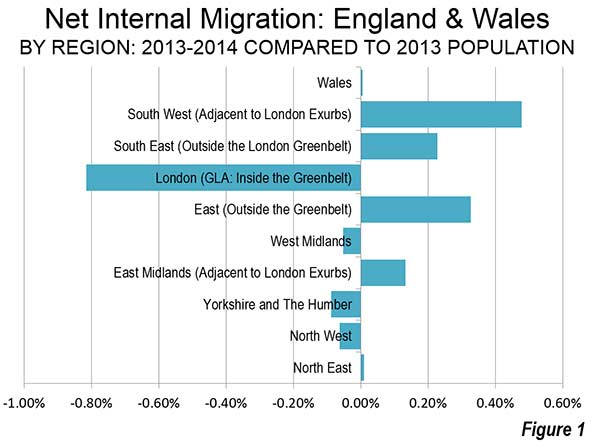
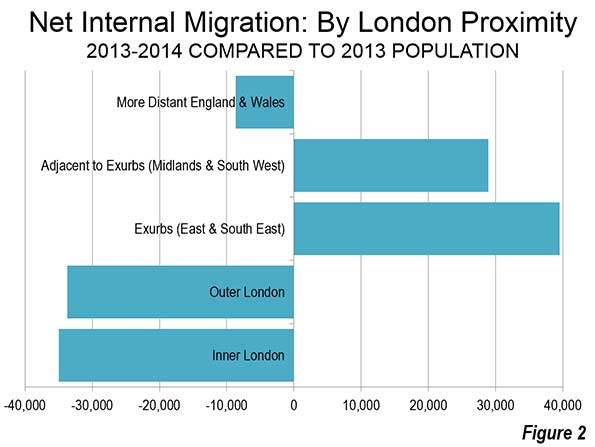
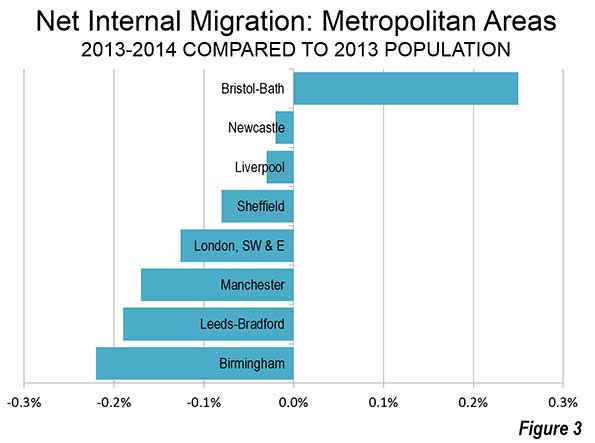
I was in Russia last week and plan to share a few relevant notes from the trip. Since you can easily find better photos of places like the Kremlin than I’ll ever take online, when it comes to Moscow I’m going to focus on more planning and transport items. There’s a lot of other commentary I might make, and if you want to read it, be sure to sign up for my exclusive content by email if you haven’t already, because I may write up further observations on the political scene there.
Writing anything positive about public space and transport in Moscow runs the risk of coming across as seeming to say that “at least Putin makes the trains run on time.” But as he is fully occupied with such critical tasks of state as destroying illicit supplies of Nutella and brie, I doubt he’s bothering himself with such prosaic concerns as transport. Should you be interested, the NYT just ran a good piece on the combination of urban improvement and authoritarianism in Russia’s capital city.
Moscow reminded me a bit of an inverted Buenos Aires. Whereas in BA you get a clear sense that this was once the Paris of South America now well faded, Moscow comes across as a dilapidated city on the rise. You definitely see plenty of run down communist era architecture – the quantity of Corbusian nightmares evident from an aerial view of the city is astonishing – but there are new buildings on the rise and significant evidence of attempts to improve the lived experience of the city.
