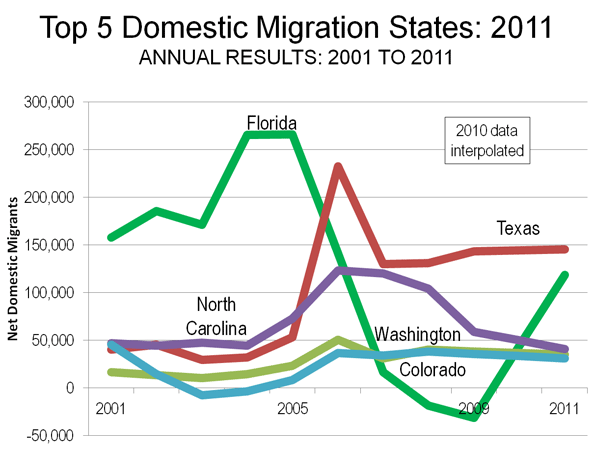
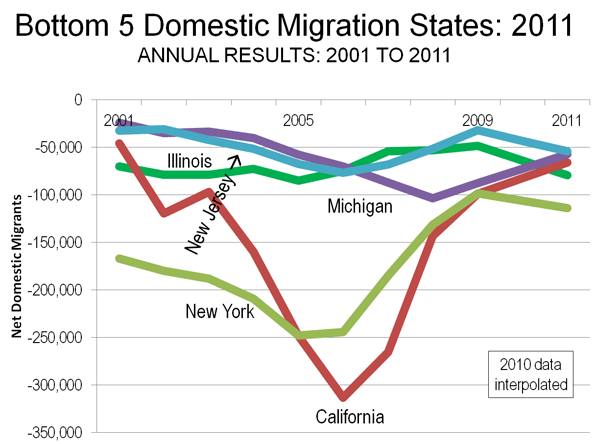
As befits this time of year, our thoughts turn to the events that await us in the days ahead. Putting aside the major imponderable — the outcome of the presidential and congressional elections that inevitably will impact the federal transportation program —what can the transportation community expect in 2012? Will Congress muster the will to enact a multi-year surface transportation reauthorization? Or will the legislation fall victim to election year paralysis? What other significant transportation-related developments lie ahead in the new year? Here are our speculations as we gaze into our somewhat clouded crystal ball.
Will Congress enact a multi-year transportation bill?
In 2011, the Senate Environment and Public Works (EPW) Committee passed a bipartisan two-year surface transportation bill (MAP-21) and the Senate Commerce Committee approved the measure’s safety, freight and research components. But at the end of the year, the bill’s titles dealing with public transportation, intercity passenger rail and financing were still tied up in their respective committees (Banking, Commerce and Finance). What’s more, the Senate bill ended up $12 billion short of meeting the $109 billion mark set by the EPW Committee as necessary to maintain the current level of funding plus inflation.
Finance Committee Chairman Max Baucus (D-MT) has yet to publicly identify the offsets needed to cover the final $12 billion of the bill’s cost. Repeated assurances by EPW committee chairman Sen. Barbara Boxer (D-CA) that the necessary "pay fors" have been found, has met with widespread skepticism. "I’ll believe it when I see it" has been a typical reaction among congressional watchers. With the Republicans opposed to using "gimmicks" (Sen. Orrin Hatch’s words) to come up with the needed money, it’s not entirely clear that the bill, as approved on the Senate floor, will contain the full $109 billion in funding.
On the House side, the fate of a multi-year bill remains equally clouded. In November, Speaker Boehner announced that he would soon unveil a combined transportation and energy bill, dubbed the "American Energy & Infrastructure Jobs Act" (HR 7). The bill would authorize expanded offshore gas and oil exploration and dedicate royalties from such exploration to "infrastructure repair and improvement" focused on roads and bridges.
However, questions have been raised about this approach. Critics, including Sen. Barbara Boxer and Sen. James Inhofe (R-OK) EPW committee’s ranking member, judge the approach as problematical. They allege, along with many other critics, that the royalties the House is counting upon would fall billions of dollars short of filling the gap in the needed revenue (the gap is estimated at approximately $75-80 billion over five years). They further contend that the revenue stream from the royalties would not be available in time to fund the multi-year transportation program. What’s more, using oil royalties to pay for transportation would essentially destroy the principle of a trust fund supported by highway user fees. In sum, the House bill, if unveiled in its currently proposed form, will meet with a highly skeptical reception in the Senate.
Assuming that both reauthorization bills in some form will gain approval in February, will the two Houses be able to reconcile their widely different versions by March 31 when the current program extension is set to expire? Or will the negotiations bog down in an impasse reminiscent of the current payroll tax stalemate? Given the importance that both sides attach to enacting transportation legislation and given the desire of both sides to avoid the blame of causing an impasse, we think the odds are in favor of reaching an accommodation — probably more along the lines of the Senate two-year bill than the still vague and unfunded House five-year version. If this simply kicks the can down the road a couple of years, that may be OK with Senate Republicans. As one senior Senate Republican confidently told us, by the bill’s expiration date the Senate will be in Republican hands and "the true long-term bill will be ours to shape."
Will California lawmakers pull the plug on the high-speed train?
In 2011 Congress effectively put an end to the Administration’s high-speed rail initiative by denying any funds to the program for a second year in a row. Does the same fate await the embattled $98 billion California high-speed rail project at the hands of the state legislature in 2012?
