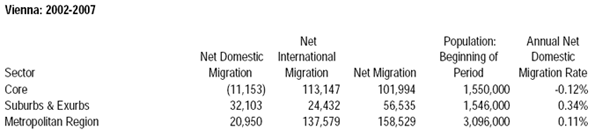
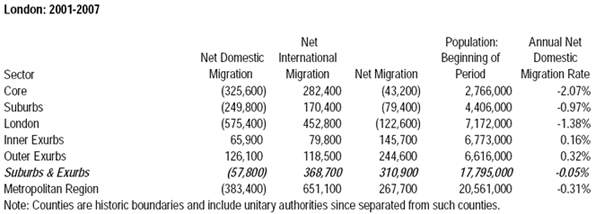
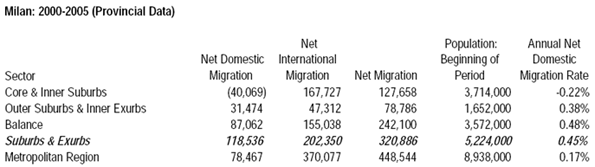
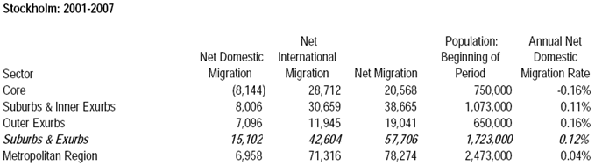
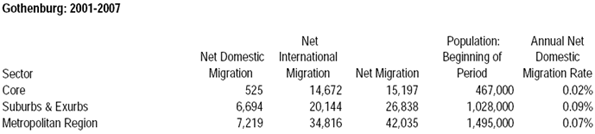
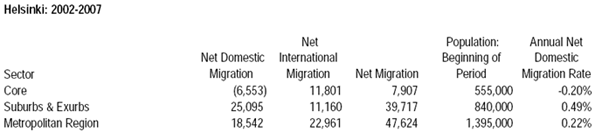
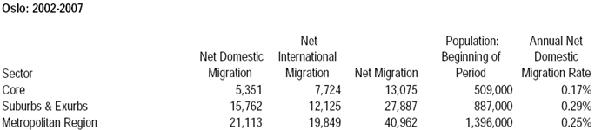
Race may be the thing that most obviously distinguishes President Barack Obama from his predecessors, but his biggest impact may be in transforming the nature of class relations — and economic life — in the United States.
In basic terms, the president is overseeing a profound shift from cowboy to what may be best described as collusive capitalism. This form of capitalism rejects the essential free-market theology embraced by the cowboys, supplanting it with a more managed, highly centralized form of cohabitation between the government apparat and the economic elite.
Never as pure as its promoters suggested, cowboy capitalism always depended on subsidies to businesses such as corporate farming, suburban development, pharmaceuticals, energy and aerospace. George W. Bush and the Republican majorities of the early 2000s simply drove this essential hypocrisy to a disastrous extreme by increasing deficits and allowing deregulated financial markets to run wild. In the process, they helped drive the world economy off the cliff.
Not surprisingly, Obama and his backers see their mission to reverse the course. However, the path they are taking may prove no friendlier — and perhaps less so — to the interests of American democracy and the middle class than those of the now-deposed cowboy posse.
The Obama policy of collusive capitalism is most evident in the financial bailout. He has placed his economic program in the hands of a man — Treasury Secretary Timothy Geithner — who can best be called, as analyst Susanne Trimbath puts it, a “lap dog of Wall Street.” A protégé of former Treasury Secretary and Citicorp board member Robert Rubin, Geithner played a pivotal role in the original Bush bailout of the Wall Street elite.
Most recently, he proposed selling toxic assets to hedge funds and other financiers, a plan widely denounced by a host of liberal commentators, notably Paul Krugman and Joseph Stiglitz. The Geithner plan, Stiglitz noted this week in a New York Times op-ed, represents “the kind of Rube Goldberg device that Wall Street loves: clever, complex and nontransparent, allowing huge transfers of wealth to the financial markets.”
The winners in the plan are the top guns of the financial industry, who would welcome further government-sponsored financial consolidation. For them, this would be vastly preferable to the more democratic alternative of selling the remaining assets of the failed large firms to dispersed, healthy, usually smaller, regional institutions.
Largely missing from even these critiques is precisely why Obama has adopted this collusive approach while mostly avoiding anything smacking of populist anger. Perhaps one has to start with the very obvious fact that the president — despite occasional attacks on the greed of Wall Street — did not run against the financial markets but, rather, with their strong support. As early as the 2008 Democratic primaries, noted New York Times Wall Street maven Andrew Ross Sorkin, Obama had “nailed [down] the hedge fund vote.”
This group includes the notorious currency speculator George Soros, a major backer of liberal groups in Washington who recently admitted to London’s Daily Mail that he was having “a nice crisis.” Whatever Geithner is doing seems to be working well for Soros and his ilk, although not so beneficently for the people who are losing their jobs and homes.
I do not mean to suggest the shift to collusive capitalism represents a conspiracy; it simply reflects a changing of the guard among the American elite. The new hegemons include not only financial barons but also powerful interests such as the burgeoning green industry, the high-tech/venture capital complex, urban landowners and, at least in the category of useful idiots, Hollywood and much of the media.
The new collusive capitalist class differs from the cowboys in its view of government. The collusive capitalists — notably, powerful IT companies and venture capitalists — now look to spur “green” technologies, which are seen as their next meal ticket.
Others standing to benefit from the rise of collusive capitalism include the university and nonprofit research establishment. Universities have become critical linchpins for the new Democratic Party — providing student shock troops and professorial financial contributions as well as the basic ideological underpinnings and much of the key personnel.
Are there any dangers for the administration from this approach? In the short run, they certainly have little to fear from the Republicans, whose strident claims about a lurch toward socialism have about as much credibility as their supposed born-again faith in fiscal conservatism.
A potentially more dangerous threat lies from those parts of the non-gentry left, who fear that collusive capitalism will promote a dangerous further concentration of wealth and power. More immediately, it may also suffer from the limitations of a top-down, green-obsessed strategy that is unlikely to generate enough private-sector jobs, particularly for blue-collar workers.
This large job creation deficit may take years to become evident but could have a long-term impact on middle-class voters and, perhaps most important, the generally pro-Obama millennial generation workers who are among the prime victims of the current economic malaise. Hopefully, before then, the president will recognize the limitations of collusive capitalism and set out on a broader, more democratic wealth-creating agenda.
This article originally appeared at Politico.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University. He is author of The City: A Global History and is finishing a book on the American future.