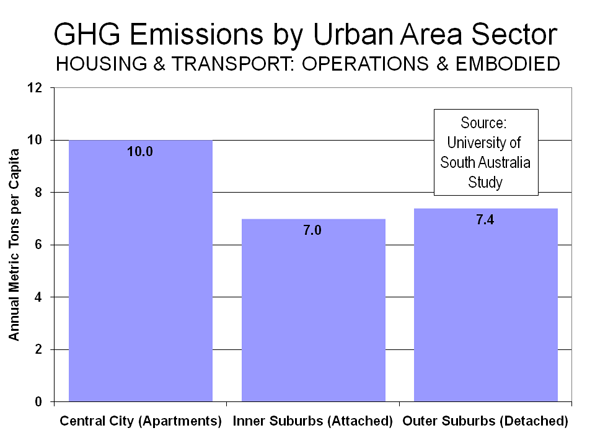
University of South Australia: The most recent (and new) offering comes from a University of South Australia report thatallocates transportation and residential energy produced GHGs by location and housing type in the Adelaide area. The researchers found that the most GHG friendly sector of the urban area was the inner suburbs, which are dominated by single-family attached housing. GHG emissions per capita from housing and transportation were estimated at 7.0 metric tons of GHG emissions per capita annually.
However, the outer suburbs, principally with detached housing, were not far behind at 7.4 tons GHG emissions per capita. The highest GHG emissions per capita, by far, were in the central area, with its predominance of multi-unit housing. There the annual GHG emissions were estimated at 10.0 tons per capita (See Figure). The University of South Australia study includes an element missing from virtually all other examinations of transportation and residential GHG emissions: “embodied emissions.” Embodied emissions are the GHGs from construction or manufacturing materials, and from building cars, transit vehicles and buildings. Embodied GHG emissions are ignored by much research, but are a significant factor in GHG emissions. For example, multi-unit housing, with higher use of concrete and more complex construction methods, tends to be substantially more GHG intensive than building detached housing or townhouses.
GHGs from Common Energy: Previous work by Sydney researchers reached similar results – townhouse development was the most GHG friendly, followed closely by detached housing. Both were substantially less GHG intensive than high-rise condominium development. A principal reason for this conclusion stems in part from the fact that this research included GHGs from common energy, such as the electricity used to power elevators, parking lot and common area lighting, building-provided heating, air conditioning and water heating. American and Canadian research attempting to quantify GHG emissions by residential building type generally has not accounted for common energy and its GHG emission. Yet a gram of GHG from a residential elevator has the same impact as one produced by driving to the local Target store.
GHG Friendly Suburbs: The most comprehensive research was conducted by the Australian Conservation Foundation. This was not the typical, incomplete or theoretical study of greenhouse gas emissions. The study included virtually every gram of greenhouse gas emissions in Australia and allocated them to consuming households in small residential zones within urban areas and around the nation. Suburban locations, with their greater use of cars and higher percentage of low density detached housing, had lower GHG emissions per capita than the core areas, with their greater use of transit and walking and their high-rise multi-unit housing.
Compact Development: These findings provided the impetus to review the potential impact of compact development policies. Compact development policies (also called “smart growth” or “growth management”) generally seek to densify urban areas, by drawing urban growth boundaries, outside of which development is prohibited, and by trying to force people to drive less and to use transit more. Again, “planning common sense” clearly indicated to planners that compact development would yield substantial benefits in GHG emissions, principally because people would drive less.
Yet the more recent research on compact development finds something much different. Densification scenarios from two recent reports, the congressionally mandated Driving and the Built Environment and a smart growth coalition’s Moving Cooler, showed that by 2050, compact development could reduce GHG emissions from driving by only 1% to 9%. At the high end of the range, the most new development would be directed to only a small part of present urban footprints, a policy outcome less believable than a balanced federal budget next year.
Moreover, these projections have to be considered overly optimistic, because they make no allowance for the higher GHG emissions that occur as traffic slows and stops more in higher density conditions.
