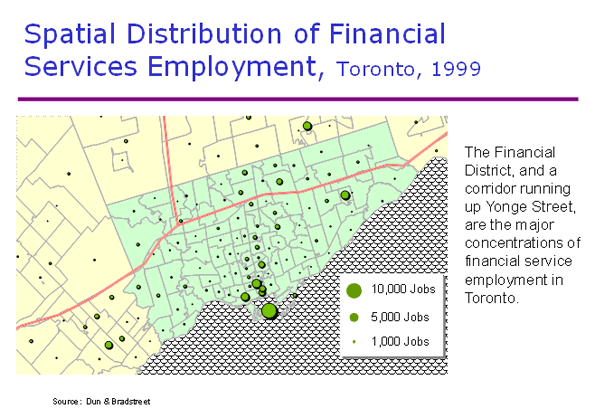
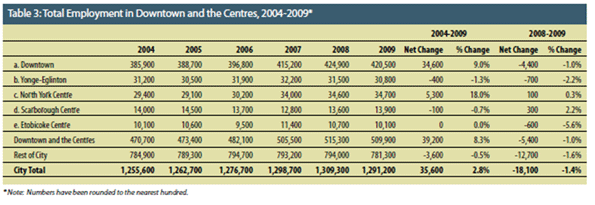
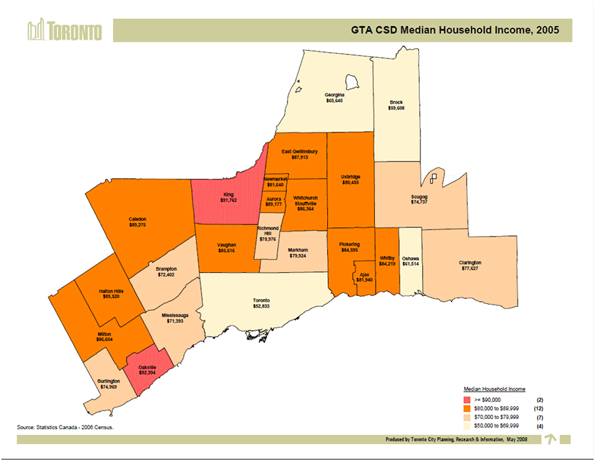
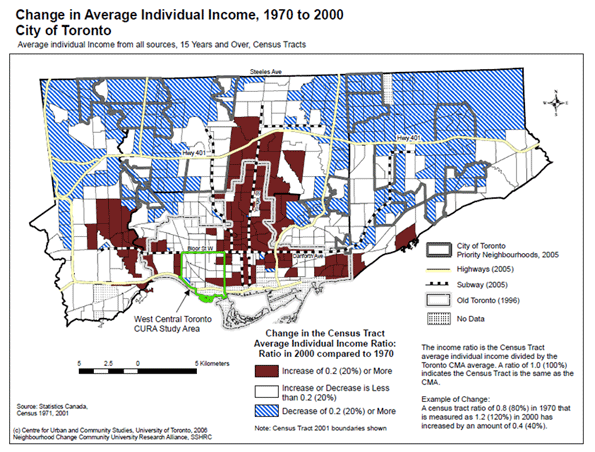
The last 10 years have been the worst for Western civilization since the 1930s. At the onset of the new millennium North America, Europe and Oceania stood at the cutting edge of the future, with new technologies and a lion’s share of the world’s GDP. At its end, most of these economies limped, while economic power – and all the influence it can buy politically – had shifted to China, India and other developing countries.
This past decade China’s economic growth rate, at 10% per annum, grew to five times that U.S.; the gap was even more disparate between China and the slower-growing E.U., Yet periods of slow economic growth occur throughout history — recall the 1970s — and economies recover. The bigger problem facing Western countries, then, is a metaphysical one — a malady that the British writer Austin Williams has dubbed “the poverty of ambition.”
This lack of ambition plagues virtually every Western country. The ability to act has become shackled by a profound pessimism that according to a recent Gallup survey contrasts with the optimism found not only in rising states like China, India and Brazil, but also deeply impoverished places like Bangladesh.
Attitudes have consequences. The rising stars of the non-Western world — from the United Arab Emirates to Singapore and China — are building cities with startling new architecture and bold infrastructure. Their entrepreneurs are expanding their operations across the planet.
Of course, you can chortle at the outrageous overbuilding in places like Dubai, but the Western world might do better to appreciate the scope of their ambition. Indeed, for years New York’s Empire State building, erected during the Depression, was derided as ”the empty state building.” Today it’s visionary developers like Iraqi-born Istabraq Janabi who are planning unlikely new structures even in troubled places like Ramadi, Iraq.
The difference in ambition can be seen clearly at airports, which now serve as the entry halls of the global economy. A traveler to John F. Kennedy Airport, Heathrow, Charles De Gualle LAX or Dulles passes through decayed remnants of fading late 20th century buildings and technology. In contrast, airports in Dubai, Hong Kong and Singapore offer clean, ultra-modern facilities with often impressive design.
The West’s retreat from space exploration further underscores its metaphysical poverty. Today, Europe and the U.S., the world’s historic leader in the field, are cutting back on plans to explore the cosmos, which has included a manned operation to the moon. President Obama wants NASA to focus more on issues regarding climate change instead. In contrast, the rising countries of Asia, notably China and India, have begun plans for manned flights to the moon and beyond.
This divergence is not about resources; it is about the growing conviction in the West that moving forward is an illusion or, as the British academic John Gray’s puts it, “progress is a myth.” Victorian empire-makers and intellectuals, like their republican American successors, believed perhaps naively in the potential of humanity, economic and technological progress. Today our intellectual and political classes have gone to the other extreme.
The West’s politics are in the grips of two profoundly retrograde mentalities. One, a small-minded conservatism, harks back to the “golden” age of the 1950s when Western power faced only a flawed Soviet challenge. The idealistic but flawed commitment to imposing democracy by force of the Bush years has faded; it has been replaced by an obsession with taming a bloated public sector. While this focus may be justified, it is fundamentally more reactive than proscriptive.
The Left, which once portrayed itself as the bastion of scientific rationalism, increasingly embraces neo-druidism, a secular form of nature worship. This tendency’s roots can be traced back to the “Limits to Growth” ideology of the early 1970s which projected, mostly mistakenly, that the planet was about to run out of everything from food to oil. Concerns over climate change have transformed this dismal sentiment into a theology, with carbon emissions treated as a form of original sin.
The anti-progress nature of the new Left is unmistakable. Rather than seek ways to control climate change, suggests The Guardian’s George Monbiot, environmentalism is engaged in “a battle to redefine humanity.” Monbiot believes the era of economic growth needs to come to an inevitable denouement; that “the age of heroism” will be followed by the decline of the “expanders” and the rise of the “restrainers.”
Europe, particularly the U.K., suffers acutely from metaphysical angst. Once touted as the new great power by its leaders and their American claque, the E.U. is quickly dissolving along cultural and historical lines; this is especially evident in the division between the resilient countries of the north (something like the Hansa trading states of the late Middle Ages) and the weaker countries along the periphery. For the most part, Europe no longer seems capable of doing much more than finding ways to control an unaffordable welfare state without tearing about its social net. The once cherished notion of a multi-racial “new” Europe largely has dissolved as immigration has devolved from a source of demographic and cultural salvation to a widely perceived threat to the E.U.’s economic and social health as well as security.
Such defeatism usually has less success in the United States. But America’s “progressive” left increasingly resembles its European cousins. Obama’s science advisor, John Holdren, has been a long-time advocate of the idea of “de-development,” the purposeful slowing of growth in advanced countries in order to protect the environment. The critical infrastructure needed to accommodate upward of another 100 million Americans — new dams in the west, intelligent development of our vast natural gas reserves and building new cities, airports and ports – are not at the center of either party’s platforms. These could be financed largely with private sources, given the right incentives.
Fortunately the West’s decline is not at inevitable. China, India, Vietnam, Brazil, South Africa all deserve their day in the sun, but this does not mean that Americans or Europeans should cower in the shadows. Western countries still possess much of the world’s cutting-edge technology and leading companies; the combined GDP for the E.U., North America and Oceania stands at over $33 trillion, almost five times that of India and China together.
More important still, the political and cultural institutions of the West — with their liberal values — represent the best hope for a stable world of self-governing peoples. Does anyone in the West, particularly the progressives in the media and academia, really want a world run by Chinese despotism?
The current financial crisis should serve as both a warning and a spur for a new focus on economic expansion. But this can only occur if the West can restore its belief in its future. This does not necessitate a return to the colonial attitudes of the past, but rather a keener appreciation of our unique human, physical and political advantages.
Only the United States – by far the richest, largest and most populous Western nation — can lead such a revival. For one thing, the U.S. remains the world’s leading immigrant magnet and most diverse large country, all of which makes it the natural center of an evolving global society. Although immigrants pose some serious issues, University of Chicago scholar Tito Sananji notes that the U.S., along with Canada and Australia, seems to be doing a better job educating their newcomers than the continental European states.
The U.S., Canada and Australia also possess resources, most critically food, that could benefit from growing demand in developing countries. Both North America and some European nations — notably the new Hansa of the Netherlands, Germany and Scandinavia – remain world leaders in scores of industrial endeavors, as well as technology- and culture-based industries.
Together these Western countries can do much more to shape the global future than is commonly understood. But to do so this century they will need how to recover the animal spirits that drove their remarkable rise in the last.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University, and an adjunct fellow of the Legatum Institute in London. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050
, released in February, 2010.