Moscow is clearly a driving and transit city, not a walking city. Though there is some street life, it’s far lower than comparable high density megacities. But before knocking them too much, keep in mind that Moscow gets bitterly cold in the winter. Even in August the temperature in the afternoon was only the low 70s. Ideal to be sure, but that’s only for a narrow window of the year. Moscow is at 56 degrees north latitude compared to 41 in New York. Moscow is actually further north than every major Canadian city. The sky was already getting light before 4am.
Nevertheless, the outdoor experience there is being enhanced through a number of projects.
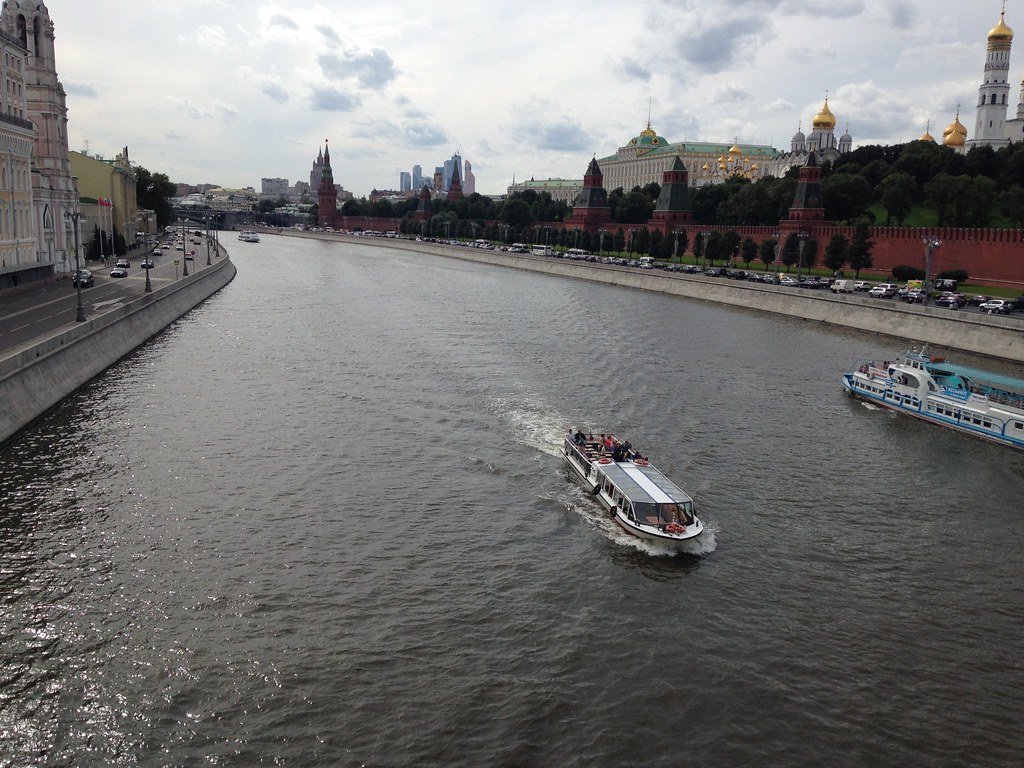
Moscow River
The Moscow River flows through the city, passing alongside the Kremlin as you can see in his photograph.
You see that on both sides it is lined with roads and very narrow sidewalks. It’s not even clear how you would easily get to the riverside on the Kremlin side. A stroll along the bank across from the Kremlin, Cathedral of Christ the Savior, and other landmarks should be amazing, but it is not.