The President Discovers the Suburbs? Meanwhile, on December 15, President Obama took the opportunity to visit a suburban Washington Home Depot, a chain that is a very symbol of American suburbanization. The President could have taken the opportunity to orate further against the suburbs in the insulation aisle, urging households to abandon the suburbs and move to high rise condominiums in the city.
That was not to be. The President instead proposed providing incentives to people to make their houses more energy efficient, which would reduce greenhouse gas emissions and save money on consumer energy bills. In particular, he cited insulation, saying that “insulation is sexy”. It is worth noting that the Home Depot’s insulation is principally sold to suburban homeowners who can readily arrange for its installation. Residents of high-rise condominiums must rely on their building managers, who tend to purchase their insulation from wholesalers, rather than retailers like Home Depot and Lowes.
The President explained why insulation was sexy, noting that saving money is sexy. Indeed, saving money is what the suburbs are about. The economic research is clear that housing costs are far less where suburban development is not limited by the compact development strategies that artificially create land scarcity. That’s why places like Dallas-Fort Worth, Atlanta and Houston, without compact development, had little, if any housing bubble, while housing bubbles of economy-wrecking proportions occurred in California and Florida, with their compact development.
Yes, Mr. President, insulation is sexy. Saving money is sexy. And, the suburbs are sexy.
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris. He was born in Los Angeles and was appointed to three terms on the Los Angeles County Transportation Commission by Mayor Tom Bradley. He is the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life.
”
-
Bernanke: For Good or For Ill
This week, Time magazine named Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke “Person of the Year 2009.” CNBC’s panel of experts gave Bernanke the “Man of the Year” title (no misogynists there!) in 2008. And well they should since their sponsors are among the biggest recipients of the Paulson-Bernanke-Geithner bailout. As I select the link from their website to imbed in this story, an ad from Wells Fargo (NYSE: WFC) is displayed in the right half of the screen. Click on “home” and it’s an ad from General Motors (OTC: MTLQQ).
I imagine Bernanke is quite embarrassed this holiday season as a result of the many, many less than flattering comparisons he is receiving. CNBC’s sister network, MSNBC, took exception to anything flattering in the designation by reminding everyone that being named Person of the Year is not an honor. Time’s definition, according to MSNBC, is: “The person or persons who most affected the news and our lives, for good or for ill…” They list a few of the previous winners, including Adolf Hitler (1938), Joseph Stalin (1939), and Ayatollah Khomeini (1979). One writer likened Bernanke receiving the award to “celebrating an arsonist for his heroics in putting out a fire that he set.”
Regardless of Time managing editor Rick Stengel’s qualifying statements, the tone of the write-up suggests, to Charles Scaliger at The New American at least, that Bernanke has a “cult of personality” within the Washington, D.C. Beltway. If you’ve never met Bernanke, which I never have, it’s hard to imagine there is the kind of personality there that one could be cult-ish about. Former Federal Reserve Chairman Alan Greenspan, who I also never met, regardless of his other shortcomings had the ability to say what it took to get the economy to do what he wanted it to do – he didn’t always pick the best things to get it to do, but he was able to get a message across. Bernanke, on the other hand, never seems quite comfortable in front of Congress the way Greenspan used to appear. A nervous central banker is very bad for the economy.
The designation – whether or not it is an honor – came the day before the Senate Banking Committee approved President Obama’s nomination of Bernanke to four more years as Chairman of the Federal Reserve. That nomination and approval represent further steps in what Rolling Stone writer Matt Taibbi calls “Obama’s Big Sellout.” The President, and 16 out of 23 Senators on the Banking Committee, seem to hold the mistaken impression that those who got us into this mess are going to be able to get us out. Republican Senator Jim DeMint of South Carolina was among the dissenters: “We can’t have a Federal Reserve that the majority of Americans no longer trust, and that’s what we have today.” Bernanke himself told Congress less than ten months ago that he didn’t know what to do about the economy. Maybe the eventual good that will come from Bernanke’s 2009 affect on our lives will be the demise of the Federal Reserve system in the United States and an end to the mountains of fiat money that it produced in vain efforts to solve the financial crisis that will forever be linked to Ben Bernanke’s name: Person of the Year “for good or for ill.”
