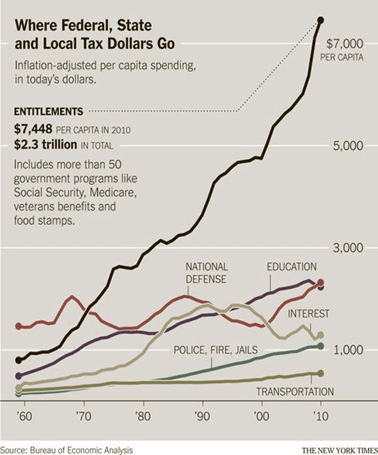
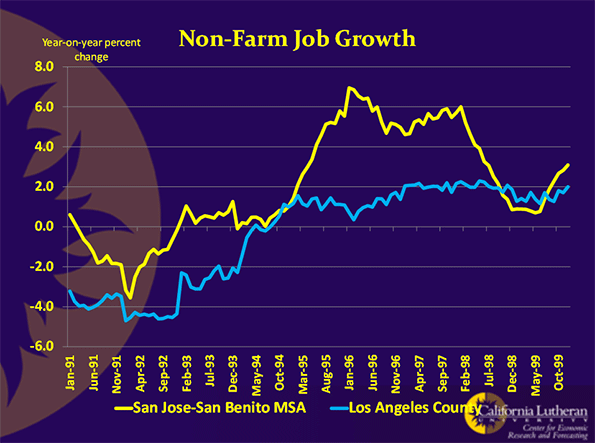
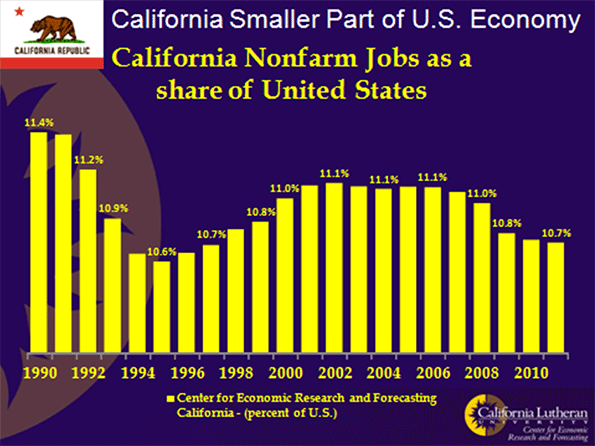
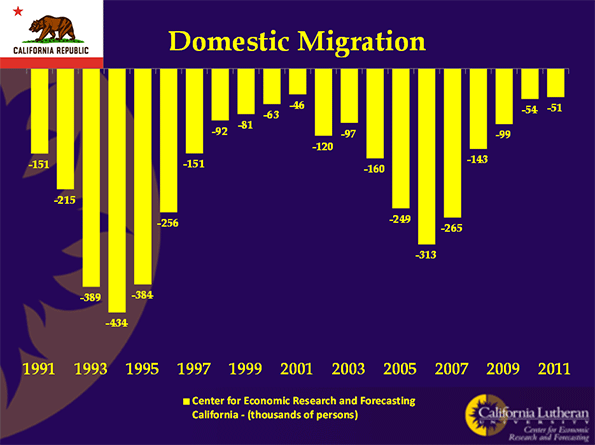
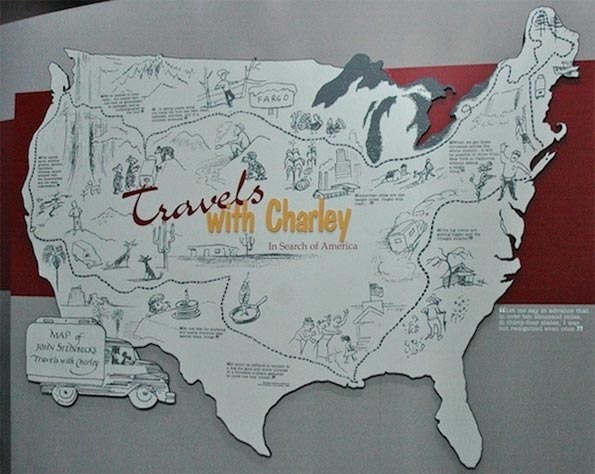
In the fall of 2010, as part of a book project, ex-newspaperman Bill Steigerwald retraced the route John Steinbeck took in 1960 and turned into his classic “Travels With Charley.” Steigerwald drove 11,276 miles in 43 days from Long Island to the top of Maine to Seattle to San Francisco to New Orleans before heading back to his home in Pittsburgh. In “Dogging Steinbeck,” his new e-book about how he discovered “Charley” was not nonfiction but a highly fictionalized and dishonest account of Steinbeck’s real trip, Steigerwald describes the America he saw.