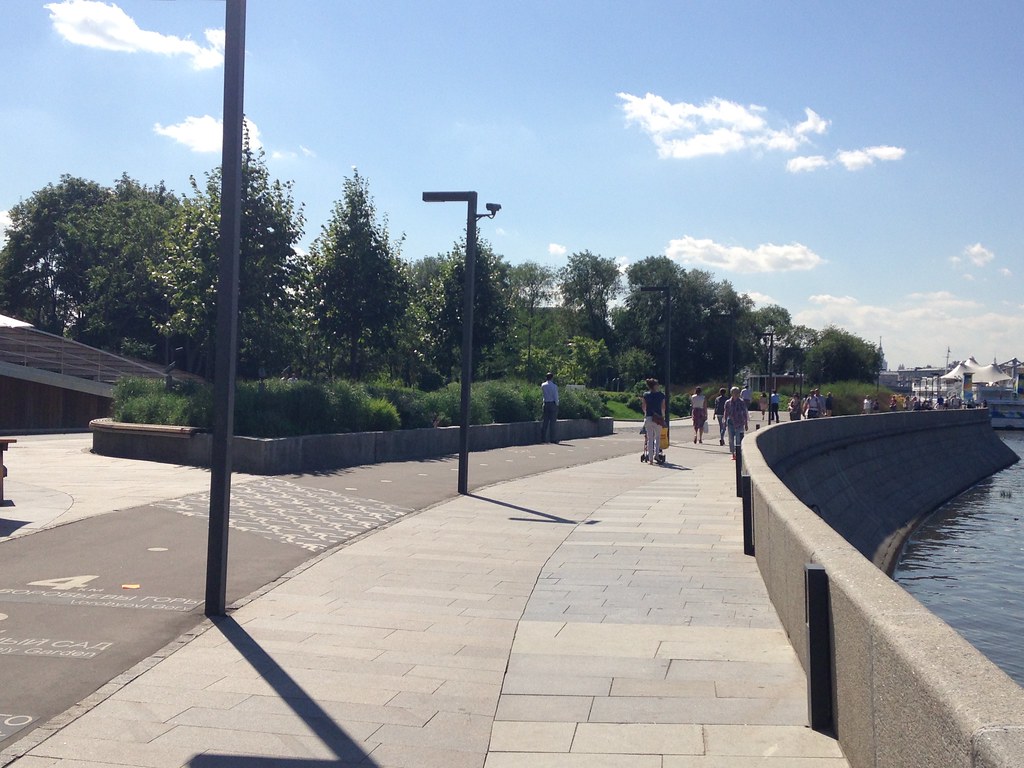
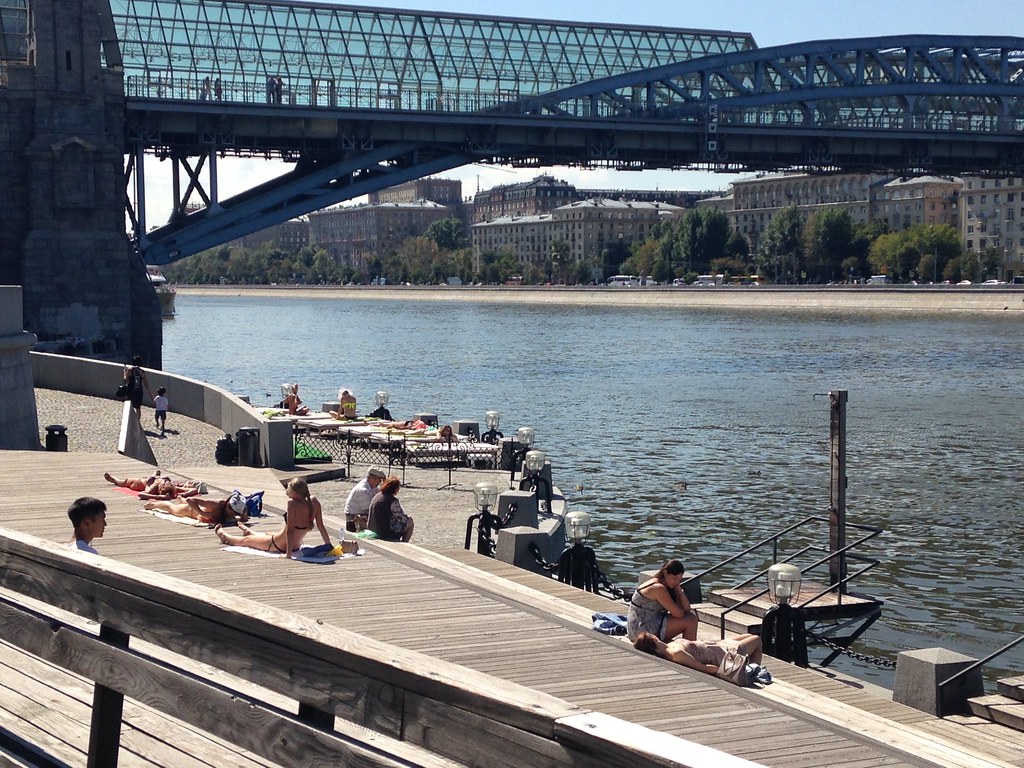
There’s apparently a tender underway that would completely redo this for the better. In the meantime, one section of the river called the Krymskaya Embankment has been redone to a slick, albeit somewhat generic design. This has radically transformed the riverfront for the better, and if the rest of the Moscow River upgrade is similar, this will be a huge transformation for the city.