-
The Economic Fallout of the Chicago Way
Many large American cities are hurting from the recent recession. Unrealistic revenue assumptions based on ever higher real estate prices and sales tax receipts have left cities unable to pay their basic bills. As asset and consumer prices deflate, from a lack of demand, those cities with “sticky” costs – the result of overly powerful unions and excessive business regulations – are stuck in an economic quagmire.
Chicago has become a leading poster child for recent urban economic malaise. With the election of Barack Obama, 2009 was supposed to be a year in which the Windy City basked in glory. The world was supposed to see the benefits of an administration run by Chicago Machine operatives such as David Axelrod, Rahm Emanuel, Valeria Jarret and Desiree Rogers.
Yet despite the new power in Washington, the Chicago Way has not turned out well back home. A series of events has put Chicago in a funk, along with structural economic problems. In June, Chicago’s unemployment rate peaked at 11.3%, far outpacing the national unemployment rate.
Since 2007 the region has lost more jobs than Detroit, and more than twice as many as New York. Over the decade that is about to end Chicagoland’s total loss was greater than any region outside Detroit. It has lost about as many jobs – 250,000 – as up and comer Houston has gained.
Columnist Mary Schmich of the Chicago Tribune, usually a reliable booster, has described the situation:
Chicago has a mood problem.
It seems edgy lately, a little sullen and scared, verging on depressed. Some days, it feels more like the angry, confused place I moved to in 1985 than the exuberant city that has swaggered through the past two decades.
One can question Schmich’s past description of Chicago as “exuberant”. But recently there’s been many Chicago problems.
Chicago’s bid for the 2016 Olympics failed. Even with Chicago’s most prominent citizens, President Obama and Oprah Winfrey, making a pitch to the International Olympic Committee, the Windy City came up short, behind all the finalists.
Oprah’s recent announcement that she’s ending her long run talk show will end Chicago’s most visible export. It appears much of the Oprah’s empire is moving to California to be closer to America’s entertainment capital, more celebrities and, of course, better weather.
On a more serious note, Chicago also has had to deal with two high profile political suicides. Chicago Board of Education President Michael Scott committed suicide in November. Scott was subpoenaed before a federal grand jury that was investigating the sale of admissions to magnet schools.
In September, a prolific Chicago fundraiser, Chris Kelley, committed suicide after pleading guilty to felony charges concerning the Blagojevich federal case. Kelly’s death was another reminder of the fallout of Chicago corruption.
But it’s just the top of the social heap that’s hurting. The national recession also has been particularly harsh for union-dominated Chicago. The loss of employment has put pressure on Chicago’s politicians to allow Wal-Mart to expand their number of stores in the city. With only one Wal-Mart store in the city, the thousands of potential new jobs could be just what Chicago needs right now. Mayor Daley wants to let Wal-Mart open several more stores but faces stiff opposition in City Council. Alderman Burke, the Chairman of the Finance Committee, is the key decision maker concerning Wal-Mart, whose local expansion is anathema to the unions. Mayor Daley said this concerning when Alderman Burke is going to hold hearings on Wal-Mart:
“That’s up to him. He could have had it six months ago or two months ago.”
The other big union problem can be found in Chicago’s fast-eroding convention business. The union run McCormick Place has been making big news lately because of its loss of three major conventions. In November when two major conventions announced they were leaving Chicago, Crain’s Chicago Business made this stunning indictment:
The chief executive officer won his post after raising campaign cash for disgraced Gov. Rod Blagojevich. The just-departed human resources director owed her job to a powerful state senator. Other top executives have long ties to Mayor Richard M. Daley’s political machine.
That’s what clout looks like at the Metropolitan Pier and Exposition Authority, known as McPier, a little-understood government entity that operates the city’s primary convention venue, the vast McCormick Place complex; the adjacent McCormick Hyatt Regency Hotel, and the lakefront tourist center Navy Pier.
