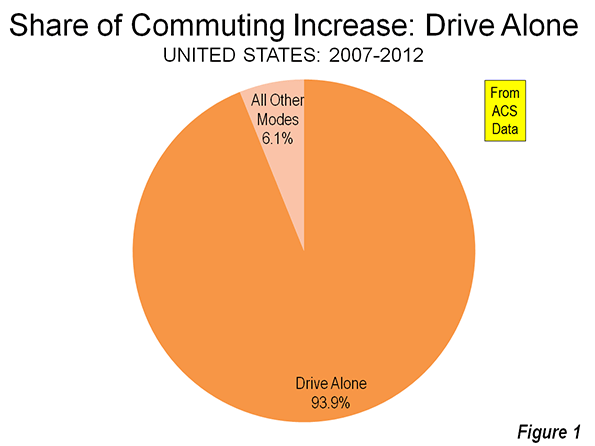
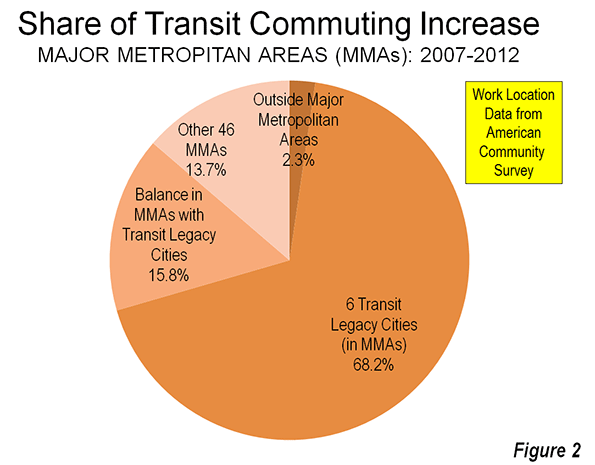
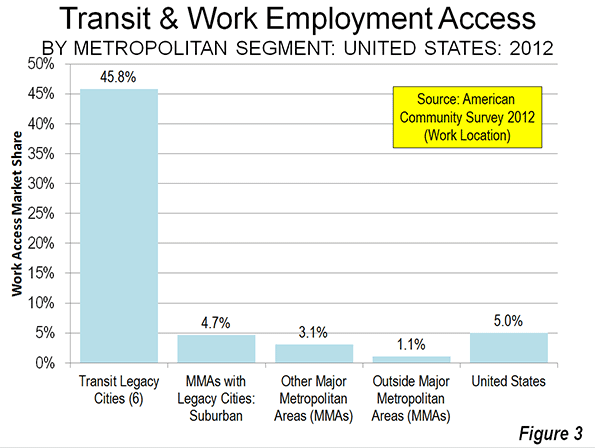
As part of his plan to boost sagging ratings at the network, CNN chief Jeff Zucker commissioned an eight part reality series about Chicago and its mayor called Chicagoland that premiers tonight at 10pm ET. The show is produced by the same people who did the Brick City series about Newark Mayor Cory Booker, with support from mega-star executive producer Robert Redford.
Rahm and the Media
Given that Brick City seems to have only helped Booker’s reputation, cynics in Chicago have already noted the fact that show’s producers are represented by the William Morris Endeavor Agency, which just so happens to be the home of Chicago Mayor Rahm Emanuel’s brother Ari. This is as much because of as in spite of a well-publicized move by directors Marc Levin and Mark Benjamin to ask the agency to recuse themselves from representing them when it comes to the show.
Trailer for CNN series “Chicagoland” – click here if the video does not display.
One need not believe in such a conspiracy to see this show as yet another example of Rahm’s media power – and his fearlessness in pursuing high profile opportunities to get his message out even in venues where he’s not in complete control. Rahm has had significant success in getting high profile national and global attention – for example, a glowing profile from NYT columnist Thomas Friedman – since taking office. He didn’t shy away from getting out there even when a spike in murders made global headlines Chicago of the type Chicago didn’t want – a time when many mayors would have crawled into their bunkers. And although he’s been in office a while now, Rahm fatigue seems not to have set in. Sun-Times columnist Neil Steinberg has a lengthy piece on him in the March issue of Esquire with the colorful title of “And Now For the Further Adventures of Rahm the Imapler.” The Financial Times recently ran a mostly positive piece called “Rahm Emanuel: Mayor America.” It even includes a high production quality six and a half minute video that will give you a flavor of it (if the video doesn’t display, click here):
With his ambition for Chicago as a global city, Rahm clearly sees global media as the ones that really count. Chicago’s status as a media center afterthought means few out of town reporters actually know that much about the city, hence Rahm has a huge opportunity to shape the message. This must infuriate the local media, which to a great extent Rahm is free to ignore because of his ability to go direct at the national and global level. Chicagoland should thus be seen as part of Rahm’s global media push, both for Chicago and for himself.