People enjoying the waterfront.
Here’s a closeup of the bike lane.
The numbers and the text in the background give distances to attractions such as Gorky Park.
Neighborhood Streets
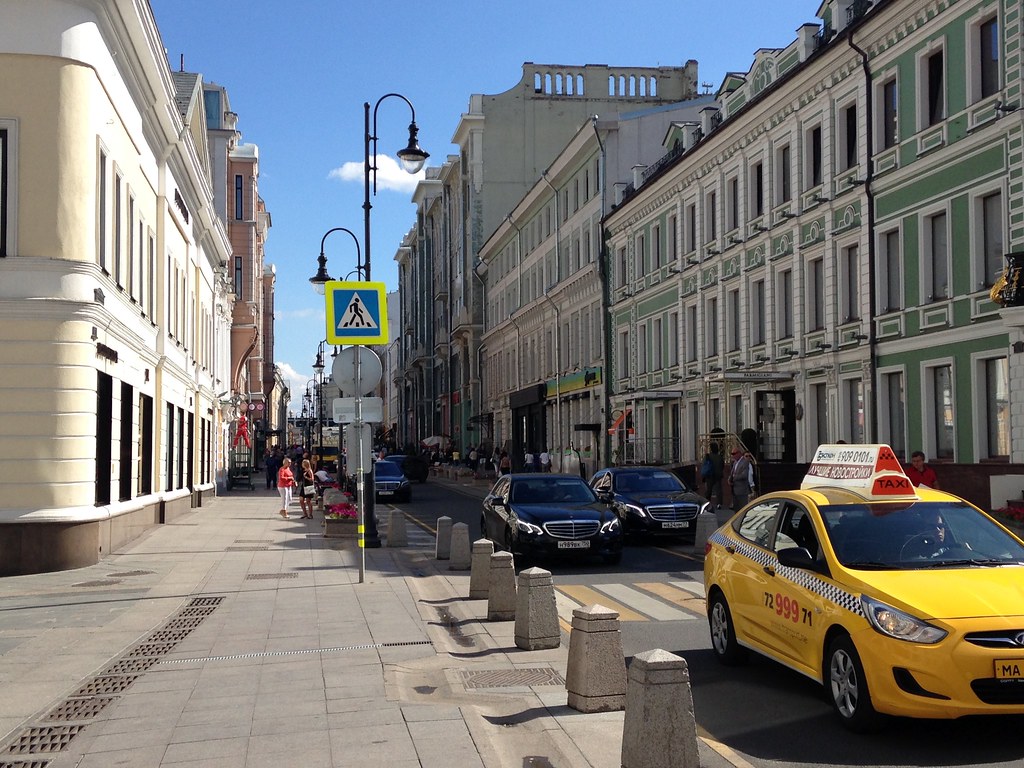
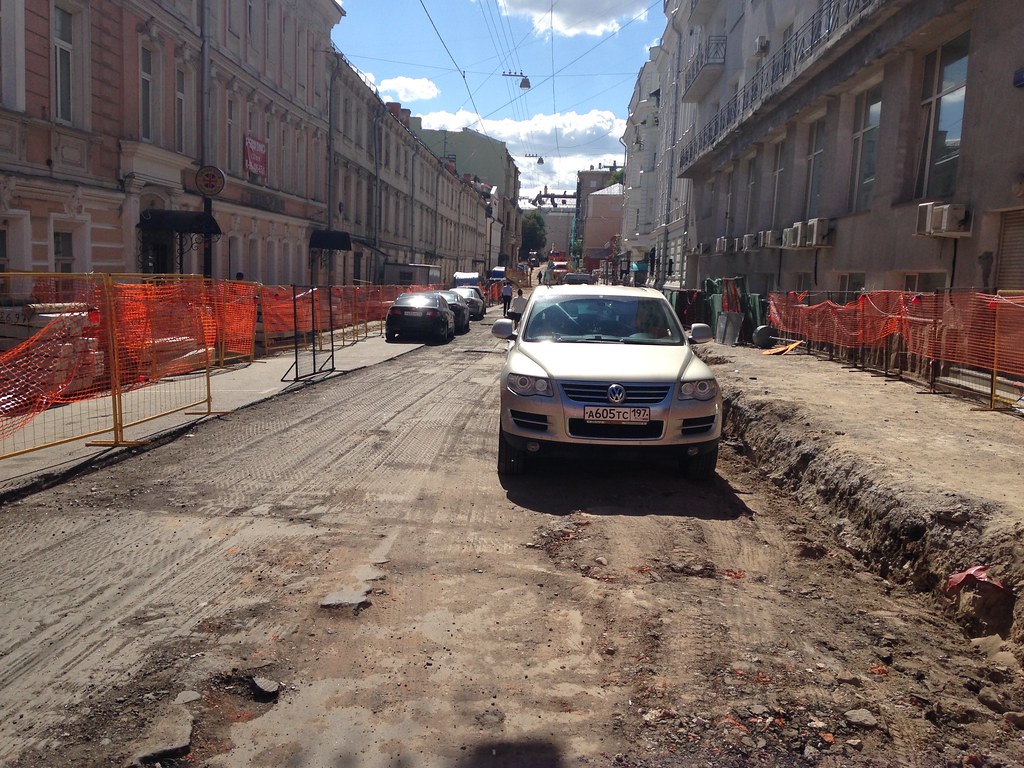
In a way similar to the riverbank, there’s been an effort to upgrade neighborhood streets to improve the pedestrian experience. Traditionally, these have had fairly narrow, basic sidewalks. Here’s a typical example:
And here’s a street that’s been put on a road diet.
This program is ongoing, as this sign touting forthcoming improvements shows.
And a picture of the construction in progress.
There’s also a bike share system.
Arterial Streets
While there are plenty of smaller, human scaled side streets in Moscow, the arterial roads are mega-wide thoroughfares (“prospekts” in the local parlance) that function as quasi-freeways. Here’s an example that isn’t a perfect photo, but let’s you get the gist of it.
You’ll see at least six lanes in a single direction. This building is actually decent, but illustrates what you also see along these high capacity arterials, namely a preponderance of horizontally oriented buildings. Even with broken up facades, these are buildings that are most legible at driving speeds, not walking.