The loss of two major trade shows this month and a deepening financial crisis raise questions of how the Chicago Way can compete with more efficient, warm-weather convention centers such as Orlando, Fla., and Las Vegas.
With labor costs much cheaper in other venues, competing becomes very difficult, particularly in tough times.
Fiscal incompetence has made the problems worse. To help with Chicago’s downturn a “rainy day” fund was set up by leasing major city assets. Chicago leased its parking meters to a private company. This controversial move was supposed to yield generous revenue up front. When Chicago recently passed the new city budget, the Chicago Sun-Times reported:
Chicago’s 75-year, $1.15 billion parking meter windfall would be nearly drained in just one year to provide token property tax relief and stave off tax increases, thanks to a $6.1 billion 2010 budget approved Wednesday.
Despite complaints that Chicago’s future was being mortgaged, the City Council voted 38-to-12 to approve Mayor Daley’s plan to drain reserves generated by asset sales to solve the city’s worst budget crisis in modern history.
Chicago’s recent economic decline is also affecting the state of Illinois’ budget. It may be unfair to blame the Chicago Machine for Illinois’ budget situation, but they certainly have played their role. Just days ago Moody’s and S&P downgraded the state of Illinois debt. Only California now has a lower debt rating.
Worse may be in the offing. Chicago’s recent economic malaise has been revealed in the stunning new documentary on the coming elimination of futures floor trading:
The exchange, a critical element of Chicago’s economy, may be on the way to downsizing if not oblivion. That’s more bad news for a city that seems to be falling apart even as its operatives try to run the country.
Steve Bartin is a resident of Cook County and native who blogs regularly about urban affairs at http://nalert.blogspot.com. He works in Internet sales.
-
The Green Movement’s People Problem
The once unstoppable green machine lost its mojo at the Climate Change Conference in Copenhagen. After all its laboring and cajoling, the movement at the end resembled not a powerful juggernaut but a forlorn lover wondering why his date never showed up.
One problem is that the people of earth and their representatives don’t much fancy the notion of a centrally dictated, slow-growth world. They proved unwilling to abandon either national interest or material aspirations for promises of a greener world.
The other problem is that divisions are now developing within the green camp. There are members, like Michael Shellenger and Ted Nordhaus, who recognize the serious fall out from the “Climategate” scandal, while others, including large parts of the media claque, dismiss any such possibility. There are the corporatists aligned with big business–who will live with any agreement that allows them to exact monopoly profits–and the zealots–like Greenpeace, Friends of the Earth and Bill McKibben–who see Copenhagen as an affront to themselves and to our endangered planet.
But the main, fundamental problem facing the movement after Copenhagen–which none of the green factions have yet addressed–is its people problem. The movement needs to break with the deep-seated misanthropy that dominates green politics and has brought it to this woeful state. Its leaders have defined our species as everything from a “cancer” to the “AIDs of the earth.” They wail in horror at the thought that by the year 2050 there will likely be another 2 or 3 billion of these inconvenient bipeds. Leading green figures such as Britain’s Jonathan Porritt, Richard Attenborough and Lester Brown even consider baby-making a grievous carbon crime–especially, notes Australian activist Robert Short, in those “highly consumptive, greenhouse-producing nations.”
Yet a slower population growth–while beneficial for poor, developing countries–can lead to a dismal, geriatric future in already low-birthrate nations like Germany, Italy, Spain, Japan, South Korea and Russia. And although birth rates are dropping in most developing countries, particularly those experiencing rapid economic growth, it will likely be decades before population stops increasing in most of the developing world.
Besides, people in developing countries have much more important things to worry about–such as earning a living and getting ahead. Fighting climate change ranks low on the list of Third World priorities. The sprawling slums of Mumbai need more energy, not less; they want better roads, not fewer. More economic development would produce the money to help clean the now foul water and air, but also provide access to better education, one of the best ways to assure more manageable birth rates.