"Big."
"Empty."
"Rich."
"No change since 1960."
Long after the old farms and new forests of New England disappeared in my rearview mirror, I was still scrawling those words in the reporter’s notebook on my knee. Big, empty, rich and unchanged – that’s a pretty boring scouting report for the America I “discovered” along the Steinbeck Highway. You can add a bunch of other boring but fitting words – “beautiful,” “safe,” “friendly,” “clean,” and “quiet.”
Like Steinbeck, I didn’t see the Real America or even a representative cross-section of America, neither of which exist anyway. Because I went almost exactly where Steinbeck went and stopped where he stopped, I saw a mostly White Anglo Saxon Protestant Republican America, not a “diverse and politically correct” Obama one. Mostly rural or open country, it included few impoverished or crime-tortured inner cities and no over-developed/underwater suburbs.
America the Beautiful was hurting in the fall of 2010, thanks to the bums and crooks in Washington and on Wall Street who co-produced the Great Recession. It still had the usual ills that make libertarians crazy and may never be cured: too many government wars overseas and at home, too many laws, politicians, cops, lawyers, do-gooders and preachers.
But America was not dead, dying or decaying. There were no signs of becoming a liberal or conservative dystopia. The U.S. of A., as always, was blessed with a diverse population of productive, affluent, generous, decent people and a continent of gorgeous natural resources.
Everyday of my trip I was surrounded by undeniable evidence of America’s underlying health and incredible prosperity. Everywhere I went people were living in good homes, driving new cars and monster pickup trucks and playing with powerboats, motorcycles and snowmobiles. Roads and bridges and parks and main streets were well maintained. Litter and trash were scarce. Specific towns and regions were hurting, and too many people were out of work, but it was still the same country I knew.
I didn’t seek out poverty or misery or pollution on my journey, and I encountered little of it. The destitute and jobless, not to mention the increasing millions on food stamps, on welfare or buried in debt, were especially hard to spot in a generous country where taking care of the less fortunate is a huge public-private industry – where even the poor have homes, cars, wide-screen TVs and smart phones.
I saw the familiar permanent American socioeconomic eyesores – homeless men sleeping on the sidewalks of downtown San Francisco at noon, the sun-bleached ruins of abandoned gas-stations on Route 66, ratty trailer homes parked in beautiful locations surrounded by decades of family junk. I saw Butte’s post-industrial carcass, New Orleans’ struggling Upper Ninth Ward and towns that could desperately use a Japanese car plant.
But the country as a whole was not crippled or even limping. In the fall of 2010, nine in 10 Americans who said they wanted jobs still had them. The one in 10 who were jobless had 99 weeks of extended unemployment benefits and more than 90 percent of homeowners were still making their mortgage payments.
Most of the states I shot through – including Maine, northern New Hampshire and Vermont, upstate New York, Wisconsin, Minnesota, North Dakota, Montana – had unemployment and foreclosure rates well below the national averages.
I didn’t visit the abandoned neighborhoods of poor Detroit. I didn’t see battered Las Vegas, where 14.5 percent of the people were unemployed and one in nine houses – five times the national average – had received some kind of default notice in 2010. But I spent almost two weeks in the Great Train Wreck State of California, where jobless and foreclosure rates were higher than the national average and municipal bankruptcies loomed.
America had 140 million more people than it did in 1960, but from coast to coast it was noticeably quiet – as if half the population had disappeared. Despite perfect fall weather, public and private golf courses were deserted. Ball fields were vacant. Parks and highway rest stops and ocean beaches were barely populated. Except for metropolises like Manhattan and San Francisco and jumping college towns like Missoula and Northampton, people in throngs simply did not exist. I went through lots of 30-mph towns that looked like they’d been evacuated a year earlier.

As I drove what’s left of the Old Steinbeck Highway – U.S. routes 5, 2, 1, 11, 20, 12, 10, 101 and 66 – it was obvious many important changes had occurred along it since 1960. Industrial Age powerhouses like Rochester, Buffalo and Gary had seen their founding industries and the humans they employed swept away by the destructive winds of technology and global capitalism. Small towns like Calais in northeastern Maine had lost people and jobs, and vice versa.
New Orleans had shrunk by half, and not just because of Katrina. The metro areas of Seattle, San Francisco and Albuquerque had exploded and prospered in the digital age. The populations of the West Coast and the Sunbelt had expanded since 1960. The South had shed its shameful system of apartheid and its overt racism, as well as much of its deep-rooted poverty and ignorance. The Northeast had bled people, manufacturing industries and its once overweening role in determining the nation’s political and cultural life.
