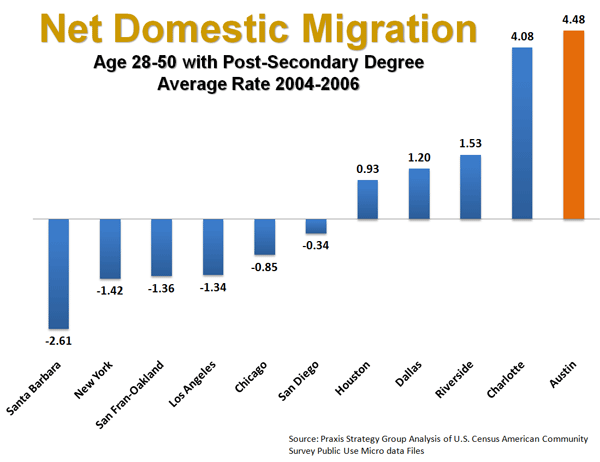
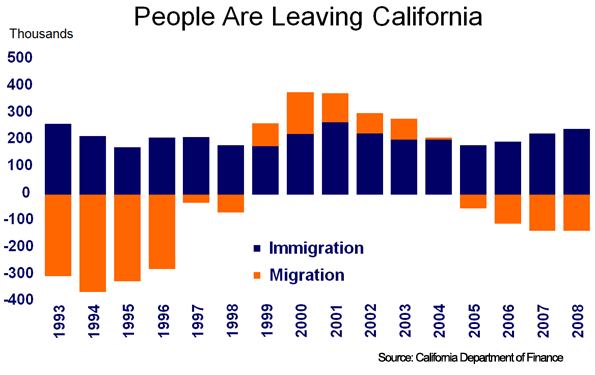
I always do my best to make time for Lenny Mills because he’s earned that sort of consideration.
Mills is the fellow who wrote several pieces under the banner of his trademark “7 Rules” outline, where he applies the tricks he learned as a telemarketer to analyses of real estate development, politics, and other matters.
Mills did an especially fine job on the “7 Rules of Downtown Gentrification,” which appeared in the Garment & Citizen’s issue of April 21, 2006. He laid out a number of reasons – seven, to be exact –to consider the possibility that the residential real estate boom ringing through Downtown Los Angeles back then would eventually turn into a busted bubble.
Events have certainly borne out Mills’ prediction, so he brought credibility with him on his latest visit to my office.
Mills waved a recent copy of USA Today at me, saying that he’s worried about the sort of folks who were featured in a recent front-page story in the national publication, a piece that described the circumstances of some of “the new homeless.” These are individuals who worked steadily their whole lives before hitting the skids and losing their homes in the current economic downturn. It’s a trend that has become familiar these days, with homeless encampments cropping up in all sorts of places, including Los Angeles.
Mills has some added credibility when he speaks about homelessness – he spent a number of years living on the streets. He knows what it means to go through life with a weather-beaten face, watching opportunities slip away for lack of a telephone number to leave behind when seeking work.
Mills has a place to live now, but he remains determined to inject his warnings about the new homeless into the public debate. The clock it ticking, he says, and the deterioration that comes with life on the streets will make it harder and harder for folks to climb back into mainstream lives. Once the wardrobe starts to fray, he says, the odds against getting back on track grow longer. Once the teeth start to go, he adds, homeless individuals can just about write off any return to the life they once knew. Each bit of deterioration makes it tougher for the homeless individuals – and more likely that they will become permanent burdens to the rest of us in one way or the other.
Mills is remarkable in a number of ways, including the ability he mustered to retain his social skills during his time on the streets – something that many individuals quickly lose. I disagree with him on some things, but I can’t fault his ability to make fine use of the language to get his points across.
Mills used such skill during our recent talk, driving home a couple of points about the new homeless: Our society has a narrow window of opportunity to pay for programs to reverse the trend – and a failure to act soon will mean far greater costs in terms of human lives and the public purse.
Mills can spout chapter and verse on what he sees as the causes of the increases in homelessness over the past 40 years. He can cite demographic trends, economic patterns, and public policies to make a compelling case that a lot of folks were swept into life on the streets by causes beyond their control. He firmly believes that we as a society could have prevented most of the homelessness we have seen over the years had we not lacked the will to do so.
I wouldn’t describe Mills as a fun guy. He’s a valuable fellow, though, because he’s willing to tell you what you’d rather not hear – and he’s capable of doing so in reasoned tones.
Give Mills his due for hitting upon something of vital importance now. It’s clear that all the talk we’ve heard about addressing the old homelessness has led to no great progress over the course of decades. What did that latest Blue-Ribbon Public-Private Committee to End Homelessness Forever accomplish besides a photo opportunity, anyway?
Someone wake the Blue Ribbon brigade and fire all of them.
We have a whole new homeless problem – and we’re in desperate need of new ideas.
Jerry Sullivan is the Editor & Publisher of the Los Angeles Garment & Citizen, a weekly community newspaper that covers Downtown Los Angeles and surrounding districts (www.garmentandcitizen.com)