Instead of looking to make developing countries even more dependent on Western largesse, greens should focus on ways to help improve the day-to-day lives of their people. Rather than prattle on about the coming apocalypse, they could work to replace treeless, dense slums with shaded low-lying clean houses that are easier to heat or cool. Those interested in nature might purchase land and rebuild natural areas. The children of cities like Mumbai should have the opportunity to experience wildlife other than crows, pigeons and rats.
The environmental movement also might as well forget fighting the aspirations of the burgeoning middle class in India, or other developing countries. No developing world politician, whether from democratic India or Brazil or authoritarian China will embrace an agenda that stifles such aspirations.
Post-Copenhagen greens need to reassess their relations with people in the developed countries as well. The popular call to transfer hundreds of billions of dollars from the so-called “rich” countries to combat the potential effects of climate change will not be very popular with the vast majority of the middle or working classes in these places.
Much of the problem revolves around the loaded term “rich.” To be sure, many top climate-change scolds–Richard Branson, Al Gore, Arnold Schwarzenegger, Michael Bloomberg and, of course, his royal highness, Prince Charles–qualify easily. After all, no sweat off their well-massaged backs. The rock stars of the green millennium can buy their environmental indulgences so they can gorge good conscience on their carbon-rich world of private jets and lush estates.
For them, going green means minimal sacrifice.
Instead, the “rich” who will suffer the most will be the middle and working class of the developed countries. For them, carbon “sacrifice” may mean more than giving up needless luxuries like gas-guzzlers or monster plasma televisions. A green regime of enforced slow growth and ever greater regulation over carbon could threaten whole industries while environmental-planning policies will make purchasing a decent suburban house even more difficult.
Such calls for sacrifice seem particularly ill-timed when 4 in 10 U.S. residents fear they could lose their jobs, with many rightly worried about holding onto their homes. With unemployment at 10%, few may be willing to wait around until the promised “green jobs” miraculously appear to save both them and the planet.
But there’s an obvious way out of this dilemma: Start shifting away from fear-mongering and look to ways to achieve green goals without catastrophic economic losses. One clear way to start this process is through land-use policy. Right now many activists and their allies in the climate-industrial complex–which includes urban land interests–want to force suburban home dwellers into dense urban areas. They also want to coerce people to give up their individual mobility for trains, even if this means longer commutes and less convenience.
Proposing a radical re-engineering of society does not constitute a winning political program. Environmentalists would do better to embrace a vision of “greenurbia,” allowing for dispersed living but in a environmentally responsible way. This could be done with practical steps–increased telecommuting, more tree-planting and flexible work arrangements–that would enhance not only the environment but also day-to-day life for hundreds of millions of people.
Similarly, environmentalists should redouble their efforts to provide more access to open space for millions of people through expanded purchases of land throughout the country. America’s highly productive agricultural sector has jettisoned millions of acres of land from cultivation, providing an excellent opportunity for purchases for public use. In some areas, abandoned industrial or mining properties could be rehabilitated as natural areas.
Such changes, however, require a re-evaluation of the values that now drive the green movement. Whether in California or Calcutta, it boils down to the existential question: Do humans matter?
Frederick Law Olmsted explained his plan for New York’s Central as an attempt “to supply to the hundreds of thousands of tired workers … a specimen of God’s handiwork.” This represents the kind of sensibility that could transform the green movement from an obstacle to people’s aspiration to a force for greater human happiness.
This article originally appeared at Forbes.com.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University. He is author of The City: A Global History
. His next book, The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050
, will be published by Penguin Press early next year.
-
Personal Rapid Transit: Twenty-First Century Transport?
Recently I had the chance to visit Taxi 2000. This Personal Rapid Transit (PRT) company is based just minutes from my office in Minneapolis. I’m no expert on rail systems, but I’ve always believed that an elevated system that can run freely over existing right-of-ways makes more sense than an antiquated system based on nearly 200 hundred year old technology.