Change is inevitable, un-stoppable, pervasive. Nevertheless, it was clear that a great deal of what I saw out my car windows had hardly changed at all since Steinbeck and his French poodle Charley raced by.
He saw more farmland and fewer forests than I did, especially in the East. But in many places I passed through almost nothing was newly built. Many farms and crossroads and small towns and churches were frozen in the same place and time they were eons ago, particularly in the East and Midwest.
In Maine the busy fishing village of Stonington was as picturesque as the day Steinbeck left it. He’d recognize the tidy farms of the Corn Belt and the raw beauty of Redwood Country and the buildings if not the people of the Upper Ninth Ward. And at 70 mph whole states – North Dakota and Montana – would look the same to him except for the cell towers and Pilot signs staked out at the interstate exits.
Steinbeck didn’t like a lot of things about Eisenhower America – sprawl, pollution, the rings of junked cars and rubbish he saw around cities. And he lamented – not in “Charley” but in letters to pals like Adlai Stevenson – that he thought America was a rotting corpse and its people had become too soft and contented to keep their country great and strong.
But Steinbeck had America’s future wrong by 178 degrees. Fifty years later, despite being stuck in an economic ditch, the country was far wealthier, healthier, smarter and more globally powerful and influential than he could have imagined. Its air, water and landscapes were far less polluted. And, most important, despite the exponential growth of the federal government’s size and scope and its nanny reach, America in 2010 was also a much freer place for most of its 310 million citizens, especially for women, blacks, Latinos and gays.
You don’t have to be a libertarian to know America is not as free as it should be. But there’s no denying that today our society is freer and more open than ever to entrepreneurs, new forms of media, alternative lifestyles and ordinary people who want to school their own kids, medicate their own bodies or simply choose Fed Ex instead of the U.S. Post Office.
As for the stereotypical complaints about America being despoiled by overpopulation, overdevelopment and commercial homogenization, forget it. Anyone who drives 50 miles in any direction in an empty state like Maine or North Dakota – or even in north-central Ohio or Upstate New York – can see America’s problem is not overpopulation. More often it’s under-population. Cities like Butte and Buffalo and Gary have been virtually abandoned. Huge hunks of America on both sides of the Mississippi have never been settled.
From Calais, Me., to Pelahatchie, Miss., I passed down the main streets of comatose small towns whose mayors would have been thrilled to have to deal with the problems of population growth and sprawl. If anyone thinks rural Minnesota, northwestern Montana, the Oregon Coast, the Texas Panhandle or New Orleans’s Upper Ninth Ward have been homogenized, taken over by chains or destroyed by too much commercial development, it’s because they haven’t been there.
The America I traveled was unchained from sea to sea. I had no problem eating breakfast, sleeping or shopping for road snacks at mom & pop establishments in every state. The motels along the Oregon and Maine coasts are virtually all independents that have been there for decades. You can go the length of old Route 66 and never sleep or eat in a chain unless you choose to.
Steinbeck, like many others have since, lamented the loss of regional customs. (I don’t think he meant the local “customs” of the Jim Crow South or the marital mores of the Jerry Lee Lewis clan.) I didn’t go looking for Native Americans, Amish, Iraqis in Detroit, Peruvians in northern New Jersey or the French-Canadians who have colonized the top edge of Maine. But I had no trouble spotting local flavor in Wisconsin’s dairy lands, in fishing towns along Oregon’s coast, in the redwood-marijuana belt of Northern California, in San Francisco’s Chinatown or the cattle country of Texas.
Not to generalize, but the New York-Hollywood elites believe the average Flyover Person lives in a double-wide or a Plasticville suburb, eats only at McDonald’s, votes only Republican, shops only at Wal-Mart and the Dollar Store, hates anyone not whiter than they are, speaks in tongues on Sunday and worships pickup trucks, guns and NASCAR the rest of the week.
Those stereotypes and caricatures are alive and well in Flyover Country. But though I held radical beliefs about government, immigration and drugs that could have gotten me lynched in many places, I never felt I was in a country I didn’t like or didn’t belong in. Maybe I just didn’t go to enough sports bars, churches and political rallies, but for 11,276 miles I always felt at home.
Bill Steigerwald, born and raised in Pittsburgh, is a former L.A. Times copy editor and free-lancer who also worked as a docudrama researcher for CBS-TV in Hollywood before becoming a reporter for The Pittsburgh Post-Gazette and a columnist for The Pittsburgh Tribune-Review. He recently retired from daily newspaper journalism.