At a December 15 congressional oversight hearing, witnesses cited a litany of reasons why the projects is a "disaster" (Rep. John Mica’s words). Among them: unrealistic assumptions concerning future funding; quixotic choice of location for the initial line section ("in a cow patch," as several lawmakers remarked); lack of evidence of any private investor interest in the project; eroding public support (nearly two-thirds of Californians would now oppose the project if given the chance, according to a recent poll); a "devastating" impact of the proposed line on local communities and farm land; unrealistic and out-of-date ridership forecasts; and lack of proper management oversight.
More recently, the project came under additional criticism. The job estimates claimed by the project’s advocates ("over one million good-paying jobs" according to House Minority Leader Nancy Pelosi) have been challenged— and acknowledged by project officials— as grossly inflated. Four local governments in the Central Valley, including the City of Bakersfield, have formally voted to oppose the project, fearing harmful effect on their communities. And agricultural interests are gearing up for a major legal battle, according to the Los Angeles Times.
But most unsettling for the project’s future is the inability of its sponsors to come up with the needed funding. To complete the "Initial Operating Segment" to San Jose (or the San Fernando Valley) would require an additional $24.7 billion. To finance this construction, the California Rail Authority’s business plan calls for $4.9 billion in Proposition 1A bonds and assumes $19.8 billion in federal contributions – $7.4 billion in federal grants and $12.4 billion in the so-called Qualified Tax Credit Bonds (QTCB). But the latter assumptions came in for sharp congressional criticism as so much wishful thinking, given the bipartisan congressional refusal to appropriate funds for high-speed rail two years in a row.
Further challenges await the project early in 2012. A group of 12 congressmen led by House Majority Whip Kevin McCarthy (R-CA) has formally requested the Government Accountability Office (GAO) to review the project’s viability and "questionable ridership and cost projections." Also expected early in January are a critique of the Authority’s business plan by the Independent Peer Review Group and a follow-up report by the State Auditor.
Meanwhile, the governor and state legislature, are being asked by the Rail Authority to approve a $2.7 billion bond issue authorized by Proposition 1A to fund and begin construction of the initial Central Valley section of the rail line from Fresno to Bakersfield. Will they be swayed by the findings of the three respected reviewing bodies and by the increasingly negative editorial and public opinion? Or will they continue to hold on to the seductive vision of bullet trains zooming from northern to southern California in two and a half hours — however distant and uncertain that vision may be? At this point, we believe the decision could go either way. However, sharply critical reports by the Peer Review Group and the General Accountability Office could tip the scale against funding the Central Valley project.
Will tolling join the gas tax as a mainstream source of highway revenue?
With the possibility of a near-term gas tax increase "less than zero," attention has turned to alternative means of raising transportation revenue. The most prominent option appears to be tolling— and 2012 may be the year when tolling becomes accepted as a mainstream source of highway revenue.
Recent toll increases on the nation’s highways attest to their growing use (if not popularity) as revenue enhancers. In New Jersey, tolls are set to rise by 53% on the New Jersey Turnpike and by 50% on the Garden State Parkway. The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey also has approved substantial toll increases on bridges linking the two states. These moves have provoked Sen. Frank Lautenberg (D-NJ) to sponsor a "commuter protection act" that would transfer toll setting powers to the U.S. Secretary of Transportation. But the Senator’s initiative does not appear to have obtained much support in Congress. IBTTA, the toll industry association, has lodged strong objections, arguing that federalizing toll rate setting would encroach on the states’ jurisdiction and interfere with their ability to use tolls as a tool of infrastructure financing, and Congress appears to be listening.
A recent Reason Foundation poll has found that people are more willing to pay tolls than increased fuel taxes (by a margin of 58 to 28 percent.) Moreover, the formation of a new "U.S. Tolling Coalition" suggests a growing interest in tolling on the part of the states. Under a pilot program that allows up to three Interstate highways to be reconstructed with tolls, Virginia will add tolls along the I-95 corridor and Missouri will toll its stretch of I-70. Arizona and North Carolina have applied for the remaining slot in the pilot program. Other states are embracing tolling to finance new capacity. Washington State, for example, has begun tolling the SR-520 floating bridge over Lake Washington to help pay for its replacement. Nor is the practice of tolling confined just to a few states. All told, 35 states already depend on toll revenue to some extent.
The Tolling Coalition wants to expand the pilot program and give the states the flexibility to toll any portions of their Interstate and other federal highways, "whether for new capacity, system preservation, or reconstruction." So far, neither the Senate nor the House have agreed to relax existing prohibitions, but they are prepared to retain the current pilot program.
However, the need to reconstruct and modernize the existing Interstates which are reaching the end of their 50-year design life, combined with the necessity to expand capacity of the Interstate highway system to meet the needs of an expanding population, may soften congressional opposition to relaxing the current Interstate tolling restrictions. With the gas tax no longer able to meet the nation’s transportation investment needs, and with the concept of a VMT (vehicle-miles travel) fee still a distant vision, the year 2012 could mark a turning point in the acceptance of tolling as a serious highway revenue enhancer.
###
Note: the NewsBriefs can also be accessed at www.infrastructureUSA.org
A listing of all recent NewsBriefs can be found at www.innobriefs.com