Since we plan new neighborhoods and cities, I saw a great opportunity to design a new town with an elevated PRT system as a major design influence, not as an afterthought. A perfect combination: a new age city based upon the latest methods, with a convenient way to access most of the region, based on a 21st century design, not an 18th century one.
I typically investigate the products and companies that I’m about to meet. I’d heard about PRT solutions for well over a decade and assumed there were many examples of installations. After searching the internet I found not a single installed PRT system serving a city.
I’ve never been a fan of light rail for a variety of reasons. Human beings are smart enough to explore space, extend life spans for decades, and remodel genetics. Yet all we can come up with is a slow (and often unsightly) train that runs on tracks conceived in the 1800s that now cost billions of dollars to implement? We are told that building a light rail line spurs economic growth. Even if true, typically only a minor portion of a town benefits because the system is linear. Most are designed to be functional, not beautiful, and most light rail trains are not inspiring.
I used to drive in Minneapolis, but now train tracks intermix with the driving lanes in some areas of town. I avoid those sections, and now do my spending in the suburbs. I’m sure I’m not the only one. This brings me to my final opposition to light rail: Because it’s typically ground-based, it’s obstructive to implement, and often requires the demolition of buildings and the acquisition of right-of-ways. All of this costs plenty.
On top of this, many businesses suffer during the construction of light rail, while it interferes with their access. Sure, they might ultimately get additional business, but first they must survive a period with reduced access.
Mike Lester, CEO of Taxi 2000 demonstrated the prototype of SkyWeb Express along with its technologies to us. Over a period of three hours, Mike proudly showed us what they have accomplished.
First, this is an on-call system. This means that you do not have to wait for the next train. Cars located only a minute or so away await your command. No more missed connections while waiting an hour for the next ride.
It is elevated far above ground — 5 meters — using existing right-of-way on posts spread far apart. In an urban area such as Minneapolis which already has a skyway system, this could coincide with existing access points on the second or third floors. It’s non-linear, and able to easily turn corners and access much of a city, not just points along a single route.
It maintains a constant rate of speed; no stops needed until you reach the destination. About 30+ miles per hour might not seem fast, but a mile every two minutes in an urban environment is indeed impressive. It’s limited to 3 persons per vehicle with plenty of extra space for luggage, boxes, or even a bicycle. No more crowding. It goes where you want, not only on a preset route. In theory it’s safer because you can access it alone, not with strangers. And one car needing maintenance does not shut down the system.
The big issue that all transit needs to address is the cost. The light rail transit in Minneapolis costs somewhere around a billion dollars. PRT cost studies show a savings of 60 to 70 percent could have been realized along the same line. Even if the estimates are wrong by double, that’s over $200 million that could have been spent elsewhere, or to make a quite comprehensive PRT system for the same dollars.
I’m not easily convinced when someone tries to “sell” me on new technologies, but that common sense meter in my brain was at 100% as I learned about the PRT possibilities. I was not sold that this will get everyone out of their cars, but it’s a solution that would be more effective than a rail system.
So why no installations?
PRT companies have been around for a while, continually upgrading and perfecting their systems. While I’m not sure how they get funded, I can tell you that cities have a hard time spending hundreds of million dollars on systems developed by small firms. As a software developer of Geographic Information Systems in the 1990’s we constantly lost sales to larger companies, even though our product was superior. It appeared that cities were more comfortable buying from companies with hundreds of employees working in tall impressive buildings than from smaller firms. It was natural to think a firm that appeared quite large had staying power compared to small companies with a handful of employees. But in the dot-com bust we learned that size does not guarantee longevity.
I’ve written this before, but it bears repeating: On August 1st, 2009 President Obama addressed the nation with: “Future economic prosperity depends on building a new, stronger foundation and recapturing the spirit of innovation …. Innovation has been essential to our prosperity in the past, and it will be essential to our prosperity in the future”.
Small PRT firms have risked everything, adhering to a belief that it is a viable solution for urban transportation problems today and in the future. How have we rewarded these innovators who certainly have the spirit? We continually invest in the most non-innovative, obtrusive, and expensive solution: Light Rail. We reward large corporations who take no risk… What happened to us? Let’s see if this new Administration can stand by the President’s words and invest in the pioneers who can create that strong American foundation.