Reality TV vs. Journalism
The series is probably as good for Rahm and the city as it could possible get. Certainly the problems – high crime, poor schools, and labor troubles – are not glossed over. But given that they’ve been well publicized globally, it’s hard to imagine how they could be without sacrificing all credibility. Within the context of realism, this is a big win for the city.
Whether it’s a big win for journalism is another story. Like most modern documentaries or reality TV shows, Chicagoland is non-fiction in a sense, but also heavily scripted and edited to provide a compelling narrative. This makes for great TV drama and characterizations, but whether it represents truth as a reporter would tell it is much more doubtful.
Just as one example, the producers clearly had extensive access to Rahm and he’s frequently shown as concerned about crime, battling with unions, boosting the local economy, talking to school kids and even mentoring an inner city kid he brought on as an intern. But is that a fair representation of how Rahm Emanuel spends his time? The Chicago Reader did a two part series analyzing Rahm Emanuel’s schedule and published a two part series about it called “The Mayor’s Millionaire Club” (see part one and part two). They show that access to Rahm is heavily dependent on your wealth, influence, and donations. Yet that doesn’t come through in Chicagoland at all. Instead when the occasional powerful people are shown, they are always doing a good turn for the city, such as a group of tech executives donating products to schools.
I’m not suggesting this series should have been a bulldog investigative piece. However, I strongly suspect that CNN’s actual journalists will be seething at seeing their network and its relatively strong reputation being used for what is clearly not the type of work they themselves would undertake. Right or wrong, the CNN brand carries an expectation of a certain type of journalistic standard that the Sundance Channel (where Brick City originally ran) doesn’t. Right now on CNN’s Chicagoland page there’s an ad for Anderson Cooper 360. Something tells me that were Anderson Cooper in charge of Chicagoland, it would look quite different.
Compelling Drama and Characters
However, taken on the terms of a Sundance series, Chicagoland succeeds, and my guess is that Rahm will be overall pleased. The show sets up the drama by structuring the series as battles between opposing forces. In the first couple episodes, this is the battle between Rahm and Chicago Public Schools leadership on the one hand, and the teachers union and some affected parent groups on the other over plans by CPS to shutter 50 schools. Frankly, I thought it overly portrayed Chicago as if it were Newark. The segments were introduced by short positive vignettes of some aspect of Chicago (like the Stanley Cup playoffs), followed by more extensive coverage of the school closing dispute, and educational and crime problems in Chicago’s impoverished South Side. It would be like doing a flyby of Times Square before doing a deep dive on some of the worst blocks in Newark. While I myself have written on the two Chicagos theme, I was feeling that Chicago was being unfairly stigmatized.
I need not have worried. After the initial focus on the school closing dispute, the focus shifts. The drama is now between the good guys (basically every single person featured in the show) and the bad guys (gangsters and such who exist almost entirely offscreen, or so we’re led to believe). Almost without exception, the good guy characters are shown as 100% white knight types. Instead of positive vignettes followed by something Newarkesque, there’s a more balanced take in time allocation and the threads start merging across the two Chicagos. The show also starts laying the Chicago sales job on with a trowel. In Chicagoland’s coverage of things like the food scene, the music scene, the comedy clubs, or even footage of Rahm protesting a neo-Nazi march back in the 70s as a teenager, it’s hard to see how this could have been any more positive in its portrayal of the city if it had been produced directly by the Chicago Convention and Tourism Bureau. This is a huge win for the city.
The show also manages to create several compelling characters. One of them is the surgeon who leads the trauma unit at Cook County Hospital, a job I certainly would not want. How that guy manages to balance family life in Roscoe Village (my old neighborhood) with the reality of what he deals with every night at his job is beyond me.
But the star of the show is clearly Elizabeth Dozier, principal at Fenger High School in the South Side neighborhood at Roseland. She’s shown fighting not only to only educate her students, but keep them safe over the summer, and even invest in their lives after graduation when they get in trouble. (Dozier trying to help a former student who’s in jail for robbery realistically shows the need for “retail” 1:1 or N:1 investment in the lives of specific troubled people, not just programs, to make a real difference in a troubled person’s life – and even so the difficulty in seeing life change happen). Her obvious passion and dedication in the face of tough odds clearly come through. Yet even here there’s a sense of manufacture. Dozier is a young, attractive, stylish black professional who not only runs a South Side High School, but also gets personal face time with Rahm, knows Grant Achutz of Alinea, and hangs out with Billy Dec on his boat. How much of this A-list hob-nobbing was happening prior to Chicagoland coming to town I wonder? Regardless, it makes for compelling TV.
While I have my quibbles, I think on the whole Chicagoland is an enjoyable watch that will end up being good for the city and the mayor. Just don’t go in expecting journalism. This is first and foremost reality TV style drama. With that caveat in mind, I recommend watching it.
Takeaways From the Chicagoland
Watching Chicagoland made me think again two bigger picture issues.
First, in watching gangs take revenge on each other in an endless cycle of retaliation that literally stretches on for years and in which no one can actually recall the original offense, I was reminded of Hannah Arendt writing on the role of forgiveness:
Forgiveness is the exact opposite of vengeance, which acts in the form of re-acting against an original trespassing, whereby far from putting an end to the consequences of the first misdeed, everybody remains bound to the process, permitting the chain reaction contained in every action to take its unhindered course. In contrast to revenge, which is a natural, automatic reaction to transgression and which because of the irreversibility of the action process can be expected and even calculated, the act of forgiving can never be predicted; it is the only reaction that acts in an unexpected way and thus retains, though being a reaction, something of the original character of action. Forgiving, in other words, is the only reaction which does not merely re-act but acts anew and unexpectedly, unconditioned by the act which provoked it and therefore freeing from its consequences both the one who forgives and the one who is forgiven. The freedom contained in Jesus’ teachings of forgiveness is the freedom from vengeance, which incloses both doer and sufferer in the relentless automatism of the action process, which by itself need never come to an end.
Forgiveness is not the only way to put a stop to a cycle of revenge. Arendt posits official punishment as another. But forgiveness is clearly the fastest and surest route. Until either the police are able to impose order and mete out genuine justice, or the grieving family and aggrieved gang compatriots of these murder victims are able to forgive and forswear vengeance, the cycle is unlikely to ever end.
I don’t want to judge too harshly teenagers in a ghetto living out the only life script they’ve ever known. But what’s our excuse? We too often live out in miniature the same process ourselves. How often do most of us forgive genuine wrong done against us, even of a much less consequential nature? Tune into the internet any day of the week and see untold amounts of shrieking over some offense or another, real or imagined. I suspect the vast majority of us would be behave no differently from those gangbangers in similar circumstances. We are blessed not to be there, however. But will we use that privileged position to end or perpetuate cycles of wrong in our own lives?
Secondly, Chicagoland made me think about the bigger picture of leadership in our cities and the major problems they face. I voted for Rahm as mayor, for three reasons. 1) I saw him as like his mentor Bill Clinton, namely someone to whom getting elected and staying in power is more important than pushing any ideological agenda. In short, I saw him as a pragmatist, not an ideologue with a policy ax to grind like Bill de Blasio. 2) Rahm spent a lot of time outside of Chicago. He’s got a global perspective and a global network that’s critical in this era. He’s also got the gravitas to interact at the highest levels of power in America, which is something few mayors can say. 3) Rahm has no natural constituency in Chicago. So if he wants to be re-elected, he needs to perform. He clearly has future political ambitions, and flaming out as mayor wouldn’t be helpful in pursuing them.
Looking back, while I’ve criticized Rahm for an excessive focus on the elite, I believe my judgment then was correct and on the whole I think he’s done a decent job in a very difficult situation. Apropos of point #3, if Chicago thinks differently, the popular and competent Cook County Board President Toni Preckwinkle is waiting in the wings. Whatever you think of his neoliberal policies, it’s clear Rahm is an actual leader, one with a ton of intelligence, drive, power, and the will to get things done.
Yet watching Chicagoland, it’s evident that even leadership ability of Rahm’s caliber struggles mightily with the city’s huge challenges. Chicago has a massive fiscal hole, and a very serious problem with a two tier society that has left vast tracts of the city behind. It’s by no means certain that Rahm will be able to make Chicago soar in the way that Daley did in the 90s, or even get re-elected if a there’s any stumble and a credible candidate like Preckwinkle gets into the race.
When I think about the difficulties in solving the problems in Chicago, which has not only Rahm’s leadership but a massively successful global city economy in the Loop and hundreds of thousands of well-heeled residents, it makes me pause. If Chicago struggles with its problems, how much more so other cities facing similar or worse problems but with much weaker leadership and no global city money and firepower? It really makes me wonder if a lot of places are simply going to die a slow death barring some lucky break from a change in the marketplace.
This ultimately is what I’d challenge the residents of other cities to think about when watching this show. Look at Chicago and what it is dealing with. Think about your own problems and your resources for combating them vis-a-vis Chicago. If that doesn’t make you sober up, I’m not sure what will.
Aaron M. Renn is an independent writer on urban affairs and the founder of Telestrian, a data analysis and mapping tool. He writes at The Urbanophile, where this piece originally appeared.