As its economy started to recover in 2010, progressives began to hail California as a kind of Scandinavia on the Pacific — a place where liberal programs also produce prosperity. The state’s recovery has won plaudits from such respected figures as The American Prospect’s Harold Meyerson and the New York Times’ Paul Krugman.
Gov. Jerry Brown, in Bill Maher’s assessment, “took a broken state and fixed it.” There’s a political lesson being injected here, as well, as blue organs like The New Yorker describe California as doing far better economically than nasty red-state Texas.
But if you take a look at long-term economic trends, or drive around the state with your eyes open, the picture is far less convincing. To be sure, since 2010 California’s job growth has outperformed the national average, propelled largely by the tech-driven Bay Area; its 14% employment expansion over the past six years is just a shade below Texas’. But dial back to 2001, and California’s job growth rate is 12%, less than half that of Texas’ 27%. With roughly 10 million fewer residents, Texas has created almost 2.8 million jobs since the turn of the millennium, compared to 2.0 million in California.
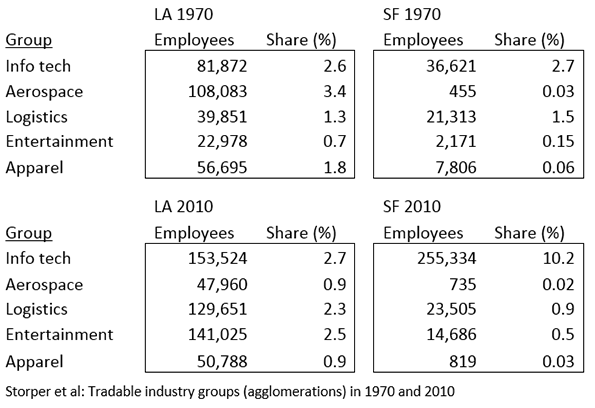
Even in the Bay Area, the picture is less than ideal. Since 2001, total employment in the San Francisco area has grown barely 12% compared to 52% in Austin, 37.8% in Dallas-Ft. Worth, 36.5% in Houston and 31.1% in San Antonio. Los Angeles, by far California’s largest metro area, scratched out pedestrian job growth of 10.3%, slightly above the national increase of 9.3% over that time span.
Remarkably, despite the recent tech boom, California’s employment growth in science, technology, engineering and mathematics-related fields (aka STEM) since 2001 is just 11%, compared to 25% in Texas. Both Austin and San Antonio have increased their STEM employment faster than the Bay Area while Los Angeles, California’s dominant urban region and one-time tech powerhouse, has achieved virtually no growth. This pattern also holds for the largest high-wage sector in the U.S., business and professional services.
Geographic Disparity: Relying On Facebook
“It’s not a California miracle, but really should be called a Silicon Valley miracle,” says Chapman University forecaster Jim Doti. “The rest of the state really isn’t doing well.”
This dependence on one region has its dangers. Silicon Valley has only recently topped its pre-dot-com boom jobs total, confirming the fundamental volatility of the tech sector. And there are clear signs of slowing, with layoffs increasing earlier in the year and more companies looking for space in less expensive, highly regulated areas.
Consolidation and dominance by a few giants like Google, Facebook, Apple threaten to make Silicon Valley less competitive and innovative, as promising start-ups are swallowed at an alarming rate. Even Sergei Brin, a co-founder of Google, recently suggested that start-ups would be better off launching somewhere else.
Housing poses perhaps the most existential threat to the Bay Area, particularly among millennials entering their 30s. Only 13% of San Franciscans could purchase the county’s median home at standard rates and term. For San Mateo, the number is 16%. No surprise that as many as one in three Bay Area residents are now contemplating an exit, according to an opinion poll this past spring.
Outside the Bay Area, where tech is weaker, the situation is much grimmer. In Orange County, the strongest Southern California economy, tech and information employment is lower today than in 2000. In Los Angeles, employment has declined in higher-wage sectors like tech, durable goods manufacturing and construction, to be replaced by lower-wage jobs in hospitality, health and education. A recent analysis by the Los Angeles Economic Development Corp. predicts this trend will continue for the foreseeable future.
Expanding Inequality
Perhaps nothing undermines the narrative of the California “comeback” more than the state’s rising inequality. A recent Pew study found California’s urban areas over-represented among the metro area where the middle class is shrinking most rapidly. California now is home of over 30% of United States’ welfare recipients, and almost 25% of Californians are in poverty when the cost of living is factored in, the highest rate in the country.
Even in Silicon Valley, the share of the population in the middle class has dropped from 56% of all households to 45.7%, according to a recent report by the California Budget Center. Both the lower and upper income portions grew significantly; today lower-income residents represent 34.8% of the population compared to 19.5% affluent.
Such disparities are, if anything, greater in Los Angeles, where high rents and home prices, coupled with meager income growth, is deepening a potentially disastrous social divide. Renters in the L.A. metro area are paying 48% of their monthly income to keep a roof above their heads, one reason why the Los Angeles area is now the poorest big metro area in the country, according to American Community Survey data. Overall California is home to a remarkable 77 of the country’s 297 most “economically challenged” cities, based on levels of poverty and employment, according to a recent study; altogether these cities have a population of more than 12 million.
One critical sign of failure: As the “boom” has matured, the number of homeless has risen to 115,000, roughly 20% of the national total. They are found not only in infamous encampments such as downtown Los Angeles “skid row” or San Jose’s “the Jungle” but also more traditionally middle class areas as Pacific Palisades and through central parts of Orange County.
The Fiscal Crisis
California’s “comeback” has been bolstered by assertions that the state has returned fiscal health. True, California’s short-term budgetary issues have been somewhat relieved, largely due to soaring capital gains from the tech and high end real estate booms; just 5,745 taxpayers earning $5 million or more generated more than $10 billion of income taxes in 2013, or about 19% of the state’s total, according to state officials.
Most likely this state deficit will balloon once asset inflation deflates. Brown is already forecasting budget deficits as high as $4 billion by the time he leaves office in 2019. The Mercatus Center ranks California 44th out of the 50 states in terms of fiscal condition, 46th in long-run solvency and 47th in terms of cash needed to cover short-run liabilities.
Despite this, the public employee-dominated state government continues to increase spending, with outlays having grown dramatically since the 2011-12 fiscal year, averaging 7.8% per year growth. No surprise that Moody’s ranked California second from the bottom among the states in its preparedness to withstand the next recession. Brown’s own Department of Finance predicts that a recession of “average magnitude” would cut revenues by $55 billion.
The Cost Of The Climate Jihad
Relieved over concerns in the short run budget, the rise in revenues has provided a pretext for Brown to push his campaign to fight climate change to extremes. New legislation backed by the governor would impose more stringent regulations on greenhouse gas emissions, mandating a 40% cut from 1990 levels by 2030.
Brown has no qualms about the economic impact of his policies since he tends to prioritize one sin — greenhouse gas emissions — even above such things as alleviating poverty. Brown’s moves will, by themselves, have no demonstrable impact on climate change given California’s size, temperate climate and loss of industry, as one recent study found. Brown knows this: he’s counting on setting an example that other states and countries will follow. Perhaps less recognized, California’s efforts to reduce emissions may account for naught, since the industry and people who have moved elsewhere have simply taken their carbon footprint elsewhere, usually to places where climate and less stringent regulation allow for greater emissions.
California’s climate policies, however, are succeeding in further damaging the middle and working class. Environmental regulations, particularly a virtual ban on suburban homes, are driving housing prices up; mandates for renewables are doing the same for energy prices. This hits hardest at traditionally higher-paying blue-collar employment in housing, manufacturing, warehousing and even agriculture.
California’s climate agenda has accelerated the state’s continued bifurcation — by region, by race and ethnicity, and even by age. Of course the green non-profit advocacy groups and the media will celebrate California’s comeback as proof that strict regulations and high taxes work. They seem not to recognize that that human societies also need to be sustainable, something that California’s trajectory certainly seems unlikely to accomplish.
This piece first appeared in Forbes.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com. He is the Roger Hobbs Distinguished Fellow in Urban Studies at Chapman University and executive director of the Houston-based Center for Opportunity Urbanism. His newest book, The Human City: Urbanism for the rest of us, will be published in April by Agate. He is also author of The New Class Conflict, The City: A Global History, and The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050. He lives in Orange County, CA.
Photo: Troy Holden