Rick Harrison is President of Rick Harrison Site Design Studio and author of Prefurbia: Reinventing The Suburbs From Disdainable To Sustainable. His website is rhsdplanning.com.
-
Memo to Big City Pols: Voters’ Suspicions on Influence Peddling Is Far Cry From Stupidity
A significant clue on why the City of Los Angeles is facing budget deficits of hundreds of million annually for the foreseeable future can be found in the relationship between elected officials and AEG, the company that’s controlled by Denver-based multi-billionaire Philip Anschutz.
AEG owns the Staples Center and the adjacent L.A. Live, which includes shops and restaurants to go with one nice hotel and another luxurious establishment that will be topped by high-priced condominiums when completed.
AEG has a prime a seat on a gravy train of benefits ladled out by our city and state governments. Those hotels came with a tax break that is expected to amount to tens of millions of dollars over coming years. The city also provided attractive terms on a $70 million loan for the project. State legislators have passed laws that appear to many rational observers to have been crafted specifically to steer tens of millions of dollars worth of benefits to AEG.
Some politicians like to say that AEG is deserving of such largesse because it has brought development and jobs to the city’s center. That’s appreciated, but let’s not forget that AEG is a private enterprise that’s in the business of making money. The company had to develop some land and hire some workers to make money on its plans Downtown. It would be nice to see the company’s investment earn a tidy profit, but there’s no case for sainthood in any of the business plan.
Meanwhile, AEG has been a patron saint of sorts when it comes to local politics, giving hundreds of thousands of dollars to various candidates and campaigns. The company even pitched in with $137,000 – the largest of all contributors – to a ballot measure that extended term limits for members of the City Council.
Do you see some possible connection there? Is there a chance that some corporate executives have used money to gain influence over public officials?
Ask around and you’ll find that most everyday, working voters see a connection – or at least the possibility of one.
And here’s where we get to the explanation on the hundreds of millions of dollars in budget deficits: It seems that members of the political class don’t ask around – and they don’t think regular folks are smart enough to call elected officials to account.
What else to make of recent comments by 9th District City Councilmember Jan Perry, who represents most of Downtown. Perry has looked like AEG’s personal body guard during the recent fan dance over suggestions that the company should pay some re-imbursement for public services dedicated to the memorial service for Michael Jackson earlier this year, a tab that came to approximately $3.2 million. Some say that AEG should pay up because the company benefited from the spectacle surrounding the singer’s death by selling rights to film footage from his final days, when he used the Staples Center for preparations on what was to be a global tour.
Perry recently took the opportunity of the flap to dismiss concerns that AEG uses political donations to exercise undue influence over city officials.
“AEG doesn’t own the place,” said Perry, referring to City Hall in a recent story in the Los Angeles Times. “I think that’s a really stupid way to think.”
Perry got away with an old political trick there, putting over-the-top words in the mouths of any mere taxpayers who might have questions about the relationship between AEG and elected officials. She ramped up the charges in a pre-emptive logical fallacy that dismisses anyone with suspicions of influence peddling as unworthy of an opinion on the matter.
Perry must think that anyone outside of City Hall is stupid, indeed. Stupid enough to fall for that verbal twist. Stupid enough to think that there’s nothing to any suspicions unless it can be proved that AEG actually holds a mortgage on City Hall.
The people are not stupid, though. Voters know that influence peddling is a shadowy business, and that big corporations and the executives who run them are careful about the legalities and perceptions that come with the flexing of their political muscles.
You’d think a politician with Perry’s experience would be just as careful about calling voters stupid. After all, they’re smart enough to pay for all of those breaks for AEG – not to mention her salary.
Jerry Sullivan is the Editor & Publisher of the Los Angeles Garment & Citizen, a weekly community newspaper that covers Downtown Los Angeles and surrounding districts (www.garmentandcitizen.com)
Photo: