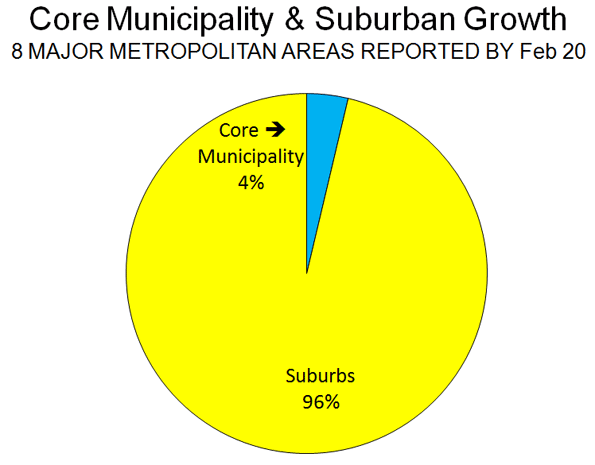
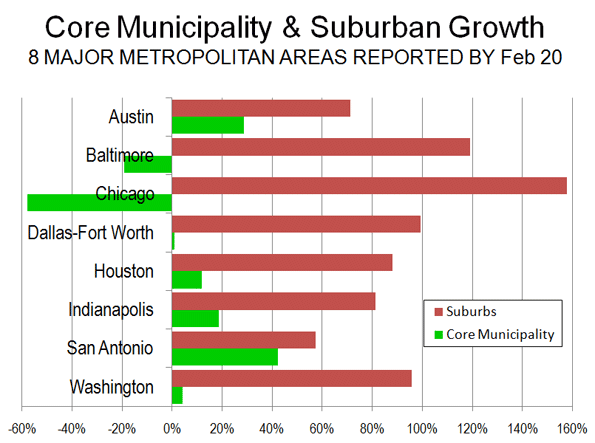
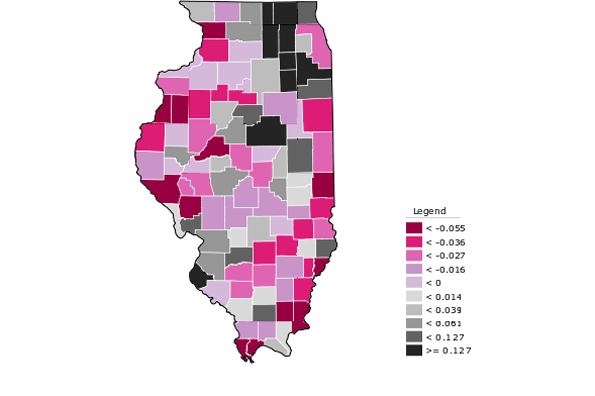
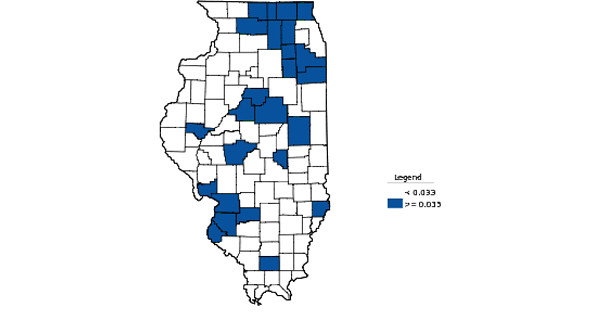
If you want to get a glimpse of the future of the U.S., check out Fort Worth, TX. Never mind the cowboy boots, but you might want to practice your Spanish.
Texas is growing explosively and much of that growth is among Latinos. The latest Census Bureau figures show the Lone Star State grew by 20%, to over 25 million people, recording about a quarter of the nation’s overall growth. The rate of growth was twice the national average. The implications are huge politically, as Texas stands to gain 4 new Congressional seats from this expansion, and Hispanic leaders want in.
A majority of the Hispanic growth came from births to families already living here. While migration from other states and countries contributed about 45%.
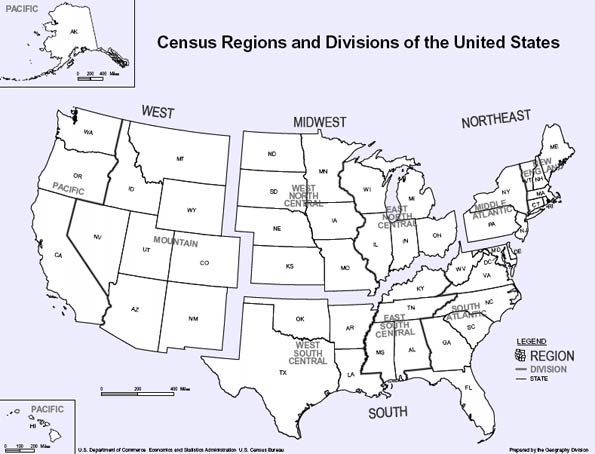
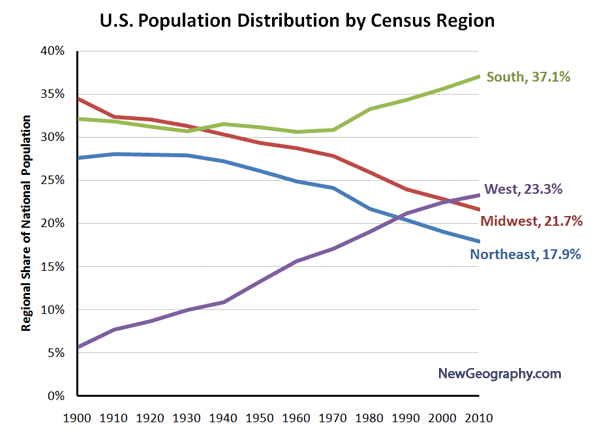
The Texas story stands in contrast to the Rust Belt states and the Northeast, where overall growth is minimal. Texas’s Hispanic-fueled growth spurt out-paced the entire countries, helped brace our housing market and our economy.
A close look at Texas growth reveals much about American’s home-buying habits. Rural areas got smaller – few want to live in the boonies of far west Texas while it appears suburban areas won over the most transplants.
But arguably the biggest winner was Ft. Worth, or Cow Town as we call it. Fort Worth grew by a whopping 38.6%, the largest increase in the state, followed by Laredo’s 33%, Austin at 20.4%, and San Antonio at 16%. In contrast the city of Dallas, my home, grew by a scant .8% – a bit deflating to a city all puffed up about a $354 million arts center, a downtown park and greenway, and the $185 million Perot Museum of Nature & Science underway.
Houston remains the state’s largest metropolitan area but sustained growth of only 7.5%, though Harris County – mostly due to growth in the suburbs – grew by 20%. As in Ft. Worth and elsewhere, Hispanics have been the driver, and now comprise 41% of the Harris County population. The biggest growth took place in formerly rural towns just outside the big cities, one-shop stop farmer’s crossings or granaries.
Curtis Tally shakes his head at how fast little Justin, north of Fort Worth, has grown. Subdivisions sprouted up on what was once farmland around his Justin Feed Co. in southern Denton County. From 1891 residents in 2000, Justin has 3,246 today.
"We were selling seed for pastures; now we’re selling seeds for lawns," Tally, 74, who has been in business in Justin since 1958, told the Fort Worth Star Telegram.
If you think that’s amazing, wait ‘till you get to Fate, Texas, 25 minutes east of Dallas on Interstate 30. Ten years ago you would have missed Fate, a town of 500 so small the utility invoicing was done on postcards if you blinked while driving. Today, Fate is the fastest-growing town in the state, with 6,357 residents – an increase of 1,179%! Residents who live there say it’s far enough away from Dallas to be in the country, but still close to the big city. Fate draws many first time homebuyers who are starting families (home prices range from $50,000 to $300,000) Here’s what Fate resident Tina Nelson told The Dallas Morning News:
“My kids can go ride bikes all day long and I don’t have to worry too much about where they are,” said Tina. “It’s like the 1950s (here) the sun goes down and everyone’s porch light comes on.”
On the western side of Lake Ray Hubbard, a few minutes from Fate and slightly closer to Dallas is Sunnyvale, another fast-growing little hick town where professionals are building $2 million dollar homes on a 124 acre family ranch turned into home sites called St James Park. They send their children to a two-year old, $50 million public school with the highest ratings in the state.
The young man building homes on the 49 two acre estate sites is Jojy Koshy of Atrium Fine Homes. At 31, Jojy holds a masters in business from the University of Texas and tells me, with pride, how his parents immigrated to the Dallas suburb of Plano in 1986 from India.
“My parents instilled a strong work ethic in us,” he says. “I know this market is challenging, but I believe that if I work longer, harder, and keep our clients completely satisfied, we will have a great business.”
It’s the same story across the state. The Interstate 35 corridor between Austin and San Antonio filled in with development as the cities merged closer to becoming one big schizophrenic metropolis. The string of counties along the Rio Grande, anchored by Brownsville and McAllen have been growing, and may be beneficiaries of the crime wave south of the border. A sharp Dallas Realtor took out an ad in the Monterrey newspaper advertising homes for sale in Dallas and snagged several buyers. Even the wife of the Monterrey mayor moved to a Dallas suburb, escaping the cartel and seeking to be closer to her family here.
Aside from escaping death in Mexico, what is driving people to Texas? Start with our rising star, Fort Worth. The city has both a cowboy pizzazz personality and a lower crime rate than Dallas. Fort Worth’s arts district has overshadowed Dallas’s for years, and the neighborhoods offer true community – places where the kids can still walk, not be bussed, to school. Rose Bowl winner Texas Christian University is on the upswing, downtown is charmingly vibrant, and an urban renaissance is taking hold on the city’s western edge called West 7th.
What are people seeking in Texas? I’d call it quality of life with room for upward mobility: affordable homes with mortgage payments that leave some money for recreation, good public schools for their kids and generally less onerous tax regime.
Yet with our many gains, Texas faces great challenges. The state has the third-highest teenage pregnancy rate in the nation, which is actually an improvement from last year, when we were number two. There are a rising number of children are living in poverty in Texas. Many of these children may be anchor babies born to illegal immigrants who cross the border to ensure their children and ultimately, themselves, citizenship. In 2006, 70% of the women who gave birth at Dallas County’s Parkland Memorial Hospital were illegal immigrants.
Increasingly, Latinos, illegal or not, take those babies home to the suburbs. Texas suburbs are no longer lily-white. This is true in working class places like Bedford, Texas, outside Fort Worth, where the black population has almost doubled. In affluent Southlake, the population this decade shifted from 95 percent Anglo down to 88 percent. Looking for a great selection of Asian food? You’ll starve (or go broke) in downtown Dallas. Go north to Carrollton, Texas where you’ll find a 78,000 square foot Super H Mart in what was once a Mervyns department store. Inside you’ll find seven types of gray, fuzzy, Chinese long, acorn, spaghetti, butternut, and kombucha squash eight food stalls said to rival any of those found in Seoul and Singapore, two cities known for their gourmet street food. Manduguk, anyone?
The new Texans are coming here not just to live, but to dig in economically.
In the end, we are seeing the birth of a Texas that is neither the white bread, big hair idyll of the cultural conservatives or the free market dystopia imagined by liberals. It is becoming more diverse, without losing its capitalist energy. With all its blemishes, the emerging Texas may well become the model for how America evolves in the coming decades.
Candy Evans is an independent journalist based in Dallas, Texas, She covers Texas for AOL’s HousingWatch and blogs at secondshelters.com.
Photo by Rick
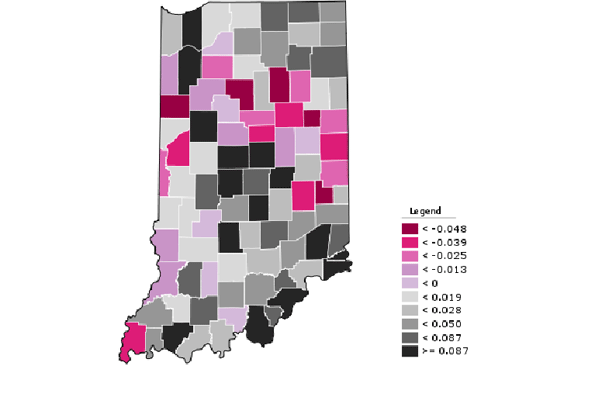
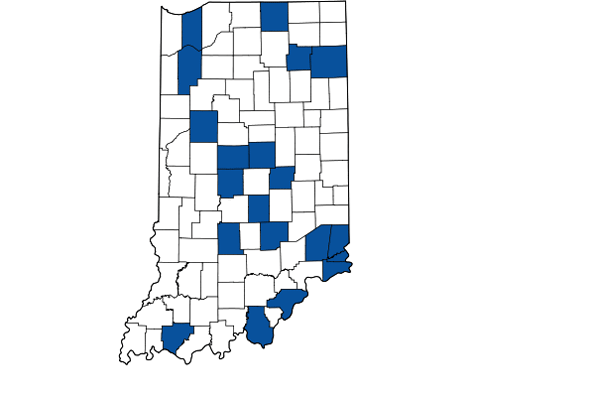
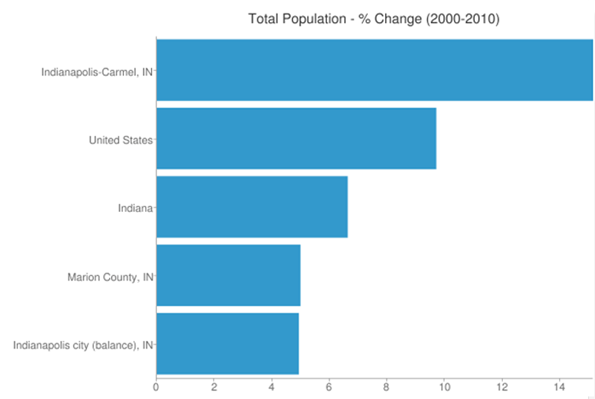
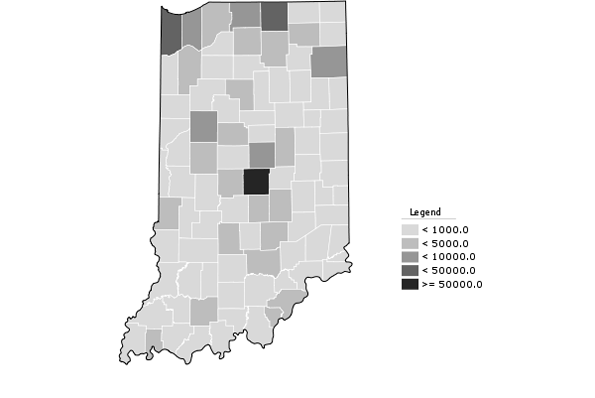 Indy’s Asian population also more than doubled to almost 40,000.. Add this all up and the metro area non-Hispanic white-only population share dropped by six percentage points, but remains at 74.6%. The city of Indianapolis itself is pushing 40% minority, however. Regardless, this is still a material change and shows that metro Indy is a strong magnet not just for whites, but for pretty much everybody. Its challenge is to continue building on this for the future, while the state’s challenge will be to pull itself up to Indy’s level of demographic and economic performance.
Indy’s Asian population also more than doubled to almost 40,000.. Add this all up and the metro area non-Hispanic white-only population share dropped by six percentage points, but remains at 74.6%. The city of Indianapolis itself is pushing 40% minority, however. Regardless, this is still a material change and shows that metro Indy is a strong magnet not just for whites, but for pretty much everybody. Its challenge is to continue building on this for the future, while the state’s challenge will be to pull itself up to Indy’s level of demographic and economic performance.