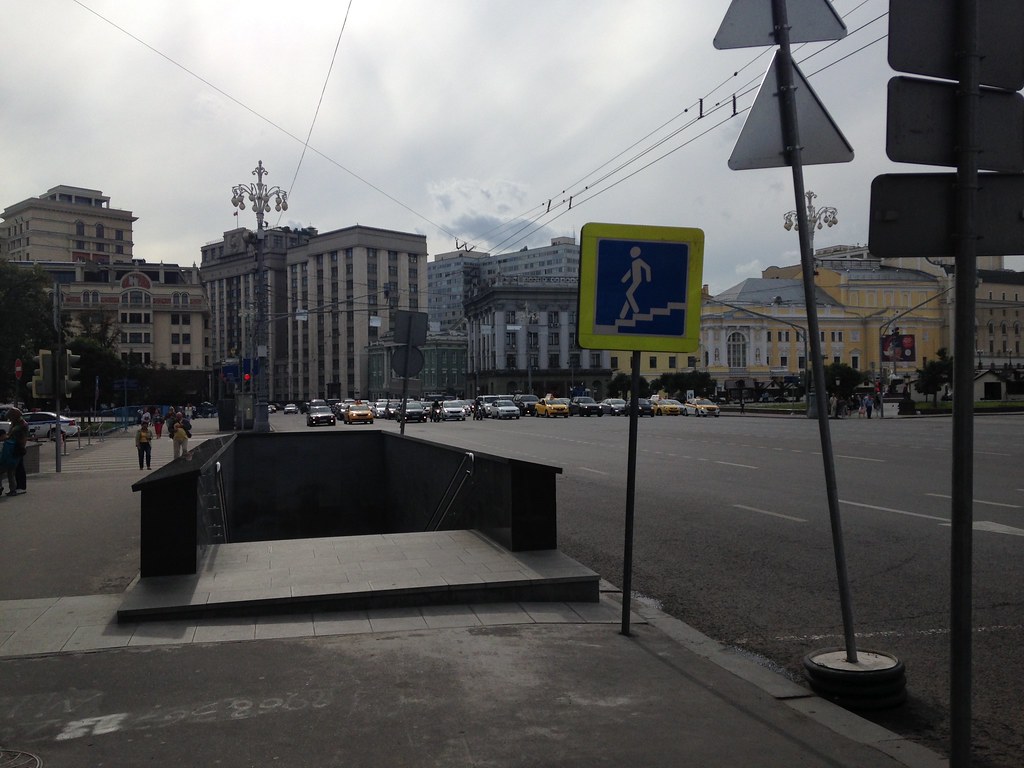
You might wonder how people cross these things, and the answer is that they mostly don’t. For these streets, there’s a heavy reliance on pedestrian underpasses for pedestrian safety. (This also reduces the number of stoplights, which allows for long distances of high speed travel even in the center city). Metro entrances also do double-duty as protected passageways through intersections. Here’s an entrance to one such pedestrian underpass along a one way street that appears to be ten lanes wide.
This might seem inhumane, and it is. But it also functions well. Though I’m told traffic is much lighter in the summer when many vacate the city, there is nothing like the gridlock of a New York, and these roads tended to move pretty good most of the time I was there.
Where there were crosswalks, they featured countdown timers on both the walk and don’t walk cycle.
That’s not a misprint. Some of these lights have extremely long cycles.
Some arterials have a nicer design. One is the so-called “boulevard ring,” which is one of the many ring roads in Moscow. I think (though can’t promise), this shot is from it. Even if not, it’s representative of its design.
