This is the introduction to a new report, California’s Social Priorties, from Chapman University’s Center for Demographics and Policy. The report is authored by David Friedman and Jennifer Hernandez. Read the full report (pdf).
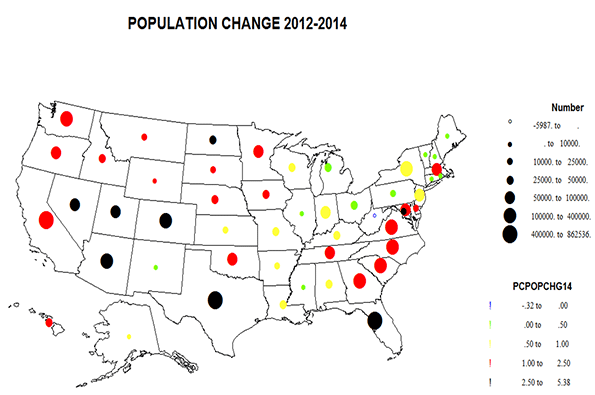
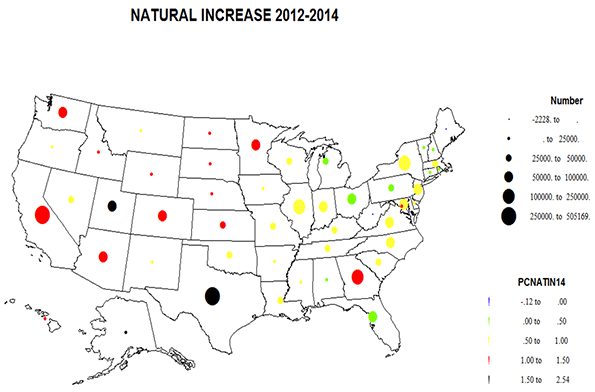
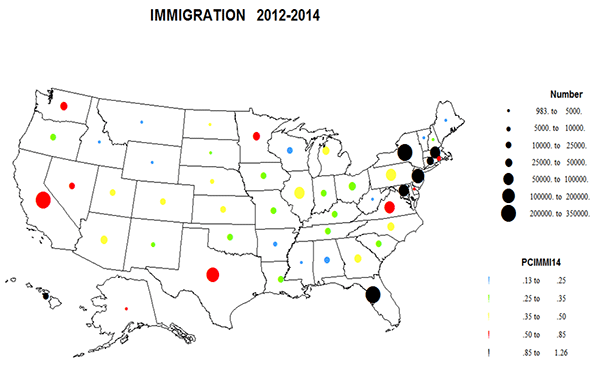
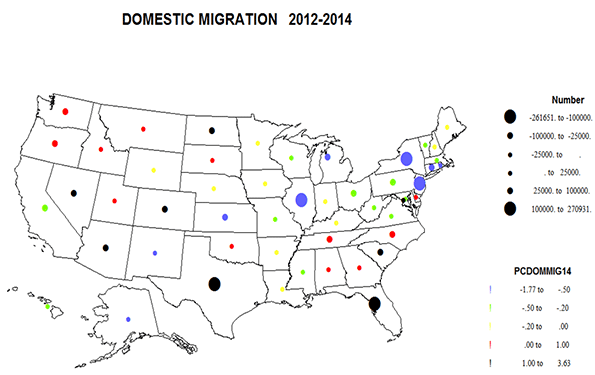
California has achieved a great deal since 1970, including much cleaner air, water and more effective resource stewardship notwithstanding a population increase from approximately 19.9 million in 1970 to over 38 million by 2014. 2 Nevertheless, the state continues to face significant, and in many cases increasingly adverse educational and social equity challenges. As summarized in more detail below:
- California’s grade 9-12 dropout rates remain high and, contrary to national trends, the state’s population of adults with less than a high school education significantly increased from 1970 and currently accounts for nearly 20% of the state’s adults, second highest in the nation. The number of Americans with less than a high school education fell by over 23 million during 1970-2012, and rose in only four states: California, Nevada, Arizona and New Mexico. California’s net increase—over 515,000 adults—was greater than the increase in the other three states combined (409,000).
- The state’s population of high school and community college graduates grew much slower than in the rest of the country, and the population of 4-year or more college educated adults barely kept pace with average national growth rates. In contrast, Texas, also a large, high-immigration state, has added high school and community college-level educated adults more rapidly than the national average since 1970, while the number of adults with less than a high school education declined.
- Inequality has dramatically increased since 1970, when California’s rate of inequality was 25th in the nation. By 2000, the state had the second worst in – come inequality in the country, trailing only New York. The state’s inequality remained fourth worst in the nation (behind only New York, Connecticut and Louisiana) in 2013.
- Income growth for all but the richest 20% of all California households was below the national average from the mid-1970s to the mid-2000s. Incomes for the richest 20% and 5% of all house – holds rose much faster than in the rest of the country.
- Between 1970 and 2013, California’s official poverty rate (which ignores cost of living differences in the U.S.) rose from less than 10% to over 16% of the population. In 2012, the U.S. Census Bureau developed a supplemental poverty measure that accounted for higher living costs in coastal locations such as California. The supplemental measure indicated that, during 2010-2012, nearly 9 million Californians, or about 24% of the state’s population, was impoverished, by far the largest poverty rate in the country. Although California accounts for 12% of the U.S. population, the state has over 18% of the nation’s poor.
- California’s capacity to generate new jobs has severely diminished over time. During 1970-1990, the state generated nearly 5.6 million new jobs and 14.5% of the total employment growth in the country although it accounted for less than 10% of the nation’s population in 1970. From 1991-2013, the state produced 2.6 million new jobs, just 9.7% of the net U.S. employment growth, and well below the state’s 12% share of the nation’s population in 1990. Although the state’s population rose by roughly similar amounts in 1970-1990 (9.8 million) and 1991-2013 (8.6 million), California was unable to generate even half the number of jobs during 1991- 2013 than were created in 1970-1990.
- Annual nonfarm employment growth averaged 3% in 1970-1990, well above the national average, but just 0.8% in 1991-2013, well below the national average. In contrast Texas, with 70% of California’s population, produced over 4 million new jobs during 1991-2013, and Florida, with half of California’s population, generated nearly the same number of new jobs as California (2.2 million). During 1991-2013, California more closely resembled historically slow growing northeastern and Midwest states than faster-growing regions of the U.S., especially in the southeast.
These data show that California needs to address significant, and growing social priorities, including significant improvement in adult educational rates at the high school and post-secondary level, increasing employment opportunities at a rate sufficient to serve past and forecast population growth, and reducing the state’s inequality and very high poverty rates.
California continues to lead the country, and by some measures even the world, in environmental quality and climate change initiatives. But public policy must evolve to leverage these environmental achievements into corresponding improvements in educational attainment and middle class job creation. With more than 18% of the nation’s poor, and less than 1%3 of global greenhouse gas emissions, California should also embrace the challenge of leading the world in the creation of middle class manufacturing jobs for the rapidly evolving clean and green technology that California’s laws mandate, California’s educational and technology sectors invent, and California’s venture capital investors bring to the global market.
Instead, California’s policies, and regulatory and legal costs and uncertainties, tend to divert thousands of middle class jobs even in emerging green industries (including those not requiring high school diplomas) to other locations, including the Tesla battery manufacturing facility, which moved to Nevada. The loss of projects that help achieve important environmental objectives, create high quality jobs, and comply with California’s strict environmental and public health protection mandates, continues to occur in part because well-funded special interest groups ranging from business competitors to labor unions file "environmental" lawsuits as leverage for achieving narrow political or pecuniary objectives rather than to protect the environment and public health. This study suggests that the state must work much harder to ensure that California’s landmark environmental laws are not misused or pursued in a manner that adversely affects other, equally important policy priorities for California’s large undereducated and underemployed population.