Moscow Metro
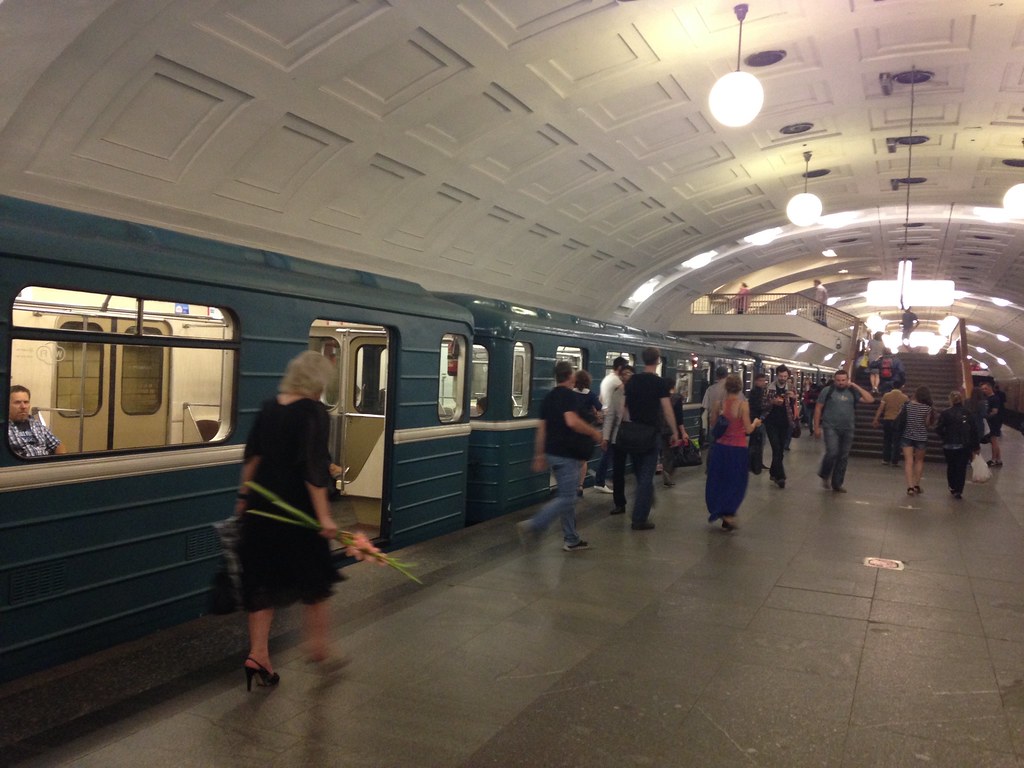
Moscow is famous for its metro system, which is one of the world’s busiest and has lavish station designs. I saw some of these and they are indeed pretty great, though this system should never be applauded without remembering that it was built with gulag labor. Again, I won’t show many pictures of the stations, since my iPhone isn’t the best at low light underground shots. Google is your friend on this.
The metro fare is about a buck. Tap cards are sold at automated kiosks that have English available. Lines are numbered and color coded. Here’s an example of the system signage.
It’s one train right after the next more or less. Even at 11:30 pm there were three minute headways. The cars are older but function well, and there is wifi, which I’m told works even between stations.
There are some newer cars that appear to be married pairs with open gangway between the two linked carriages, but not between pairs.
While you can buy a ticket in English, the bulk of the signage is in Russian only. This isn’t a problem for the most part, but I found the remembering station names in the Cyrillic alphabet was a challenge compared with Latin alphabet stations in other foreign countries. I would suggest that the station name be transliterated into Latin script to make the system more friendly to international users. (The rest of the signage is fine as is). Here’s an example:
If I translate that right, this station is Kropotkinskaya (Kropotkin was a Russian intellectual of the 19th and early 20th centuries). The name is certainly easier to recognize in Latin script for westerners (and probably most others who use English as their international lingua franca). But even in Russian only, you should be able to figure it out how to navigate the system if you pay close attention.
Here’s an example of some transliterated signage. This probably goes above and beyond the call of duty as the numeric indicators suffice.
Air Travel
Moscow has two main airports, I believe, both at a significant distance from the city center. I flew using Sheremetyevo, which is serviceable if not overly pleasant. You have to pass through security immediately upon entering the terminal, then again when going to the gate area. Even domestic transfers require re-screening and passport checks. (I was told by a local, “Russians love checking passports.”)
The most depressing part of the trip was flying three domestic segments on Aeroflot. When I was younger they had an extremely bad reputation, and flew of a fleet of dodgy Soviet made jets. Today, the planes I flew on were newish A-320s and the service levels exceeded US domestic standards (though that’s a low hurdle to jump). They even still serve food on short haul flights. Quite a role reversal there. Red is still their flight attendant colors, and their hammer and sickle logo is still in use.
High Speed Rail
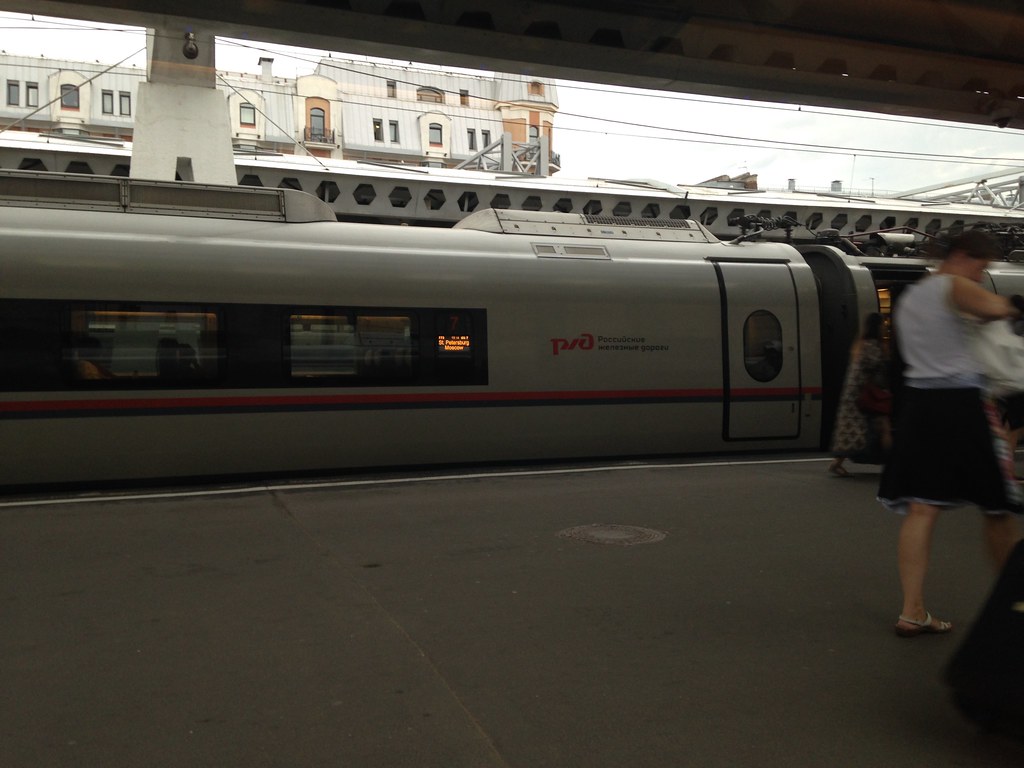
There are a number of rail routes throughout the country, and while I didn’t make a comprehensive survey, I did ride the high speed “Sapsan” service from St. Petersburg to Moscow. IIRC, the fare was around $55. Though using Siemens trainsets derived from the rolling stock used on Germany’s ICE trains, the max speed was 220 km/h (135 mph), comparable to the Acela. However, unlike the Acela, the Sapsan cruises at 200 km/h or higher most of the trip. The journey takes a bit less than four hours and is a pleasant way to travel.
Here’s a picture of one of the trains I took in St. Petersburg’s Moscow Station.
An interior shot.
Conclusion
I hope this gives a bit of a feel for transport in Moscow. The city is obviously spending to try to upgrade its urban environment. Whether physical improvements in Moscow or elsewhere will survive Putin’s authoritarian turn is to be seen, but as the examples of the Moscow subway and many of the historic ruins we visit around the world show, it’s certainly possible for the cruelest of dictatorships to produce magnificent physical artifacts in select places. The success of these regimes should not be judged by that measure.
In closing, I’ll leave translating the following as an exercise for the reader.
If you are interested, there’s an album of iPhone photos I took available on my Flickr page.
Aaron M. Renn is a senior fellow at the Manhattan Institute and a Contributing Editor at City Journal. He writes at The Urbanophile, where this piece first appeared.